Abstract
Objective
We reviewed our institutional experience with cases of multimodality treatment for advanced thymic carcinoma to determine patient outcomes and prognostic indicators.
Methods
Between 1998 and 2014, 16 patients with a Masaoka stage III or IV thymic carcinoma underwent surgical resection after induction therapy at Osaka University Hospital. These were considered to have great vessel invasion or metastasis to the mediastinal or intrathoracic lymph nodes based on the preoperative workup findings, and received induction therapy.
Results
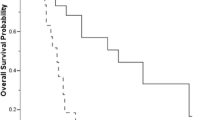
Complete tumor resection was achieved in 11 (69 %) after the induction therapy. Pathological findings revealed that 10 patients had Masaoka stage III disease, 1 had IVa, and 5 had IVb. The histological diagnosis was squamous cell carcinoma in 13, neuroendocrine carcinoma in 2, and undifferentiated carcinoma in 1. The 5-year survival rate for all patients was 71 %. Survival was significantly better in patients who underwent a complete resection (R0 disease) as compared to those with incompletely resected tumors (R1 or R2 disease).
Conclusions
Multimodality treatment offers encouraging results and complete resection provides high survival rate for patients with advanced thymic carcinoma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okereke IC, Kesler KA, Freeman RK, Rieger KM, Birdas TJ, Ascioti AJ, Badve S, Nelson RP, Loehrer PJ. Thymic carcinoma: outcomes after surgical resection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:1668–72 (discussion 1672–1663).
Takeda S, Sawabata N, Inoue M, Koma M, Maeda H, Hirano H. Thymic carcinoma. Clinical institutional experience with 15 patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;26:401–6.
Rea F, Marulli G, Di Chiara F, Schiavon M, Perissinotto E, Breda C, Favaretto AG, Calabrese F. Multidisciplinary approach for advanced stage thymic tumors: long-term outcome. Lung Cancer. 2011;72:68–72.
Wright CD, Choi NC, Wain JC, Mathisen DJ, Lynch TJ, Fidias P. Induction chemoradiotherapy followed by resection for locally advanced Masaoka stage III and IVA thymic tumors. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:385–9.
Girard N. Thymic epithelial tumours: from basic principles to individualised treatment strategies. Eur Respir Rev. 2013;22:75–87.
Komaki R, Gomez DR. Radiotherapy for thymic carcinoma: adjuvant, inductive, and definitive. Front Oncol. 2014;3:330.
Korst RJ, Bezjak A, Blackmon S, Choi N, Fidias P, Liu G, Marx A, Wright C, Mock S, Rutledge JR, Keshavjee S. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced thymic tumors: a phase II, multi-institutional clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:36–44, 46 e31.
Shintani Y, Ohta M, Hazama K, Miyoshi S, Kagisaki K, Matsuda H. Thymic carcinoma successfully resected with superior vena cava after chemoradiotherapy. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001;49:717–21.
Ose N, Inoue M, Morii E, Shintani Y, Sawabata N, Okumura M. Multimodality therapy for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the thymus. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:e85–7.
Venuta F, Rendina EA, Longo F, De Giacomo T, Anile M, Mercadante E, Ventura L, Osti MF, Francioni F, Coloni GF. Long-term outcome after multimodality treatment for stage III thymic tumors. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;76:1866–72 (discussion 1872).
Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Tan D, Cipolla D, Connolly G, Debb G, Ramnath N. Multimodality therapy for thymic carcinoma (TCA): results of a 30-year single-institution experience. Am J Clin Oncol. 2004;27:68–72.
Kondo K, Monden Y. Therapy for thymic epithelial tumors: a clinical study of 1,320 patients from Japan. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;76:878–84 (discussion 884–875).
Tseng YL, Wang ST, Wu MH, Lin MY, Lai WW, Cheng FF. Thymic carcinoma: involvement of great vessels indicates poor prognosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;76:1041–5.
Yano M, Sasaki H, Yokoyama T, Yukiue H, Kawano O, Suzuki S, Fujii Y. Thymic carcinoma: 30 cases at a single institution. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:265–9.
Attaran S, Acharya M, Punjabi PP, Anderson JR. Does surgical debulking for advanced stages of thymoma improve survival? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012;15:494–7.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shintani, Y., Inoue, M., Kawamura, T. et al. Multimodality treatment for advanced thymic carcinoma: outcomes of induction therapy followed by surgical resection in 16 cases at a single institution. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 63, 159–163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-014-0486-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-014-0486-7