Abstract
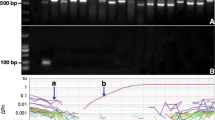
Prorocentrum donghaiense is a dinoflagellate that is widely distributed in the East China Sea and has become increasingly involved in Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs). Therefore, it is necessary to study this dinoflagellate to monitor HABs. In this study, 13 pairs of primers specific to P. donghaiense (within its internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions) were designed for SYBR Green I real-time PCR. As the SYBR Green I real-time PCR could not identify P. donghaiense in a specific manner, a Taqman real-time PCR method was developed by designing a set of specific primers and a Taqman probe. A 10-fold serial dilution of recombinant plasmid containing ITS regions of P. donghaiense was prepared as standard samples and the standard curve was established. Additionally, we quantified the genomic DNA in P. donghaiense cells and utilized this DNA to prepare another 10-fold serial dilution of standard sample and accordingly set up the standard curve. The mathematic correlation between the cell number and its corresponding plasmid copy number was also established. In order to test the efficiency of the real-time PCR method, laboratory samples and P. donghaiense HAB field samples were employed for identification and quantitative analysis. As to laboratory samples, as few as 102 cells of P. donghaiense could be quantified precisely utilizing both centrifugation and filtration techniques. The quantification results from field samples by real-time PCR were highly similar to those by light microscopy. In conclusion, the real-time PCR could be applied to identify and quantify P. donghaiense in HABs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. M., 1989. Toxic algal blooms and red tides: a global perspective. In: Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science and Toxicology. Okaichi, T., et al., eds., Elsevier, New York, 11–16.
Baxa, D. V., Kurobe, T., Ger, K. A., Lehman, P. W., and The, S. J., 2010. Estimating the abundance of toxic Microcystis in the San Francisco Estuary using quantitative real-time PCR. Harmful Algae, 9: 342–349.
Bell, A. S., and Ranford-Cartwright, L. C., 2002. Real-time quantitative PCR in parasitology. Trends in Parasitology, 18: 337–342.
Bowers, H. A., Tengs, T., Jr. Glasgow, H. B., Burkholder, J. M., Rublee, P. A., and Oldach, D. W., 2000. Development of real-time PCR assays for rapid detection of Pfiesteria piscicida and related dinoflagellates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66: 4641–4648.
Broberg, E. K., Nygårdas, M., Salmi, A. A., and Hukkanen, V., 2003. Low copy number detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA and mouse Th1 type cytokine mRNAs by light cycler quantitative real-time PCR. Journal of Virological Methods, 112: 53–65.
Casper, E. T., Paul, J. H., Smith, M. C., and Gray, M., 2004. Detection and quantification of the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis by real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70: 4727–4732.
Chen, H. L., Lv, S. H., Zhang, C. S., and Zhu, D. D., 2006. A survey on the red tide of Prorocentrum donghaiense in East China Sea 2004. Ecologic Science, 25: 226–230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cherry, J. M., Stewart, C., Frankenberger, C., Martin, K., Tudor, G., Owens, G., Bhat, N. K., and Munroe, D. J., 2004. Automated process of Q-PCR/gene expression. Journal of the Association for Laboratory Automation, 9: 28–34.
Cocolin, L., Manzano, M., Cantoni, C., and Comi, G., 1998. Use of polymerase chain reaction and restriction enzyme analysis to directly detect and identify Salmonella typhimurium in food. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 85: 673–677.
Connell, L., 2002. Rapid identification of marine algae (Raphidophyceae) using three-primer PCR amplification of nuclear internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions from fresh and archived material. Phycologia, 41: 15–21.
Countway, P. D., and Caron, D. A., 2006. Abundance and distribution of Ostreococcus sp. in the San Pedro Channel, California, as revealed by quantitative PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72: 2496–2506.
Dyhrman, S. T., Erdner, D., Du, J. L., Galac, M., and Anderson, D. M., 2005. Molecular quantification of toxic Alexandrium fundyense in the gulf of maine using real-time PCR. Harmful Algae, 5: 242–250.
Foulds, I. V., Granacki, A., Xiao, C., Krull, U. J., Castle, A., and Horgen, P. A., 2001. Quantification of microcystin-producing Cyanobacteria and E. coli in water by 5′-nuclease PCR. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 93: 825–834.
Galluzzi, L., Penna, A., Bertozzini, E., Vila, M., Garcés, E., and Magnani, M., 2004. Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Alexandrium minutum. (a dinoflagellate). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70: 1199–1206.
Haley, S. T., Cavender, J. F., and Murray, T. E., 1999. Detection of Alexandrium tamarensis by rapid PCR analysis. Biotechniques, 26: 88–91.
He, S. Y., Cheng, G., Gou, W. L., Li, R. X., Mi, T. Z., and Yu, Z. G., 2006. Development of a real-time PCR for rapid detection of Skeletonema costatum. High Technology Letters, 16: 313–318 (in Chinese with English abstract).
He, S. Y., and Yu, Z. G., 2009. A real-time PCR method for rapid detection of Gymnodinium sanguineum. Journal of Zhejiang University, 35: 119–126.
He, S. Y., Yu, Z. G., and Mi, T. Z., 2007. Development of a real-time PCR method for Thalassiosira rotula rapid detection. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26: 133–139.
He, S. Y., Yu, Z. G., and Mi, T. Z., 2008. Development of real-time PCR method for rapid detection and quantification of Heterosigma akashiwo. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 15: 118–123.
Hosoi-Tanabe, S., and Sako, Y., 2005. Species-specific detection and quantification of toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella by real-time PCR assay. Marine Biotechnology, 7: 506–514.
Hou, J. J., Huang, B. Q., Hu, J., Lin, L. Z., and Hong, H. S., 2008. Fourteen FITC-conjugated lectins as a tool for the recognition and differentiation of some harmful algae in Chinese coastal waters. Journal of Applied Phycology, 20:35–46
Kamikawa, R., Nagai, S., Hosoi-Tanabe, S., Itakura, S., Yamaguchi, M., Uchida, Y., Baba, T., and Sako, Y., 2007. Application of real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Alexandrium tamarense and Alexandrium catenella cysts from marine sediments. Harmful Algae, 6: 413–420.
Lang, R., Pfeffer, K., Wagner, H., and Heeg, K., 1997. A rapid method for semiquantitative analysis of the human Vβ-repertoire using TaqmanR PCR. Journal of Immunological Methods, 203: 181–192.
Löfström, C., Knutsson, R., Axelsson, C. E., and Rådström, P., 2004. Rapid and specific detection of Salmonella spp. In animal feed samples by PCR after culture enrichment. Applied and Environmental Biology, 70: 69–75.
Lu, D. D., Goebel, J., Qi, Y. Z., Zou, J. Z., Han, X. T., Gao, Y. H., and Li, Y. G., 2005. Morphological and genetic study of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu from East China Sea, and comparison with some related Prorocentrum species. Harmful Algae, 4: 493–505.
Lu, D. D., Qi, Y. Z., Goebel, J., Zou, J. Z., and Gao, Y. H., 2003. Redescription of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu and comparison with relevant Prorocentrum species. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14: 1060–1064 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo, H., Yousef, A. E., and Wang, H. H., 2004. A real-time polymerase chain reaction based method for rapid and specific detection of spoilage Alicyclobacillus spp. in apple juice. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 39: 376–382.
Marín, I., Aguilera, A., Reguera, B., and Abad, J. P., 2001. Preparation of DNA suitable for PCR amplification from fresh or fixed single dinoflagellate cells. Biotechniques, 30: 88–93.
Medina, M., Collins, A. G., Silberman, J. D., and Sogin, M. L., 2001. Evaluating hypotheses of basal animal phylogeny using complete sequences of large and small subunit rRNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98: 9707–9712.
Penna, A., and Magnani, M., 1999. Identification of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) using PCR and rDNA-targeted probes. Journal of Phycology, 35: 615–621.
Penna, A., and Magnani, M., 2000. A PCR immunoassay method for the detection of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species. Journal of Phycology, 36: 1183–1186.
Sako, Y., Hosoi-Tanabe, S., and Uchida, A., 2004. Fluorescence in situ hybridization using rRNA-targeted probes for simple and rapid identification of the toxic dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense and Alexandrium catenella. Journal of Phycology, 40: 598–605.
Schnürch, H. G., Niederacher, D., An, H. X., Ellenberger, I., Roeyen, C. R. C. V., Cho, J. Y., and Beckmann, M. W., 1998. Multistep carcinogenesis of sporadic breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 34(Suppl.): 17–17 (1).
Smayda, T. J., 1997. Harmful algal blooms: their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology and Oceanography, 42: 1137–1153.
Sun, J., Yu, Z. G., Zhen, Y., Zhao, T., Zhao, L. Y., Yuan, J., and Mi, T. Z., 2010. Difference analysis of 18S rDNA partial sequences of three species of Prorocentrum using PCR-DGGE. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40(2): 052–056.
Walburger, D. K., Afonina, I. A., and Wydro, R., 2001. An improved real time PCR method for simultaneous detection of C282Y and H63D mutations in the HFE gene associated with hereditary hemochromatiosis. Mutation Research Genomics, 432: 69–78.
Wang, D. Z., Huang, X. G., Chan, L. L., and Hong, H. S., 2007. Development of an immunofluorescence technique for detecting Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu. Journal of Applied Phycology, 19: 325–332.
Wang, P., Liang, J. R., Gao, Y. H., Gao, Y., Lv, S. H., Qi, Y. Z., Li, X. S., and Yu, Z. M., 2005. Identification of Prorocentrum donghaiense in genus Prorocentrum from the East China Sea based on partial LSU rDNA. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 44(3): 437–440 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, M., and Miller, M. S., 2004. Determination of murine fetal Cyp lal and lbl expression by real-time fluorescence reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 201: 295–302.
Yu, R. C., Tang, X. H., Zhang, Q. C., Chen, Y., Wang, Y. F., Yan, T., and Zou, M. J., 2006. Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method to detect ‘tamarense/catenella species complex’ (’Temperate Asian’ ribotype) in genus Alexandrium along Chinese coast. Acta Scientiae Circum Stantiae, 26: 646–651 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, B. Y., Wang, G. C., Zhang, Y., Han, X. T., Lv, S. H., Qi, Y. Z., Zou, J. Z., and Zeng, C. K., 2004. Cloning and sequence analysis of 5.8S and ITS region from Prorocentrum donghaiense and P. micans APBM. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 35: 264–272 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, H., and Lin, S. J., 2005. Development of a cob-18S rRNA Gene Real-time PCR assay for quantifying Pfiesteria shumwayae in the natural environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71: 7053–7063.
Zhang, L. Y., Yan, T., Han, G., and Zou, M. J., 2007. A shipboard study of the effects of HAB species Prorocentrum donghaiense on protozoan communities at three sites in the East China Sea, involving 72 h inoculation experiments to stimulate HAB bloom events. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27: 1926–1936 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, T., Mi, T. Z., Lu, Q., Sun, J., Zhao, L. Y., Yuan, J., and Yu, Z. G., 2009. Distinct ion of red tide causing algae by using the PCR-RFLP technology. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39(Suppl.): 105–108.
Zhang, X. F, Yang, G. P., Liu, Y. J., Liu, R. X., and Zhu, M. Y., 2006. Construction of the cDNA library and trial EST analysis of Prorocentrum donghaiense. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 36: 361–364 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, L. Y., Mi, T. Z., Zhen, Y., Li, M. Y., He, S. Y., Sun, J., and Yu, Z. G., 2009. Cloning of proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense and monitoring its expression profiles by real-time RT-PCR. Hydrobiologia, 627: 19–30.
Zhen, Y., Mi, T. Z., and Yu, Z. G., 2009. Detection of several harmful algal species by sandwich hybridization integrated with a nuclease protection assay. Harmful Algae, 8: 651–657.
Zhou, W. H., Yin, K. D., and Zhu, D. D., 2006. Phytonplankton biomass and high frequency of Prorocentrum donghaiense harmful algal blooms in Zhoushan sea area in spring. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17: 887–893 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Mi, T., Zhen, Y. et al. Development of a real-time PCR method (Taqman) for rapid identification and quantification of Prorocentrum donghaiense . J. Ocean Univ. China 11, 366–374 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-012-1911-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-012-1911-0