Abstract
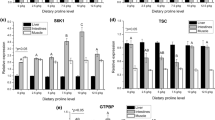
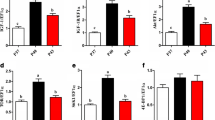
A growth experiment was conducted on cobia (Rachycentron canadum, initial weight 108.2 g ± 3.0 g) to investigate the effects of dietary corn gluten meal (CGM) levels on the fish growth, whole body composition and protein metabolism in relation to specific gene expression. Five isonitrogenous (crude protein 45%) and isoenergetic (gross energy 20 kJ g−1) practical diets were formulated by replacing 0% (the control), 17.5%, 35.0%, 52.5%, and 70.0% of fish meal (FM) protein with CGM protein. No significant differences were observed in the survival, feed intake (FI), specific growth rate (SGR), feed efficiency (FE) and protein productive value (PPV) among fish fed diets with 0%, 17.5%, 35.0%, and 52.5% of CGM protein. However, these indices were significantly lower in fish fed the diet with 70.0% of CGM protein than those in fish fed the control diet (P < 0.05). The whole-body crude protein and lipid contents were significantly lower while the whole-body moisture content was significantly higher in fish fed the diet with 70.0% of CGM protein compared with the control group (P < 0.05). When 70.0% of FM protein was replaced by CGM, plasma total protein and cholesterol contents were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Fish fed the diet with 70.0% of CGM protein had significantly lower hepatic insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) expression levels than those in the control group (P < 0.05). However, no significant differences were observed in hepatic target of rapamycin (TOR), dorsal muscle IGF-I and TOR expression levels among dietary treatments. Results of the present study indicated that 52.5% of FM protein could be replaced by CGM in the diets without significant influences on the growth, feed utilization and protein metabolism of juvenile cobia. The present results might be useful for developing cost effective and sustainable cobia dietary formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC), 1995. Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th Edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA, USA.
Bradford, M. M., 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72: 248–254.
Chen, G. F., Feng, L., Kuang, S. Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Hu, K., Jiang, W. D., Li, S. H., Tang, L., and Zhou, X. Q., 2011. Effect of dietary arginine on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and gene expression in muscle, hepatopancreas and intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). British Journal of Nutrition, 107: 1–13.
Cheng, Z. Y., Ai, Q. H., Mai, K. S., Xu, W., Ma, H. M., li, Y., and Zhang, J. M., 2010. Effects of dietary canola meal on growth performance, digestion and metabolism of Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Aquaculture, 305: 102–108.
Chou, R. L., Her, B. Y., Su, M. S., Hwang, G., Wu, Y. H., and Chen, H. Y., 2004. Substituting fish meal with soybean meal in diets of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Aquaculture, 229: 325–333.
Deng, J. M., Mai, K. S., Ai, Q. H., Zhang, W. B., Wang, X. J., Tan, B. P., Xu, W., Liufu, Z. G., and Ma, H. M., 2010. Interactive effects of dietary cholesterol and protein sources on growth performance and cholesterol metabolism of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquacuture Nutrition, 16: 419–429.
Duan, C., and Hirano, T., 1992. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin on the in vitro uptake of sulfate by eel branchial cartilage: evidence for the presence of independent hepatic and pancreatic sulfation factors. Journal of Endocrinology, 133: 211–219.
Duan, C., and Plisetskaya, E. M., 1993. Nutritional regulation of insulin-like growth factor I mRNA expression in salmon tissues. Journal of Endocrinology, 139: 243–252.
Duan, C., Ren, H., and Gao, S., 2010. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF receptors, and IGF-binding proteins: roles in skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 167: 344–351.
Ellis, A. E., 1990. Lysozyme assays. In: Techniques in Fish Immunology. Stolen, J. S., et al., eds., SOS Publications, Fair Haven, NJ, 101–103.
Gomes, E. F., Rema, P., and Kaushik, S. J., 1995. Replacement of fish meal by plant proteins in the diet of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): digestibility and growth performance. Aquaculture, 130: 177–186.
Gómez-Requeni, P., Mingarro, M., Calduch-Giner, J. A., Médale, F., Martin, S. A., Houlihan, D. F., Kaushik, S. J., and Perez-Sanchez, J., 2004. Protein growth performance, amino acid utilisation and somatotropic axis responsiveness to fish meal replacement by plant protein sources in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture, 232: 493–510.
Hansen, A. C., Karlsen, Ø., Rosenlund, G., Rimbach, M., and Hemre, G., 2007a. Dietary plant protein utilization in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. Aquaculture Nutrition, 13: 200–215.
Hansen, A. C., Rosenlund, G., Karlsen, Ø., Koppe, W., and Hemre, G. I., 2007b. Total replacement of fish meal with plant proteins in diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L) I: effects on growth and protein retention. Aquaculture, 272: 599–611.
Hardy, R. W., 2010. Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquaculture Research, 41: 770–776.
Hevrøy, E. M., El-Mowafi, A., Taylor, R., Olsvik, P. A., Norberg, B., and Espe, M., 2007. Lysine intake affects gene expression of anabolic hormones in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 152: 39–46.
Hevrøy, E. M., El-Mowafi, A., Taylor, R., Norberg, B., and Espe, M., 2008. Effects of a high plant protein diet on the somatotropic system and cholecystokinin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology-Part A, 151: 621–627.
Kikuchi, K., 1999. Partial Replacement of fish meal with corn gluten meal in diets for Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 30: 357–363.
Kumar, S., Sahu, N. P., Pal, A. K., Choudhury, D., and Mukherjee, S. C., 2006. Studies on digestibility and digestive enzyme activities in Labeo rohita (Hamilton) juveniles: effect of microbial α-amylase supplementation in non-gelatinized or gelatinized corn based diet at two protein levels. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 32: 209–220.
Lansard, M., Panserat, S., Seiliez, I., Polakof, S., Plagnes-Juan, E., Geurden, I., Medale, F., Kaushik, S., Corraze, G., and Skiba-Cassy, S., 2009. Hepatic protein kinase B (Akt)-target of rapamycin (TOR)-signalling pathways and intermediary metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) are not significantly affected by feeding plant-based diets. British Journal of Nutrition, 102: 1564–1573.
Lansard, M., Panserat, S., Plagnes-Juan, E., Seiliez, I., and Skiba-Cassy, S., 2010. Integration of insulin and amino acid signals that regulate hepatic metabolism-related gene expression in rainbow trout: role of TOR. Amino Acids, 39: 801–810.
Lewis, H. A., and Kohler, C. C., 2008. Corn gluten meal partially replaces dietary fish meal without compromising growth or fatty acid composition of sunshine bass. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 70: 50–60.
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D., 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods, 25: 402–408.
Lunger, A. N., McLean, E., and Craig, S. R., 2007. The effects of organic protein supplementation upon growth, feed conversion and texture quality parameters of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture, 264: 342–352.
Matthews, S. J., Kinhult, A. K., Hoeben, P., Sara, Y. R., and Anderson, T. A., 1997. Nutritional regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA expression in barramundi, Lates calcarifer. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 18: 273–276.
Melo, J. F. B., Lundstedt, L. M., and Metón, I., 2006. Effects of dietary levels of protein on nitrogenous metabolism of Rhamdia quelen (Teleostei Pimelodidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology-Part A, 145: 181–187.
Mente, E., Deguara, S., Santos, M. B., and Houlihan, D., 2003. White muscle free amino acid concentrations following feeding a maize gluten dietary protein in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture, 225: 133–147.
Pedroso, F. L., de Jesus-Ayson, E. G., Cortado, H. H., Hyodo, S., and Ayson, F. G., 2006. Changes in mRNA expression of grouper (Epinephelus coioides) growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I in response to nutritional status. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 145: 237–246.
Pereira, T. G., and Oliva-Teles, A., 2003. Evaluation of corn gluten meal as a protein source in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) juveniles. Aquaculture Research, 34: 1111–1117.
Regost, C., Arzel, J., and Kaushik, S. J., 1999. Partial or total replacement of fish meal by corn gluten meal in diet for turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture, 180: 99–117.
Ren, M. C., Ai, Q. H., Mai, K. S., Ma, H. M., and Wang, X. J., 2011. Effects of dietary carbohydrate level on growth performance, body composition, apparent digestibility coefficient and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum L. Aquaculture Research, 42: 1467–1475.
Salze, G., McLean, E., Battle, P. R., Schwarz, M. H., and Craig, S. R., 2010. Use of soy protein concentrate and novel ingredients in the total elimination of fish meal and fish oil in diets for juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Aquaculture, 298: 294–299.
Seiliez, I., Gabillard, J. C., Skiba-Cassy, S., Garcia-Serrana, D., Gutierrez, J., Kaushik, S., Panserat, S., and Tesseraud, S., 2008. An in vivo and in vitro assessment of TOR signaling cascade in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 295: 329–335.
Sitja-Bobadilla, A., Pena-Llopis, S., Gomez-Requeni, P., Medale, F., Kaushik, S., and Perez-Sanchez, J., 2005. Effect of fish meal replacement by plant protein sources on non-specificdefence mechanisms and oxidative stress in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture, 249: 387–400.
Takagi, S., Hosokawa, H., Shimeno, S., and Ukawa, M., 2000. Utilization of corn gluten meal in a diet for red sea bream Pagrus major. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 66: 417–427.
Thissen, J. P., Underwood, L. E., and Ketelslegers, J. M., 1999. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I in starvation and injury. Nutrition Reviews, 57: 167–176.
Twibell, R. G., and Wilson, R. P., 2004. Preliminary evidence that cholesterol improves growth and feed intake of soybean meal-based diets in aquaria studies with juvenile channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Aquaculture, 236: 539–546.
WU, P., Feng, L., Kuang, S. Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Hu, K., Jiang, W. D., Li, S. H., Tang, L., and Zhou, X. Q., 2011. Effect of dietary choline on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and relative expressions of target of rapamycin and eIF4E-binding protein 2 gene in muscle, hepatopancreas and intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Aquaculture, 317: 107–116.
Wullschleger, S., Loewith, R., and Hall, M. N., 2006. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell, 124: 471–484.
Yun, B., Mai, K. S., Zhang, W. B., and Xu, W., 2011. Effects of dietary cholesterol on growth performance, feed intake and cholesterol metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture, 319: 105–110.
Zhong, G., Hua, X., Yuan, K., and Zhou, H., 2011. Effect of CGM on growth performance and digestibility in puffer (Takifugu fasciatus). Aquaculture International, 19: 395–403.
Zhou, Q. C., Tan, B. P., Mai, K. S., and Liu, Y. J., 2004a. Apparent digestibility of selected feed ingredients for juvenile cobia Rachycentron canadum. Aquaculture, 241: 441–451.
Zhou, M., Cao, J. M., Wu, J. K., Liang, H. O., Zhu, W. M., Zhao, H. X., Zhang, H. T., Yang, D. W., Ma, L., and Lan, H. B., 2004b. Dietary phosphorus requirement of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 17: 62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, Q. C., Mai, K. S., Tan, B. P., and Liu, Y. J., 2005. Partial replacement of fishmeal by soybean meal in diets for juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Aquaculture Nutrition, 11: 175–182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Ai, Q., Mai, K. et al. Effects of dietary corn gluten meal on growth performance and protein metabolism in relation to IGF-I and TOR gene expression of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). J. Ocean Univ. China 12, 418–426 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-013-2021-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-013-2021-3