Abstract
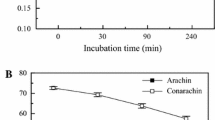
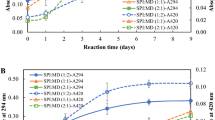
Peanut protein isolate (PPI) were conjugated with dextran or gum arabic through glycation to study the physiochemical properties of PPI–polysaccharides conjugates. Structural features, solubility as well as emulsifying properties of the two conjugates were compared. The degree of graft value of the two conjugates suggested that glycation of PPI with gum arabic took place more easily than with dextran. Glycated conjugates had better solubility and emulsifying ability than native PPI. Analysis of structural features of the conjugates suggested that their improved functional properties could be the result of less α-helix secondary structure, lower surface hydrophobicity and less compact tertiary structure. The solubility of PPI–dextran conjugates was improved for the pH range 3–9, while that of PPI–gum arabic conjugates was improved above neutral pH range. Moreover, better emulsifying ability was observed in PPI–gum arabic conjugates than PPI–dextran conjugates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Su G, Ren J, Yang B, Cui C, Zhao M (2011) Comparison of hydrolysis characteristics on defatted peanut meal proteins between a protease extract from Aspergillus oryzae and commercial proteases. Food Chem 126:1306–1311
Zhao G, Liu Y, Zhao M, Ren J, Yang B (2011) Enzymatic hydrolysis and their effects on conformational and functional properties of peanut protein isolate. Food Chem 127:1438–1443
Wu H, Wang Q, Ma T, Ren J (2009) Comparative studies on the functional properties of various protein concentrate preparations of peanut protein. Food Res Int 42:343–348
Lawal OS, Adebowale KO, Adebowale YA (2007) Functional properties of native and chemically modified protein concentrates from bambarra groundnut. Food Res Int 40:1003–1011
Dong X, Zhao M, Yang B, Yang X, Shi J, Jiang Y (2011) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on the functional property of peanut protein. J Food Process Eng 34:2191–2204
Dong X, Zhao M, Shi J, Yang B, Li J, Luo D, Jiang G, Jiang Y (2011) Effects of combined high-pressure homogenization and enzymatic treatment on extraction yield, hydrolysis and function properties of peanut proteins. Innov Food Sci Emerg 12:478–483
Hu X, Zhao M, Sun W, Zhao G, Ren J (2011) Effects of microfluidization treatment and transglutaminase cross-linking on physicochemical, functional, and conformational properties of peanut protein isolate. J Agr Food Chem 59:8886–8894
Jackson SP, Tjian R (1988) O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell 55(1):125–133
Liu J, Ru Q, Ding Y (2012) Glycation a promising method for food protein modification: physicochemical properties and structure, a review. Food Res Int 49:170–183
Kato A (2002) Industrial applications of maillard-type protein-polysaccharide conjugates. Food Sci Technol Res 8(3):193–199
Kato A, Mifuru R, Matsudomi N, Kobayashi K (1992) Functional casein-polysaccharides conjugates prepared by controlled dry heating. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 56(4):567–571
Song Y, Babiker EE, Usui M, Saito A, Kato A (2002) Emulsifying properties and bactericidal action of chitosan–lysozyme conjugates. Food Res Int 35:459–466
Sun Y, Hayakawa S, Izumori K (2004) Modification of ovalbumin with a rare ketohexose through the Maillard reaction: effect on protein structure and gel properties. J Agr Food Chem 52:1293–1299
Liu Y, Zhao G, Zhao M, Ren J, Yang B (2012) Improvement of functional properties of peanut protein isolate by conjugation with dextran through Maillard reaction. Food Chem 131(3):901–906
Nakamura A, Sasaki F, Watanabe K, Ojima T, Ahn DH, Saeki H (2006) Changes in allergenicity and digestibility of squid tropomyosin during the Maillard reaction with ribose. J Agr Food Chem 54:9529–9534
Nakamur S, Suzuki Y, Ishikaw E, Yakushi T, Jing H, Miyamotoc T, Hashizumec K (2008) Reduction of in vitro allergenicity of buckwheat Fag e 1 through the Maillard-type glycosylation with polysaccharides. Food Chem 109(3):538–545
Yang ZH, Chen Li, Li YY, Wang ZH (2013) Effects of Maillard reaction on allergenicity of buckwheat allergen Fag t 3 during thermal processing. J Sci Food Agr 93(6):1510–1515
Jiménez-Castaño L, López-Fandiño R, Olano A, Villamiel M (2005) Study on β-lactoglobulin glycosylation with dextran: effect on solubility and heat stability. Food Chem 93:689–695
Diftis N, Kiosseoglou V (2006) Physicochemical properties of dry-heated soy protein isolate–dextran mixtures. Food Chem 96:228–233
Jiménez-Castaño L, Villamiel M, López-Fandiño R (2007) Glycosylation of individual whey proteins by Maillard reaction using dextran of different molecular mass. Food Hydrocoll 21:433–443
Chanamai R, McClements DJ (2002) Comparison of gum arabic, modified starch, and whey protein isolate as emulsifiers: influence of pH, CaCl2 and temperature. J Food Sci 67(1):120–125
Shepherd R, Robertson A, Ofman D (2000) Dairy glycoconjugate emulsifiers: casein–maltodextrins. Food Hydrocoll 14:281–286
Miralles B, Martínez-Rodríguez A, Santiago A, Van de Lagemaat J, Heras A (2007) The occurrence of a Maillard-type protein-polysaccharide reaction between β-lactoglobulin and chitosan. Food Chem 100:1071–1075
Chevalier F, Chobert JM, Popineau Y, Nicolas MG, Haertléa T (2001) Improvement of functional properties of β-lactoglobulin glycated through the Maillard reaction is related to the nature of the sugar. Int Dairy J 11:145–152
Mu L, Zhao M, Yang B, Zhao H, Cui C, Zhao Q (2010) Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the graft reaction between soy protein isolate and gum acacia and on the physicochemical properties of conjugates. J Agr Food Chem 58:4494–4499
Alizadeh-Pasdar N, Li-Chan EC (2000) Comparison of protein surface hydrophobicity measured at various pH values using three different fluorescent probes. J Agr Food Chem 48:328–334
Lowry OH, Rosembroug HJ, Lewis A, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 19:265–275
Pearce KN, Kinsella JE (1978) Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J Agr Food Chem 26(3):716–723
Islam AM, Phillips GO, Sljivo A, Snowden MJ, Williams PA (1997) A review of recent developments on the regulatory, structural and functional aspects of gum arabic. Food Hydrocoll 4(11):493–505
Schmitt C, Bovay C, Frossard P (2005) Kinetics of formation and functional properties of conjugates prepared by dry-state incubation of β-lactoglobulin/acacia gum electrostatic complexes. J Agr Food Chem 53:9089–9099
Chen L, Chen J, Ren J, Zhao M (2011) Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein isolates and on the emulsifying properties of hydrolysates. J Agr Food Chem 59:2600–2609
Hattori M, Nagasawa K, Ametani A, Kaminogawa S, Takahashi K (1994) Functional changes in β-lactoglobulin by conjugation with carboxymethyl dextran. J Agr Food Chem 42:2120–2125
Hayakawa S, Nakai S (1985) Relationships of hydrophobicity and net charge to the solubility of milk and soy proteins. J Food Sci 50:486–491
Hattori M, Ogino A, Nakai H, Takahashi K (1997) Functional improvement of β-lactoglobulin by conjugating with alginate lyase-lysate. J Agr Food Chem 45:703–708
Kobayashi K, Hirano A, Ohta A, Yoshida T, Takahashi K, Hattori M (2001) Reduced immunogenicity of β-lactoglobulin by conjugation with carboxymethyl dextran differing in molecular weight. J Agr Food Chem 49:823–831
Liu Y, Zhao G, Ren J, Zhao M, Yang B (2011) Effect of denaturation during extraction on the conformational and functional properties of peanut protein isolate. Innov Food Sci Emerg 12:375–380
Nakamura S, Kato A, Kobayashi K (1992) Bifunctional lysozyme-galactomannan conjugate having excellent emulsifying properties and bactericidal effect. J Agr Food Chem 40:735–739
Nagasawa K, Takahashi K, Hattori M (1996) Improved emulsifying properties of β-lactoglobulin by conjugating with carboxymethyl dextran. Food Hydrocoll 1(10):63–67
Diftis N, Kiosseoglou V (2003) Improvement of emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate by conjugation with carboxymethyl cellulose. Food Chem 81:1–6
Dickinson E (2009) Hydrocolloids as emulsifiers and emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll 23:1473–1482
Shu YW, Sahara S, Nakamura S, Kato A (1996) Effects of the length of polysaccharide chains on the functional properties of the Maillard-type lysozyme-polysaccharide conjugate. J Agr Food Chem 44:2544–2548
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. Feng Xue, College of Food Science and Engineering, Northwest A&F University, for his support in the work. This research was also supported by the Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2011BAD02B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zhu, B., Xue, H. et al. Physicochemical Properties of Dry-Heated Peanut Protein Isolate Conjugated with Dextran or Gum Arabic. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90, 1801–1807 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2331-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2331-z