Abstract
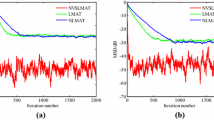
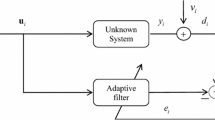
This paper proposes an optimized least mean absolute third (OPLMAT) algorithm to improve the capability of the adaptive filtering algorithm against Gaussian and non-Gaussian noises when the unknown system is a time-varying parameter system under low signal–noise rate. The optimal step size of the OPLMAT is obtained based on minimizing the mean-square deviation at the current time. In addition, the mean convergence and steady-state error of the OPLMAT algorithm are derived theoretically, and the computational complexity of OPLMAT is analyzed. Furthermore, the simulation experimental results of system identification presented illustrate the principle and efficiency of the OPLMAT algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm performs much better than the LMAT and NLMAT algorithms.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sayed, A.H.: Adaptive Filters. Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Shin, H.C., Sayed, A.H., Song, W.J.: Variable step size NLMS and affine projection algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(2), 132–135 (2004)
Kwong, R.H., Johnston, E.W.: A variable step size LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40(7), 1633–1642 (1992)
Ang, W.P., Farhang-Boroujeny, B.: A new class of gradient adaptive step size LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(4), 805–810 (2001)
Wang, P., Kam, P.-Y.: An automatic step size adjustment algorithm for LMS adaptive filters and an application to channel estimation. Phys. Commun. 5, 280–286 (2012)
Liu, J.C., Yu, X., Li, H.R.: A nonparametric variable step size NLMS algorithm for transversal filters. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(17), 7365–7371 (2011)
Benesty, J., Rey, H., Vega, L.R., et al.: A nonparametric VSSNLMS algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 13(10), 581–584 (2006)
Huang, H.-C., Lee, J.: A new variable step size NLMS algorithm and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(4), 2055–2060 (2012)
Zhao, S., Jones, D.L., Khoo, S., et al.: New variable step sizes minimizing mean-square deviation for the LMS-type algorithms. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(7), 2251–2265 (2014)
Lee, C.H., Park, P.G.: Optimal step size affine projection algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(7), 431–434 (2012)
Zhi, Y.F., Shang, F.F., Zhang, J., et al.: Optimal step size of pseudo affine projection algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 273, 82–88 (2016)
Ciochină, S., Paleologu, C., Benesty, J.: An optimized NLMS algorithm for system identification. Signal Process. 118, 115–121 (2016)
Lee, Y.H., Mok, J.D., Kim, S.D., Cho, S.H.: Performance of least mean absolute third (LMAT) adaptive algorithm in various noise environments. IET Electron. Lett. 34(2), 241–243 (1998)
Walach, E., Widrow, B.: The least mean fourth (LMF) adaptive algorithm and its family. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 30(2), 275–283 (1984)
Eweda, E., Bershad, N.J.: Stochastic analysis of a stable normalized least mean fourth algorithm for adaptive noise canceling with a white Gaussian reference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(12), 6235–6244 (2012)
Zhao, H., Yu, Y., Gao, S., et al.: A new normalized LMAT algorithm and its performance analysis. Signal Process. 105(12), 399–409 (2014)
Arikan, O., Cetin, A.E., Erzin, E.: Adaptive filtering for non-Gaussian stable processes. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2(11), 1400–1403 (1995)
Aydin, G., Arikan, O., Cetin, A.E.: Robust adaptive filtering algorithms for \(\alpha \)-stable random processes. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 46(2), 198–202 (1999)
Price, R.: A useful theorem for nonlinear devices having Gaussian inputs. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 4(2), 69–72 (1958)
Spiegel, M.R.: Mathematical Handbook of Formulas and Tables. McGraw-Hill, New York (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61074120, 61673310) and the State Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control and Decision of Complex Systems of Beijing Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Li, Z. Optimal step size of least mean absolute third algorithm. SIViP 11, 1105–1113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1064-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1064-0