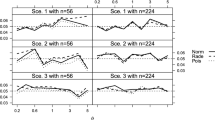
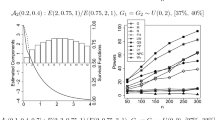
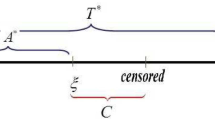
Abstract
The Mann–Whitney effect is an intuitive measure for discriminating two survival distributions. Here we analyse various inference techniques for this parameter in a two-sample survival setting with independent right-censoring, where the survival times are even allowed to be discretely distributed. This allows for ties in the data and requires the introduction of normalized versions of Kaplan–Meier estimators from which adequate point estimates are deduced. Asymptotically exact inference procedures based on standard normal, bootstrap, and permutation quantiles are developed and compared in simulations. Here, the asymptotically robust and—under exchangeable data—even finitely exact permutation procedure turned out to be the best. Finally, all procedures are illustrated using a real data set.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla S, Montez-Rath ME, Parfrey PS, Chertow GM (2016) The win ratio approach to analyzing composite outcomes: an application to the EVOLVE trial. Contemp Clin Trials 48:119–124
Acion L, Peterson JJ, Temple S, Arndt S (2006) Probabilistic index: an intuitive non-parametric approach to measuring the size of treatment effects. Stat Med 25(4):591–602
Akritas MG (1986) Bootstrapping the Kaplan–Meier estimator. J Am Stat Assoc 81(396):1032–1038
Akritas MG (2011) Nonparametric models for ANOVA and ANCOVA designs. In: International encyclopedia of statistical science. Springer, pp 964–968
Akritas MG, Brunner E (1997) Nonparametric methods for factorial designs with censored data. J Am Stat Assoc 92(438):568–576
Albert M, Bouret Y, Fromont M, Reynaud-Bouret P (2015) Bootstrap and permutation tests of independence for point processes. Ann Stat 43(6):2537–2564
Allignol A, Schumacher M, Beyersmann J (2011) Empirical transition matrix of multi-state models: the etm package. J Stat Softw 38(4):1–15
Arboretti R, Basso D, Campigotto F, Salmaso L (2009) Permutation tests for survival data analysis. In: Proceedings of the conference of the italian statistical society, book of short papers, 23–25 September 2009, Pescara, pp 311–314
Arboretti R, Bolzan M, Campigotto F, Corain L, Salmaso L (2010) Combination-based permutation testing in survival analysis. Quad Stat 12:21–44
Arboretti R, Fontana R, Pesarin F, Salmaso L (2017) Nonparametric combination tests for comparing two survival curves with informative and non-informative censoring. Stat Methods Med Res. doi:10.1177/0962280217710836
Arcones MA, Kvam PH, Samaniego FJ (2002) Nonparametric estimation of a distribution subject to a stochastic precedence constraint. J Am Stat Assoc 97(457):170–182
Bagdonavičius V, Nikulin M (2002) Accelerated life models: modeling and statistical analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Bajorunaite R, Klein JP (2008) Comparison of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks. J Stat Comput Simul 78(10):951–966
Basso D, Pesarin F, Salmaso L, Solari A (2009) Permutation tests for stochastic ordering and ANOVA. Springer, New York
Bebu I, Lachin JM (2016) Large sample inference for a win ratio analysis of a composite outcome based on prioritized components. Biostatistics 17(1):178–187
Bonnini S (2014) Testing for heterogeneity with categorical data: permutation solution vs. bootstrap method. Commun Stat Theory Methods 43(4):906–917
Bonnini S, Corain L, Marozzi M, Salmaso L (2014) Nonparametric hypothesis testing: rank and permutation methods with applications in R. Wiley, London
Boos D, Janssen P, Veraverbeke N (1989) Resampling from centered data in the two-sample problem. J Stat Plan Inference 21(3):327–345
Brendel M, Janssen A, Mayer CD, Pauly M (2014) Weighted logrank permutation tests for randomly right censored life science data. Scand J Stat 41(3):742–761
Brückner M, Brannath W (2016) Sequential tests for non-proportional hazards data. Lifetime Data Anal 23(3):339–352
Brunner E, Munzel U (2000) The nonparametric Behrens–Fisher problem: asymptotic theory and a small-sample approximation. Biometric J 42(1):17–25
Chung E, Romano JP (2013) Exact and asymptotically robust permutation tests. Ann Stat 41(2):484–507
Chung E, Romano JP (2016a) Asymptotically valid and exact permutation tests based on two-sample U-statistics. J Stat Plan Inference 168:97–105
Chung E, Romano JP (2016b) Multivariate and multiple permutation tests. J Econom 193(1):76–91
Cramer E, Kamps U (1997) The UMVUE of \(P(X< Y)\) based on type-II censored samples from Weinman multivariate exponential distributions. Metrika 46(1):93–121
Davidov O, Herman A (2012) Ordinal dominance curve based inference for stochastically ordered distributions. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 74(5):825–847
Davidov O, Peddada S (2013) The linear stochastic order and directed inference for multivariate ordered distributions. Ann Stat 41(1):1–40
De Neve J, Thas O, Ottoy JP, Clement L (2013) An extension of the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test for analyzing RT-qPCR data. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 12(3):333–346
De Neve J, Meys J, Ottoy JP, Clement L, Thas O (2014) unifiedWMWqPCR: the unified Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test for analyzing RT-qPCR data in R. Bioinformatics 30(17):2494–2495
Delaigle A, Hall P, Jin J (2011) Robustness and accuracy of methods for high dimensional data analysis based on Student’s t-statistic. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 73(3):283–301
Dobler D (2016) Bootstrapping the Kaplan–Meier estimator on the whole line. Preprint arXiv:1507.02838
Dunkler D, Schemper M, Heinze G (2010) Gene selection in microarray survival studies under possibly non-proportional hazards. Bioinformatics 26(6):784–790
Efron B (1967) The two sample problem with censored data. Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability 4:831–853
Efron B (1981) Censored data and the bootstrap. J Am Stat Assoc 76(374):312–319
Friedrich S, Brunner E, Pauly M (2017) Permuting longitudinal data in spite of the dependencies. J Multivar Anal 153:255–265
Gel YR, Chen B (2012) Robust Lagrange multiplier test for detecting ARCH/GARCH effect using permutation and bootstrap. Can J Stat 40(3):405–426
Gill RD (1983) Large sample behaviour of the product–limit estimator on the whole line. Ann Stat 11(1):49–58
Gill RD, Johansen S (1990) A survey of product–integration with a view toward application in survival analysis. Ann Stat 18(4):1501–1555
Good PI (2010) Permutation tests: a practical guide to resampling methods for testing hypotheses, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Hall P, Wilson S (1991) Two guidelines for bootstrap hypothesis testing. Biometrics 47(2):757–762
Hess KR (2010) Comparing survival curves using an easy to interpret statistic. Clin Cancer Res 16(20):4912–4913
Horvath L, Yandell B (1987) Convergence rates for the bootstrapped product–limit process. Ann Stat 15(3):1155–1173
Janssen A (1997) Studentized permutation tests for non-i.i.d. hypotheses and the generalized Behrens–Fisher problem. Stat Prob Lett 36(1):9–21
Janssen A (1999) Testing nonparametric statistical functionals with applications to rank tests. J Stat Plan Inference 81(1):71–93
Janssen A, Pauls T (2005) A Monte Carlo comparison of studentized bootstrap and permutation tests for heteroscedastic two-sample problems. Comput Stat 20(3):369–383
Kieser M, Friede T, Gondan M (2013) Assessment of statistical significance and clinical relevance. Stat Med 32(10):1707–1719
Klein JP, Moeschberger ML (2003) Survival analysis: techniques for censored and truncated data. Springer, New York
Konietschke F, Pauly M (2014) Bootstrapping and permuting paired t-test type statistics. Stat Comput 24(3):283–296
Konietschke F, Hothorn LA, Brunner E (2012) Rank-based multiple test procedures and simultaneous confidence intervals. Electron J Stat 6:738–759
Kotz S, Lumelskii Y, Pensky M (2003) The stress-strength model and its generalizations: theory and applications. World Scientific, Singapore
Koziol JA, Jia Z (2009) The concordance index C and the Mann–Whitney parameter \({P}r(X>Y)\) with randomly censored data. Biometric J 51(3):467–474
Lange K, Brunner E (2012) Sensitivity, specificity and ROC-curves in multiple reader diagnostic trials—a unified, nonparametric approach. Stat Methodol 9(4):490–500
Lehmann EL, Romano JP (2010) Testing statistical hypotheses, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Lo SH, Singh K (1986) The product-limit estimator and the bootstrap: some asymptotic representations. Probab Theory Relat Fields 71(3):455–465
Luo X, Tian H, Mohanty S, Tsai WY (2015) An alternative approach to confidence interval estimation for the win ratio statistic. Biometrics 71(1):139–145
Martinussen T, Pipper CB (2013) Estimation of odds of concordance based on the Aalen additive model. Lifetime Data Anal 19(1):100–116
Medina J, Kimberg DY, Chatterjee A, Coslett HB (2010) Inappropriate usage of the Brunner–Munzel test in recent voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping studies. Neuropsychologia 48(1):341–343
Moore DF (2016) Applied survival analysis using R. Springer, Cham
Nandi SB, Aich AB (1994) A note on confidence bounds for \({P(X> Y)}\) in bivariate normal samples. Sankhyā: Indian J Stat Ser B 56(2):129–136
Neubert K, Brunner E (2007) A studentized permutation test for the non-parametric Behrens–Fisher problem. Comput Stat Data Anal 51(10):5192–5204
Neuhaus G (1994) Conditional rank tests for the two-sample problem under random censorship: treatment of ties. In: Recent advances in statistics and probability: proceedings of the 4th international meeting of statistics in the Basque Country, San Sebastián, Spain, 4–7 August, 1992, VSP, pp 127–138
Neuhaus G (1993) Conditional rank tests for the two-sample problem under random censorship. Ann Stat 21(4):1760–1779
Pauly M (2011) Discussion about the quality of F-ratio resampling tests for comparing variances. TEST 20(1):163–179
Pauly M, Brunner E, Konietschke F (2015) Asymptotic permutation tests in general factorial designs. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 77(2):461–473
Pauly M, Asendorf T, Konietschke F (2016) Permutation-based inference for the AUC: a unified approach for continuous and discontinuous data. Biometric J 58(6):1319–1337
Pesarin F, Salmaso L (2010) Permutation tests for complex data: theory, applications and software. Wiley, Sussex
Pesarin F, Salmaso L (2012) A review and some new results on permutation testing for multivariate problems. Stat Comput 22(2):639–646
Pocock SJ, Ariti CA, Collier TJ, Wang D (2012) The win ratio: a new approach to the analysis of composite endpoints in clinical trials based on clinical priorities. Eur Heart J 33(2):176–182
R Development Core Team (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Rauch G, Jahn-Eimermacher A, Brannath W, Kieser M (2014) Opportunities and challenges of combined effect measures based on prioritized outcomes. Stat Med 33(7):1104–1120
Ryu E, Agresti A (2008) Modeling and inference for an ordinal effect size measure. Stat Med 27(10):1703–1717
Santos ENF, Ferreira DF (2012) Multivariate multiple comparisons by bootstrap and permutation tests. Biometric Braz J 30(3):381–400
Thas O, De Neve J, Clement L, Ottoy JP (2012) Probabilistic index models. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 74(4):623–671
Therneau TM, Lumley T (2017) A package for survival analysis in S. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival, version 2.41-3
van der Vaart AW, Wellner J (1996) Weak convergence and empirical processes. Springer, New York
Wang D, Pocock S (2016) A win ratio approach to comparing continuous non-normal outcomes in clinical trials. Pharm Stat 15(3):238–245
Yan N, Mei CL, Wang N (2015) A unified bootstrap test for local patterns of spatiotemporal association. Environ Plan A 47(1):227–242
Ying Z (1989) A note on the asymptotic properties of the product–limit estimator on the whole line. Stat Prob Lett 7(4):311–314
Zapf A, Brunner E, Konietschke F (2015) A wild bootstrap approach for the selection of biomarkers in early diagnostic trials. BMC Med Res Methodol 15(1):43
Zhou XH, McClish DK, Obuchowski NA (2002) Statistical methods in diagnostic medicine. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors appreciate the support from the DFG (German Research Foundation) Grant No. DFG-PA 2409/4-1.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobler, D., Pauly, M. Bootstrap- and permutation-based inference for the Mann–Whitney effect for right-censored and tied data. TEST 27, 639–658 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-017-0565-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-017-0565-z