Abstract
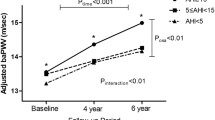
The correlation of both obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome (OSAS) and snoring with cardiovascular risk is well known, but its investigation is complex and not suitable for studying large cohorts of subjects. Thus, we prospectively evaluated 1476 non-pharmacologically treated subjects selected from the last survey of the Brisighella Heart Study. Snoring and sleep apnoea were investigated asking the subjects if they were aware of snoring during the night, and if this was associated with episodes of apnoea. A full set of clinical and laboratory parameters were evaluated, while augmentation index (AIx), and pulse wave velocity (PWV) were recorded with the Vicorder® apparatus. A logistic regression analysis identifies as main independent predictors of AIx age (OR 1.058, 95 % CI 1.043–1.065, p < 0.001), Body Mass Index (OR 1.046, 95 % CI 1.014–1.079, p = 0.005), and apolipoprotein B (OR 1.014, 95 % CI 1.004–1.023, p = 0.001). The main independent predictors of PWV are snoring (OR 1.215, 95 % CI 1.083–1.390, p < 0.001), and snoring with apnoea (OR 1.351, 95 % CI 1.135–1.598, p = 0.014), age (OR 1.078, 95 % CI 1.052–1.089, p < 0.001), serum uric acid [SUA] (OR 1.093, 95 % CI 1.026–1.151, p < 0.001) and mean arterial pressure (OR 1.042, 95 % CI 1.024–1.056, p < 0.001). In conclusion, in our cohort of overall healthy subjects, self-reported snoring and sleep apnoea are independently associated with a higher PVW, and AIx is statistically significantly higher in snorers with or without sleep apnoea than in non-snorers. Body Mass Index and apolipoprotein B are associated with AIx, while SUA and mean arterial pressure are related to PWV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Destors M, Tamisier R, Baguet JP, Levy P, Pepin JL (2014) Cardiovascular morbidity associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rev Mal Respir 31(4):375–385. doi:10.1016/j.rmr.2013.12.003
Laaban JP, Mounier L, Roque d’Orbcastel O, Veale D, Blacher J, Melloni B, Cornette A, Muir JF, Chailleux E, ANTADIRWorkinggroup “CV risk in OSAS”; CMTS; ANTADIR (2010) Cardiovascular risk factors in men and women with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Respir Med 104(7):1063–1068. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2010.02.021
Floras JS (2014) Sleep apnea and cardiovascular risk. J Cardiol 63(1):3–8. doi:10.1016/j.jjcc.2013.08.009
Somers VK, White DP, Amin R, Abraham WT, Costa F, Culebras A, Daniels S, Floras JS, Hunt CE, Olson LJ, Pickering TG, Russell R, Woo M, Young T (2008) Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease : an American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Foundation Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Council for High Blood Pressure Research Professional Education Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke Council, and Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. In collaboration with the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Center on Sleep Disorders Research (National Institutes of Health). J Am Coll Cardiol 52(8):686–817
Li D, Liu D, Wang X, He D (2014) Self-reported habitual snoring and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. Atherosclerosis 235(1):189–195. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.04.031
Behl M, Bliwise D, Veledar E, Cunningham L, Vazquez J, Brigham K, Quyyumi A (2014) Vascular endothelial function and self-reported sleep. Am J Med Sci 347(6):425–428. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31829bc950
Endeshaw Y, Rice TB, Schwartz AV, Stone KL, Manini TM, Satterfield S, Cummings S, Harris T, Pahor M; Health ABC Study (2013) Snoring, daytime sleepiness, and incident cardiovascular disease in the health, aging, and body composition study. Sleep 36(11):1737–1745. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3140
Nagayoshi M, Tanigawa T, Yamagishi K, Sakurai S, Kitamura A, Kiyama M, Okada T, Maeda K, Ohira T, Imano H, Sato S, Iso H, Investigators CIRCS (2012) Self-reported snoring frequency and incidence of cardiovascular disease: the Circulatory Risk in Communities Study (CIRCS). J Epidemiol 22(4):295–301
Van Bortel LM, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Chowienczyk P, Cruickshank JK, DeBacker T, Filipovsky J, Huybrechts S, Mattace-Raso FU, Protogerou AD, Schillaci G, Segers P, Vermeersch S, Weber T; Artery Society; European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Vascular Structure and Function; European Network for Noninvasive Investigation of Large Arteries (2012) Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens 30(3):445–448
Tanriverdi H, Evrengul H, Kaftan A, Kara CO, Kuru O, Tanriverdi S, Ozkurt S, Semiz E (2006) Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on aortic elastic parameters: relationship to left ventricular mass and function. Circ J 70(6):737–743
Pedrosa RP, Barros IM, Drager LF, Bittencourt MS, Medeiros AK, Carvalho LL, Lustosa TC, Carvalho MM, Ferreira MN, Lorenzi-Filho G, Costa LO (2014) OSA is common and independently associated with hypertension and increased arterial stiffness in consecutive perimenopausal women. Chest 146(1):66–72
Seetho IW, Asher R, Parker RJ, Craig S, Duffy N, Hardy KJ, Wilding JP (2015) Effect of CPAP on arterial stiffness in severely obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath [Epub ahead of print]
Kitahara Y, Hattori N, Yokoyama A, Nakajima M, Kohno N (2006) Effect of CPAP on brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in patients with OSAS: an open-labelled study. 100(12):2160–2169
Litvin AY, Sukmarova ZN, Elfimova EM, Aksenova AV, Galitsin PV, Rogoza AN, Chazova IE (2013) Effects of CPAP on “vascular” risk factors in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and arterial hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 9:229–235
Kartali N, Daskalopoulou E, Geleris P, Chatzipantazi S, Tziomalos K, Vlachogiannis E, Karagiannis A (2014) The effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on blood pressure and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 18(3):635–640
Cicero AFG, Dormi A, D’Addato S, Borghi C, on behalf of the Brisighella Heart Study Staff (2011) From risk factor assessment to cardiovascular disease risk and mortality modification: the first 40 years of the Brisighella Heart Study. Clin Lipidol 6(3):269–276
Cicero AF, D’Addato S, Santi F, Ferroni A, Borghi C; Brisighella Heart Study (2012) Leisure-time physical activity and cardiovascular disease mortality: the Brisighella Heart Study. J Cardiovasc Med 13(9):559–564
Cicero AF, Rosticci M, Tocci G, Bacchelli S, Urso R, D’Addato S, Borghi C (2015) Serum uric acid and other short-term predictors of electrocardiographic alterations in the Brisighella Heart Study cohort. Eur J Intern Med 26(4):255–258. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2015.02.007
Cicero AF, Derosa G, Rosticci M, D’Addato S, Agnoletti D, Borghi C; on behalf of the Brisighella Heart Study group (2014) Long-term predictors of impaired fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes in subjects with family history of type 2 diabetes: a 12-years follow-up of the Brisighella Heart Study historical cohort. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 104(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.02.005
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Members Task Force (2013) 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 31(7):1281–1357. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000431740.32696.cc
Marque V, Van Essen H, Struijker-Boudier HA, Atkinson J, Lartaud-Idjouadiene I (2001) Determination of aortic elastic modulus by pulse wave velocity and wall tracking in a rat model of aortic stiffness. J Vasc Res 38(6):546–550
Hirata K, Kawakami M, O’Rourke MF (2006) Pulse wave analysis and pulse wave velocity: a review of blood pressure interpretation 100 years after Korotkov. Circ J 70(10):1231–1239
Ageenkova OA, Purygina MA (2011) Central aortic blood pressure, augmentation index, and reflected wave transit time: reproducibility and repeatability of data obtained by oscillometry. Vasc Health Risk Manag 7:649–656. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S24877
Hickson SS, Butlin M, Broad J, Avolio AP, Wilkinson IB, McEniery CM (2009) Validity and repeatability of the Vicorder apparatus: a comparison with the SphygmoCor device. Hypertens Res 32:1079–1085. doi:10.1038/hr.2009
Pucci G, Cheriyan J, Hubsch A, Hickson SS, Gajendragadkar PR, Watson T, O’Sullivan M, Woodcock-Smith J, Schillaci G, Wilkinson IB, McEniery CM (2013) Evaluation of the Vicorder, a novel cuff-based device for the noninvasive estimation of central blood pressure. J Hypertens 31:77–85. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835a8eb1
McGreevy C, Barry M, Bennett K, Williams D (2013) Repeatability of the measurement of aortic pulse wave velocity (aPWV) in the clinical assessment of arterial stiffness in community-dwelling older patients using the Vicorder® device. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 73(4):269–273. doi:10.3109/00365513.2013.770162
Earley A, Miskulin D, Lamb EJ, Levey AS, Uhlig K (2012) Estimating equations for glomerular filtration rate in the era of creatinine standardization: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 156:785–795
Deary V, Ellis JG, Wilson JA, Coulter C, Barclay NL (2014) Simple snoring: not quite so simple after all? Sleep Med Rev 18(6):453–462. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2014.04.006
Lee YH, Kweon SS, Choi BY, Kim MK, Chun BY, Shin DH, Shin MH (2014) Self-reported snoring and carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged and older adults: the Korean Multi-Rural Communities Cohort Study. J Epidemiol 24(4):281–286
Deeb R, Judge P, Peterson E, Lin JC, Yaremchuk K (2014) Snoring and carotid artery intima-media thickness. Laryngoscope 124(6):1486–1491
Marshall NS, Ayer JG, Toelle BG, Harmer JA, Phillips CL, Grunstein RR, Celermajer DS, Marks GB (2011) Snoring is not associated with adverse effects on blood pressure, arterial structure or function in 8-year-old children: the Childhood Asthma Prevention Study (CAPS). J Paediatr Child Health 47(8):518–523
Kwok KL, Ng DK, Cheung YF (2003) BP and arterial distensibility in children with primary snoring. Chest 123(5):1561–1566
McEniery CM, Yasmin, Hall IR, Qasem A, Wilkinson IB, Cockcroft JR; ACCT Investigators (2005) Normal vascular aging: differential effects on wave reflection and aortic pulse wave velocity: the Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial (ACCT). J Am Coll Cardiol. 46(9):1753–1760
Cicero AF, Salvi P, D’Addato S, Rosticci M, Borghi C, Brisighella Heart Study group (2014) Association between serum uric acid, hypertension, vascular stiffness and subclinical atherosclerosis: data from the Brisighella Heart Study. J Hypertens 32(1):57–64
Mulè G, Riccobene R, Castiglia A, D’Ignoto F, Ajello E, Geraci G, Guarino L, Nardi E, Vaccaro F, Cerasola G, Cottone S (2014) Relationships between mild hyperuricaemia and aortic stiffness in untreated hypertensive patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24(7):744–750
Baena CP, Lotufo PA, Mill JG, Cunha RS, Benseñor IJ (2015) Serum uric acid and pulse wave velocity among healthy adults: baseline data from the Brazilian longitudinal study of adult health (ELSA-Brasil). Am J Hypertens (pii: hpu298) [Epub ahead of print]
Mehta T, Nuccio E, McFann K, Madero M, Sarnak MJ, Jalal D (2014) Association of uric acid with vascular stiffness in the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Hypertens (pii: hpu253) [Epub ahead of print]
Liang J, Li Y, Zhou N, Teng F, Zhao J, Zou C, Qi L (2012) Synergistic effects of serum uric acid and cardiometabolic risk factors on early stage atherosclerosis: the cardiometabolic risk in Chinese study. PLoS One 7(12):e51101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051101
Guo X, Lu X, Yang J, Kassab GS (2014) Increased aortic stiffness elevates pulse and mean pressure and compromises endothelial function in Wistar rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 307(6):H880–H887. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00265.2014
Wagenseil JE, Mecham RP (2012) Elastin in large artery stiffness and hypertension. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 5(3):264–273. doi:10.1007/s12265-012-9349-8
Verwoert GC, Franco OH, Hoeks AP, Reneman RS, Hofman A, V Duijn CM, Sijbrands EJ, Witteman JC, Mattace-Raso FU (2014) Arterial stiffness and hypertension in a large population of untreated individuals: the Rotterdam Study. J Hypertens 32(8):1606–1612. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000237
Coutinho T, Bailey KR, Turner ST, Kullo IJ (2014) Arterial stiffness is associated with increase in blood pressure over time in treated hypertensives. J Am Soc Hypertens 8(6):414–421. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2014.03.330
Boutouyrie P, Tropeano AI, Asmar R, Gautier I, Benetos A, Lacolley P, Laurent S (2002) Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of primary coronary events in hypertensive patients: a longitudinal study. Hypertension 39(1):10–15
Paschetta E, Belci P, Alisi A, Liccardo D, Cutrera R, Musso G, Nobili V (2015) OSAS-related inflammatory mechanisms of liver injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mediators Inflamm 2015:815721. doi:10.1155/2015/815721
Acknowledgments
We particularly acknowledge Marina Giovannini and Elisabetta Rizzoli for their support for the Brisighella Heart Study laboratory activity and Marcella Cagnati for her work on data managing. We also sincerely thank the Faenza public health district and all the General Practitioners of Brisighella for their continuous support of the study.
The Brisighella Study Group
Arrigo F.G. Cicero, Martina Rosticci, Cristina Baronio, Martino Morbini, Angelo Parini, Giulia Grossi, Elisa Grandi, Sergio D’Addato, Elena Ancarani, Silvia Palmesano, Marina Giovannini, Elisabetta Rizzoli, Marcella Cagnati, Giovanni Gardini, Riccardo Urso, Giuseppe Derosa, Stefano Bacchelli, Claudio Borghi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding sources
This work has been conducted with funding by the University of Bologna, and with an unrestricted grant from the “Fondazione del Monte” (Bank foundation).
Conflict of interest
No author has a specific conflict of interest in the publication of this paper.
Statement of human and animal rights
The BHS protocol and its sub-studies, largely described elsewhere, have been approved by the Ethical Board of the University of Bologna.
Informed consent
All involved volunteers gave their signed consent to participate in the study.
Additional information
A. F. G. Cicero and M. Morbini are the first authors since they equally contributed to the paper.
A full list of Brisighella Heart Study Group is given in the "Acknowledgments".
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cicero, A.F.G., Morbini, M., Urso, R. et al. Association between self-reported snoring and arterial stiffness: data from the Brisighella Heart Study. Intern Emerg Med 11, 77–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1310-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1310-9