Abstract
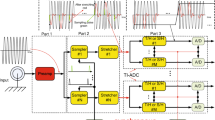
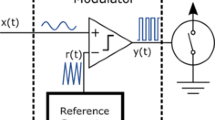
A kind of architecture of Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC) for Ultra-WideBand (UWB) application is presented. The proposed TDC is based on pulse shrinking, and implemented in a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) device. The pulse shrinking is realized in a loop containing two Programmable Delay Lines (PDLs) or a two-channel PDL. One line (channel) delays the rising edge and the other line (channel) delays the falling edge of a circulating pulse. Delay resolution of PDL is converted into a digital output code under known conditions of pulse width. This delay resolution measurement mechanism is different from the conventional time interval measurement mechanism based on pulse shrinking of conversion of unknown pulse width into a digital output code. This mechanism automatically avoids the influence of unwanted pulse shrinking by any circuit element apart from the lines. The achieved relative errors for four PDLs are within 0.80%-1.60%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Grazzini, M. Pieraccini, F. Parrini, et al.. An ultra-wideband high-dynamic range GPR for detecting buried people after collapse of buildings. 2010 13th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), Lecce, Italy, June 21–25, 2010, 1–6.
J. Hu, G. Zhu, T. Jin, et al.. Adaptive through-wall indication of human target with different motions. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11 (2014)5, 911–915.
S. Shirodkar, P. Barua, D. Anuradha, et al.. Heart-beat detection and ranging through a wall using ultra wide band radar. 2011 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Calicut, India, February 10–12, 2011, 579–583.
E. M. Johansson and J. E. Mast. Three-dimensional ground-penetrating radar imaging using synthetic aperture time-domain focusing. Proceedings of 1994 SPIE Conference on Advanced Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Detectors, San Diego, CA, USA, July 24, 1994, 205–214.
Y. Yang and A. E. Fathy. Development and implementation of a real-time see-through-wall radar system based on FPGA. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(2009)5, 1270–1280.
R. Szplet and K. Klepacki. An FPGA-integrated time-to-digital converter based on two-stage pulse shrinking. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 59(2010)6, 1663–1670.
Y. Liu, U. Vollenbruch, Y. Chen, et al.. Multi-stage pulse shrinking time-to-digital converter for time interval measurements. Proceedings of 2007 European Conference on Microwave Integrated Circuit, Munich, Germany, October 8–10, 2007, 267–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (No. 2012AA121901).
Communication author: Chen Chao, born in 1987, male, Doctor Degree.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Meng, S., Xia, Z. et al. Pulse shrinking time-to-digital converter for UWB application. J. Electron.(China) 31, 180–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-4031-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-4031-8
Key words
- Ultra-WideBand (UWB)
- Pulse shrinking
- Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- Programmable Delay Line (PDL)
- Delay resolution measurement