Abstract
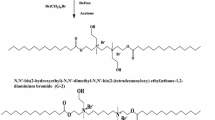
Bio-/environment-friendly cationic gemini surfactant, ethane-1,2-diyl bis(N,N-dimethyl-N-hexadecylammoniumacetoxy)dichloride, referred to as 16-E2-16, was synthesized and characterized. Corrosion inhibition effects of 16-E2-16 on mild steel (MS) surface in 1 M HCl solution at 30, 40, 50 and 60 °C were evaluated using gravimetric analysis, potentiodynamic polarisation and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. The nature of the protective inhibitor film formed on the MS surface was analysed by SEM, EDAX and FT-IR, while TGA was used to assure the thermal behaviour and stability of the film at high temperature. The formation of [inhibitor-Fe2+] on the surface of MS was confirmed by UV–visible spectroscopy. The inhibition efficiency of the studied inhibitor increased with increasing concentration and solution temperature. The compound behaved as a mixed type inhibitor and acted by blocking the electrode surface by means of adsorption obeying the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Surface active properties and corrosion inhibition effects of 16-E2-16 in the presence of inorganic (NaI) and organic (NaSal) salts were also investigated and are discussed. Density functional theory calculations have been carried out to correlate the efficiency of the compound with its intrinsic molecular parameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popova E, Sokolova S, Raicheva M, Christov. Frequency dispersion of the interfacial impedance at mild steel corrosion in acid media in the presence of benzimidazole derivatives. Corros Sci. 2003;45:33–58.
Bentiss F, Jama C, Mernari B, El Attari H, El Kai L, Lebrini M, Traisnel M, Lagrene M. Corrosion control of mild steel using 3,5-bis(4-methoxy)-4-amino-1,24-triazole in normal hydrochloric acid medium. Corros Sci. 2009;51:1628–35.
Daoud D, Douadi T, Issaadi S, Chafaa S. Adsorption and corrosion inhibition of new synthesized thiophene Schiff base on mild steel X52 in HCl and H2SO4 solutions. Corros Sci. 2014;79:50–8.
Hamani H, Douadi T, El-Naoimi M, Issaadi S, Daoud D, Chafaa S. Electrochemical and quantum chemical studies of some azomethine compounds as corrosion inihibitors for mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid. Corros Sci. 2014;88:234–45.
Yadav DK, Quraishi MA. Electrochemical investigation of substituted pyranopyrazoles adsorption on mild steel in acid solution. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51:8194–210.
Herrage L, Hammouti B, Elkadiri S, Aounti A, Jama C, Vezin H, Bentiss F. Adsorption properties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric solution by some newly synthesized diamine derivatives: experimenal and theoretical investigations. Corros Sci. 2010;52:3042–51.
Ansari KR, Quraishi MA, Singh A. Schiff base of pyridyl substituted triazoles as new and effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2014;79:5–15.
Hassan HH, Adbelghani E, Amin MA. Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution by triazole derivatives Part I. Polarization and EIS studies. Electrochim Acta. 2007;52:6359–66.
Abdoud Y, Abourrriche A, Saffaj T, Berrada M, Charrouf M, Bennamara A, Al Himidi N, Hannache H. 2,3-Quinoxalinedione as a novel corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl. Mater Chem Phys. 2007;105:1–5.
Menger FM, Keiper JS. Gemini surfactants. Angew Chem Int. 2000;39:1906–1920.
Zana R, Xia J. Gemini surfactants. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
El Achouri M, Kertit S, Gouttaya HM, Nciri B, Bensouda Y, Perez L, Infante MR, Elkacemi K. Corrosion inhibition of iron in 1 M HCl by some gemini surfactants in the series of alkanediyl-α,ω-bis-(dimethyl tetradecyl ammonium bromide). Prog Org Coat. 2001;43:267–73.
Mobin M, Aslam J, Al-Lohedan HA. Study on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion by cationic gemini surfactant in 1 M HCl. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2016;37:1002–9.
Motamedi M, Tehrani-Bagha AR, Mahdavian M. Effect of aging time on corrosion inhibition of cationic surfactant on mild steel in sulfamic acid cleaning solution. Corros Sci. 2013;70:46–54.
Tehrani-Bagha AR, Holmberg K. Cationic ester-containing gemini surfactants: physical-chemical properties. Langmuir. 2010;26:9276–82.
Tehrani-Bagha AR, Holmberg K, Nyden M, Nordstierna L. Micelle growth of cationic gemini surfactants studied by NMR and by time-resolved fluorescence quenching. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;405:145–9.
Fatma N, Ansari WH, Panda M, Kabir-ud-Din. A systematic study of mixed surfactant solutions of a cationic ester-bonded dimeric surfactant with cationic, anionic and nonionic monomeric surfactants in aqueous media. J Surfactant Deterg. 2013;16:1448–52.
Fuchs-Godec R. Effects of surfactants and their mixtures on inhibition of the corrosion process of ferritic stainless steel. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54:2171–9.
Fuchs-Godec R, Pavlovic MG. Synergistic effect between non-ionic surfactants and halide ions in the forms of inorganic and organic salts for the corrosion inhibition of stainless-steel X4Cr13 in sulphuric acid. Corros Sci. 2012;58:192–201.
Umoren SA, Ebenso EE. The synergistic effect of polyacrylamide and iodide ions on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in H2SO4. Mater Chem Phys. 2007;106:387–93.
Asefi D, Arami M, Mahmoodi NM. Electrochemical effect of cationic gemini surfactant and halide salts on corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in acid medium. Corros Sci. 2010;52:794–800.
Ansari WH, Fatma N, Panda M, Kabir-ud-Din. Solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by novel biodegradable cationic gemini surfactant ethane-1,2-diyl bis(N, N-dimethyl-N-hexadecylammoniumacetoxy)dichloride and its binary mixtures with conventional surfactants. Soft Matter. 2013;9:1478–87.
Neese F (2009) Orca. An ab initio, density functional and semiempirical program package version.
Lee TC, Yang WT, Parr RG. Development of the Colic-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B. 1988;37:785–9.
Krishnan R, Binkley JS, Seeger R, Pople JA. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XX. A basis set for correlated wave functions. J Chem Phys. 1980;72:650–4.
Frisch MJ, Pople JA, Binkley JS. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods 25: supplementary functions for gaussian basis sets. J Chem Phys. 1984;80:3265–9.
Eichkorn K, Treutler O, Ohm H, Haser M, Ahlrichs R. Auxiliary basis sets to approximate coulomb potentials. Chem Phys Letters. 1995;240:283–90.
Eichkorn K, Weigend F, Treutler O, Ahlrichs R. Auxiliary basis sets for main row atoms and transition metals and their use to approximate Coulomb potentials. Theor Chem Acc. 1997;97:119–24.
Rosen MJ. Surfactants and interfacial phenomenon. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; 1991.
Quagliotto P, Barbero N, Barolo C, Artuso E, Compari C, Fisicaro E, Viscardi G. Synthesis and properties of cationic surfactants with tuned hydrophylicity. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;340:269–75.
Sayed GH, Ghuiba FM, Abdou MI, Badr EAA, Tawfik SM, Negm NAM. Synthesis, surface and thermodynamic parameters of some biodegradable non-ionic surfactants derived from tannic acid. Colloids Surf A. 2012;393:96–104.
Akram M, Bhat IA, Kabir-ud-Din. Self-Aggregation of Surfactant Ethane-1,2-diyl bis(N, N-dimethyl-N-hexadecylammoniumacetoxy) Dichloride: tensiometric, Microscopic, and Spectroscopic Studies. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119:3499–509.
Akram M, Yousuf S, Sarwar T, Kabir-ud-Din, (2014) Micellization and interfacial behavior of 16-E2-16 in presence of inorganic and organic salt counterions Colloids Surf A 441:281–290.
Shaban SM, Aiada I, El-Sukkary MM, Soliman EA, El-Awady MY. Surface and biological activity of N-(((dimethoxybenzylidene) amino) propyl)-N, N-dimethylalkyl-1-ammonium derivatives as cationic surfactants. J Mol Liq. 2015;207:256–65.
Aramaki K, Hackerman N. Inhibition mechanism of medium-sized polymethyleneimine. J Electrochem Soc. 1969;116:568–74.
Musa AY, Mohamad AB, Kadhum AAH, Takriff MS, Tien LT. Synergistic effect of potassium iodide with phthalazone on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 1.0 M HCl. Corros Sci. 2011;53:3672–7.
Umoren SA, Ogbobe O, Igwe IO, Ebenso EE. Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acidic medium using synthetic and naturally occurring polymers and synergistic halide additives. Corros Sci. 2008;50:1998–2006.
Umoren SA, Solomon MM. Effect of halide ions on the corrosion inhibition efficiency of different organic species—a review. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015;21:81–100.
Solomon MM, Umoren SA, Udosoro II, Udoh AP. Inhibitive and adsorption behaviour of carboxymethyl cellulose on mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2010;52:1317–25.
Bentiss F, Lebrini M, Lagrenee M. Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in mild steel/2,5-bis(n-thienyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazoles/hydrochloric acid system. Corros Sci. 2005;47:2915–31.
Roy P, Pal A, Sukul D. Origin of the synergistic effect between polysaccharide and thiourea towards adsorption and corrosion inhibition for mild steel in sulphuric acid. RSC Adv. 2014;4:10607–13.
Wang X, Yang H, Wang F. Inhibition performance of a gemini surfactant and its co-adsorption effect with halides on mild steel in 0.25 M H2SO4 solution. Corros Sci. 2012;55:145–52.
He X, Jiang Y, Li C, Wang W, Hou B, Wu L. Inhibition properties and adsorption behavior of imidazole and 2-phenyl-2-imidazoline on AA5052 in 1.0 M HCl solution. Corros Sci. 2014;83:124–36.
Bai L, Feng LJ, Wang HY, Lu YB, Lei XW, Bai FL. Comparison of the synergistic effect of counterions on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acid solution: electrochemical, gravimetric and thermodynamic studies. RSC Adv. 2015;5:4716–26.
Abd El-Lateef HM. Experimental and computational investigation on the corrosion inhibition characteristics of mild steel by some novel synthesized imines in hydrochloric acid solutions. Corros Sci. 2015;92:104–17.
Lebrini M, Bentiss F, Vezin H, Lagrene M. The inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acidic solutions by 2,5-bis(4-pyridyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole:structure-activity correlation. Corros Sci. 2016;8:1279–91.
Solmaz R. Investigation of adsorption and corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution by 5-(4-Dimethylaminobenzylidene)rhodanine. Corros Sci. 2014;79:169–78.
Yildiz R. An electrochemical and theoretical evaluation of 4,6-diamino-2-pyrimidinethiol as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl solutions. Corros Sci. 2015;90:544–53.
Zhu Y, et al. The effects of surfactants concentration, adsorption, aggregation and solution conditions on steel corrosion inhibition and associated modelling in aqueous media. Corros Sci. 2015;. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.012.
Tian H, et al. Triazolyl-acylhydrazone derivatives as novel inhibitors for copper corrosion in chloride solutions. Corros Sci. 2015;. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2015.08.022.
Outirite M, Lagrenee M, Lebrini M, Traisnel M, Jama C, Vezin H, Bentiss F. AC impedance, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and density functional theory studies of 3,5-bis(n-pyridyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as efficient corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid solution. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55:1670–81.
John S, Joseph A. Effective inhibition of mild steel corrosion in 1 M hydrochloric acid using substituted triazines: an experimental and theoretical study. RSC Adv. 2012;2:9944–51.
Prabhu RA, Venkatesha TV, Shanbhag AV, Kulkarni GM, Kalkhambkar RG. Inhibition effects of some schiff’s bases on the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2008;50:3356–62.
Li X, Deng S, Fu H. Allylthiourea as corrosion inhibitor for cold rolled steel in H3PO4 solution. Corros Sci. 2012;55:280–8.
Gece G, Bilgic S. A theoretical study on the inhibition efficiencies of some amino acids as corrosion inhibitors of nickel. Corros Sci. 2010;52:3435–43.
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO. Adsorption properties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid solution by ketoconazole: experimental and theoretical investigation. Corros Sci. 2010;52:198–204.
Kovacevic N, Kokaji A. The relation between adsorption bonding and corrosion inhibition of azole molecules on copper. Corros Sci. 2013;73:7–17.
Solmaz R, Kardas G, Yazici B, Erbil M. Adsorption and corrosion inhibitive properties of 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole on mild steel in hydrochloric acid media. Colloids Surf A. 2008;312:7–17.
El Adnani Z, Charfi M, Sraira M, Benzakou M, Benjelloum AT, Ebn Touhami M. DFT theoretical study of 7-R-3-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-thiones (R=H; CH3; Cl) as corrosion inhibitor in hydrochloric acid. Corros Sci. 2013;68:223–30.
Yadav DK, Quraishi MA. Application of some condensed uracils as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel: gravimetric, electrochemical, surface morphology, UV–visible and theoretical investigations. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51:14966–79.
Amin MA, Abd El-Rehim SS, El-Sherbini EEF, Bayoumi RS. The inhibition of low carbon steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solutions by succinic acid: part I. Weight loss, polarization, EIS, PZC, EDX and SEM studies. Electrochim Acta. 2007;52:3588–600.
Pavithra MK, Venkatesha TV, Punith Kumar MK, Anantha NS. Electrochemical, gravimetric and quantum chemical analysis of mild steel corrosion inhibition by colchicines in 1 M HCl medium. Res Chem Intermed. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s11164-015-2158-3.
Yuce AO, Kardas G. Adsorption and inhibition effect of 2-thiohydantoin on mild steel corrosion in 0.1 M HCl. Corros Sci. 2012;58:86–94.
Deng S, Li X, Fu H. Two pyrazine derivatives as inhibitors of the cold rolled steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2011;53:822–8.
Deng S, Li X, Fu H. Acid violet 6B as a novel corrosion inhibitor for cold rolled steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2011;53:760–8.
Oguzie EE, Li Y, Wang FH. Corrosion inhibition and adsorption behavior of methionine on mild steel in sulfuric acid and synergistic effect of iodide ion. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;310:90–8.
Yadav DK, Maiti B, Quraishi MA. Electrochemical and quantum chemical studies of 3, 4-dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H)-ones as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2010;52:3586–98.
Acknowledgements
The financial support of UGC, New Delhi in the form of MAN Fellowship is gratefully acknowledged by Ruby Aslam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Mobin, M., Aslam, R., Zehra, S. et al. Bio-/Environment-Friendly Cationic Gemini Surfactant as Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 1 M HCl Solution. J Surfact Deterg 20, 57–74 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1904-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1904-x