Abstract
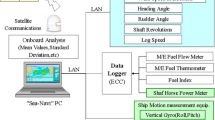
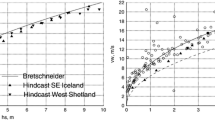
The inclining experiment is the only regulatory tool to assess ship stability. This experiment is a time consuming process for both real-life tests and ship model experiments. The difficulty is mainly due to a bias in the measurement of heel angle. Nowadays, digital inclinometers are available but they are expensive. In this study, the use of a smartphone application is presented for ship inclination and rolling-period tests. The idea consists of using accelerometer and gyroscope sensors built into the current smartphones for the measurements. Therefore, some experiments are carried out on an example trawler model to exhibit the uses and advantages of this method. The obtained results are in good agreement with those provided from the pendulum method and natural roll-period test. This application is new, easy, and more accurately assesses metacentric height during the inclining and rolling-period tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett SS, Brooks CJ, Winden B, Taunton DJ, Forrester AIJ, Turnock SR, Hudson DA (2014). Measurement of ship hydroelastic response using multiple wireless sensor nodes. Ocean Engineering, 79, 67–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2013.12.011
Biran A (2003). Ship hydrostatics and stability. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, Great Britain, 166–171.
Cota A (1985). GM-Meter automatic instrument for continues measurement of ships stability. ATMA, 97–113. (in French)
Daponte P, De Vito L, Picariello F, Riccio M (2013). State of the art and future developments of measurement applications on smartphones. Measurement, 46(9), 3291–3307. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2013.05.006
Griffin MJ, Lawther A, Lewis C (1985). Stability meter for floating objects. World Patent WO1987003855 A1.
Gudmundsson A (2009). Safety practices related to small fishing vessel stability. FAO Food and Agriculture Organisation, Rome, Italy, FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 517.
IMO (2009). SOLAS, consolidated edition, 2009. 5th edition, International Maritime Organization, London, UK.
InvenSense™ (2013). MPU-6000/MPU-6050 Product Specification Datasheet, PS-MPU-6000A-00, InvenSense™, Sunnyvale, USA. (2013).
Kuhn J, Vogt P (2013). Applications and examples of experiments with mobile phones and smartphones in physics lessons. Frontiers in Sensors (FS), 1(4), 67–73.
Lewis EV (1988). Principles of naval architecture, Volume I: Stability and strength. SNAME, New York, USA.
Lewis EV (1989). Principles of naval architecture, Volume III: Motion in waves and controllability. SNAME, New York, USA.
Pattulo RNM, Thomson GR (1965). The B.S.R.A. trawler series. Transactions of Royal Institution of Naval Architects, 107, 216–236.
Ripka P, Tipek A (2007). Modern sensors handbook. ISTE Ltd., London UK, 200–242. DOI: 10.1002/9780470612231
Webster JG (1999). Measurement, instrumentation, and sensors handbook. CRC Press LLC, New York, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djebli, M.A., Hamoudi, B., Imine, O. et al. The application of a smartphone in ship stability experiment. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 14, 406–412 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-015-1331-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-015-1331-9