Abstract
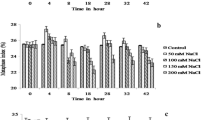
Recretohalophytes with specialized salt-secreting structures, including salt glands and salt bladders, can secrete excess salts from plant tissues and enhance salinity tolerance of plants. However, the pathway and property of salt secretion by the salt gland has not been elucidated. In the article, Limonium bicolor Kuntze was used to investigate the pathway and characteristics of salt secretion of salt gland. Scanning electron microscope micrographs showed that each of the secretory cells had a pore in the center of the cuticle, and the rice grain-like secretions were observed above the pore. The chemical composition of secretions from secretory pores was mainly NaCl using environmental scanning electron microscope technique. Non-invasive micro-test technology was used to directly measure ion secretion rate of salt gland, and secretion rates of Na+ and Cl− were greatly enhanced by a 200-mmol/L NaCl treatment. However, epidermal cells and stoma showed little secretion of ions. In conclusion, our results provide evidence that the salt glands of L. bicolor have four secretory pores and that NaCl is secreted through these pores of salt gland.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Dry mass
- EDS:
-
Energy dispersive spectroscopy
- ESEM:
-
Environmental scanning electron microscope
- FS:
-
Freeze substitution
- HPF:
-
High-pressure freezing
- NMT:
-
Non-invasive micro-test technology
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
References
Arisz WH, Camphuis IJ, Heikens H, van Tooren AJ (1955) The secretion of the salt glands of Limonium latifolium Ktze. Acta Bot Neerl 4:322–338
Balsamo RA, Adams ME, Thomson WW (1995) Electrophysiology of the salt glands of Avicennia germinans. Int J Plant Sci 156:658–667
Barhoumi Z, Djebali W, Smaoui A, Chaıbi W, Abdelly C (2007) Contribution of NaCl excretion to salt resistance of Aeluropus littoralis (Willd) Parl. J Plant Physiol 164:842–850
Berry WL (1970) Characteristics of salts secreted by Tamarix aphylla. Am J Bot 57:1226–1230
Bosabalidis AM (2012) Programmed cell death in salt glands of Tamarix aphylla L.: an electron microscope analysis. Cent Eur J Biol 7:927–930
Bradley PM, Morris JT (1991) Relative importance of ion exclusion, secretion and accumulation in Spartina alterniflora Loisel. J Exp Bot 42:1525–1532
Breckle SW (1995) How do halophytes overcome salinity. In: Khan MA, Ungar IA (eds) Biology of salt tolerant plants. Book Crafters, Chelsea, pp 199–213
Campbell CJ, Strong JE (1964) Salt gland anatomy in Tamarix pentandra (Tamaricaceae). Southwest Nat 9:232–238
Campbell N, Thomson WW (1975) Chloride localization in the leaf of Tamarix. Protoplasma 83:1–14
Carter JM, Nippert JB (2011) Physiological responses of Tamarix ramosissima to extreme NaCl concentrations. Am J Plant Sci 2:808–815
Chen J, Xiao Q, Wu F, Dong XJ, He JX, Pei ZM, Zheng HL (2010) Nitric oxide enhances salt secretion and Na+ sequestration in a mangrove plant, Avicennia marina, through increasing the expression of H+-ATPase and Na+/H+ antiporter under high salinity. Tree Physiol 30:1570–1585
Dang JMC, Copeland L (2004) Studies of the fracture surface of rice grains using environmental scanning electron microscopy. J Sci Food Agr 84:707–713
Danilatos GD (1981) The examination of fresh or living plant material in an environmental scanning electron microscope. J Microsc 121:235–238
Danilatos GD (1990) Mechanisms of detection and imaging in the ESEM. J Microsc 160:9–19
Ding F, Song J, Ruan Y, Wang BS (2009) Comparison of the effects of NaCl and KCl at the roots on seedling growth, cell death and the size, frequency and secretion rate of salt glands in leaves of Limonium sinense. Acta Physiol Plant 31:343–350
Ding F, Yang JC, Yuan F, Wang BS (2010) Progress in mechanism of salt excretion in recretohalophytes. Front Biol 5:164–170
Dschida WJ, Platt-Aloia KA, Thomson WW (1992) Epidermal peels of Avicennia germinans (L.) Stearn: a useful system to study the function of salt glands. Ann Bot 70:501–509
Fahn A (2000) Structure and function of secretory cells. Adv Bot Res 31:37–75
Faraday CD, Thomson WW (1986a) Structural aspects of the salt glands of the Plumbaginaceae. J Exp Bot 37:461–470
Faraday CD, Thomson WW (1986b) Functional aspects of the salt glands of the Plumbaginaceae. J Exp Bot 37:1129–1135
Faraday CD, Quinton PM, Thomson WW (1986) Ion fluxes across the transfusion zone of secreting Limonium salt glands determined from secretion rates, transfusion zone areas and plasmodesmatal frequencies. J Exp Bot 37:482–494
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Flowers TJ, Galal HK, Bromham L (2010) Evolution of halophytes: multiple origins of salt tolerance in land plants. Funct Plant Biol 37:604–612
Hill AE, Hill BS (1973) The electrogenic chloride pump of the Limonium salt gland. J Membrane Biol 12:129–144
Jin YJ, Dai ZY, Liu F, Kim H, Tong MP, Hou YL (2013) Bactericidal mechanisms of Ag2O/TNBs under both dark and light conditions. Water Res 47:1837–1847
Kingsbury RW, Epstein E (1986) Salt sensitivity in wheat a case for specific ion toxicity. Plant Physiol 80:651–654
Kong XQ, Luo Z, Dong HZ, Eneji AE, Li WJ (2012) Effects of non-uniform root zone salinity on water use, Na+ recirculation, and Na+ and H+ flux in cotton. J Exp Bot 63:2105–2116
Levering CA, Thomson WW (1971) The ultrastructure of the salt gland of Spartina foliosa. Planta 97:183–196
Li N, Li YD, Wang YB, Li M, Cheng Y, Wu YH, Zheng YF (2013) Corrosion resistance and cytotoxicity of a MgF2 coating on biomedical Mg-1Ca alloy via vacuum evaporation deposition method. Surf Interface Anal 45:1217–1222
Liphschitz N, Waisel Y (1974) Existence of salt glands in various genera of the Gramineae. New Phytol 73:507–513
Lu AH, Li Y, Wang X, Ding HR, Zeng CP, Yang XX, Hao RX, Wang CQ, Santosh M (2013) Photoelectrons from minerals and microbial world: a perspective on life evolution in the early Earth. Precambrian Res 231:401–408
Lüttge U (1971) Structure and function of plant glands. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 22:23–44
Ma HY, Tian CY, Feng G, Yuan JF (2011) Ability of multicellular salt glands in Tamarix species to secrete Na+ and K+ selectively. Sci China Life Sci 54:282–289
Manero JM, Gil FJ, Padros E, Planell JA (2003) Applications of environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) in biomaterials field. Microsc Res Techniq 61:469–480
Mello PA, Barin JS, Duarte FA, Bizzi CA, Diehl LO, Muller EI, Flores EMM (2013) Analytical methods for the determination of halogens in bioanalytical sciences: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:7615–7642
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant, Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Oross JW, Thomson WW (1982) The ultrastructure of the salt glands of Cynodon and Distichlis (Poaceae). Am J Bot 69:939–949
Ramadan T, Flowers TJ (2004) Effects of salinity and benzyl adenine on development and function of microhairs of Zea mays L. Planta 219:639–648
Rozema J, Flowers T (2008) Crops for a salinized world. Science 322:1478–1480
Rozema J, Gude H, Pollak G (1981) An ecophysiological study of the salt secretion of four halophytes. New Phytol 89:201–217
Ruhland W (1915) Untersuchungen über die Hautdrüsen der Plumbaginaceen. Ein Beitrag zur Biologie der Halophyten. Jb Wiss Bot 55:409–498
Semenova GA, Fomina IR, Biel KY (2010) Structural features of the salt glands of the leaf of Distichlis spicata ‘Yensen 4a’ (Poaceae). Protoplasma 240:75–82
Shimony C, Fahn A, Reinhold L (1973) Ultrastructure and ion gradients in the salt glands of Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. New Phytol 72:27–36
Skelding AD, Winterbotham J (1939) The structure and development of the hydathodes of Spartina townsendii Groves. New Phytol 38:69–79
Smart KE, Smith JAC, Kilburn MR, Martin BGH, Hawes C, Grovenor CRM (2010) High-resolution elemental localization in vacuolate plant cells by nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometry. Plant J 63:870–879
Somaru R, Naidoo Y, Naidoo G (2002) Morphology and ultrastructure of the leaf salt glands of Odyssea paucinervis (Stapf) (Poaceae). Flora 197:67–75
Suárez N, Medina E (2008) Salinity effects on leaf ion composition and salt secretion rate in Avicennia germinans (L.) L. Braz J Plant Physiol 20:131–140
Sun J, Zhang CL, Deng SR, Lu CF, Shen X, Zhou XY, Zheng XJ, Hu ZM, Chen SL (2012) An ATP signalling pathway in plant cells: extracellular ATP triggers programmed cell death in Populus euphratica. Plant, Cell Environ 35:893–916
Tan WK, Lin Q, Lim TM, Kumar P, Loh CS (2013) Dynamic secretion changes in the salt glands of the mangrove tree species Avicennia officinalis in response to a changing saline environment. Plant, Cell Environ 36:1410–1422
Tarchoune I, Degl′Innocenti E, Kaddour R, Guidi L, Lachaal M, Navari-Izzo F, Ouerghi Z (2012) Effects of NaCl or Na2SO4 salinity on plant growth, ion content and photosynthetic activity in Ocimum basilicum L. Acta Physiol Plant 34:607–615
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Thomson WW, Liu LL (1967) Ultrastructural features of the salt gland of Tamarix aphylla L. Planta 73:201–220
Thomson WW, Berry WL, Liu LL (1969) Localization and secretion of salt by the salt glands of Tamarix aphylla. Proc Nat Acad Sci 63:310–317
Tyerman SD (2013) The devil in the detail of secretions. Plant, Cell Environ 36:1407–1409
Waisel Y (1961) Ecological studies on Tamarix aphylla (L.) Karst. Plant Soil 13:356–364
Wieneke J, Sarwar G, Roeb M (1987) Existence of salt glands on leaves of kallar grass (Leptochloa fusca L. Kunth.). J Plant Nutr 10:805–819
Wilkinson RE (1966) Seasonal development of anatomical structures of saltcedar foliage. Bot Gaz 127:231–234
William SS (1974) Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray analysis of chalk secreting leaf glands of Plumbago Capensis. Am J Bot 61:94–99
Yang YQ, Qin YX, Xie CG, Zhao FY, Zhao JF, Liu DF, Chen SY, Fuglsang AT, Palmgren MG, Schumaker KS, Deng XW, Guo Y (2010) The Arabidopsis chaperone J3 regulates the plasma membrane H+-ATPase through interaction with the PKS5 kinase. Plant Cell 22:1313–1332
Zhou LZ, Li S, Feng QN, Zhang YL, Zhao XY, Zeng YL, Wang H, Jiang LW, Zhang Y (2013) PROTEIN S-ACYL TRANSFERASE10 is critical for development and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:1093–1107
Ziegler H, Lüttge U (1966) Die Salzdrüsen von Limonium vulgare. Planta 70:193–206
Ziegler H, Lüttge U (1967) Die Salzdrüsen von Limonium vulgare. Planta 74:1–17
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Li Chen (Electron Microscopy Laboratory, School of Physics, Peking University, Haidian, Beijing, 100871, P.R. China) for technical assistance in ESEM analysis. Our TEM and SEM work was performed at the Center for Bio-imaging, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We also thank Dr. Yue Xu and his team from Xuyue (Beijing) Sci. and Tech. Co., Ltd. (http://xuyue.net) for their professional advice and technical support for Na+, K+, and Cl− flux measurements using NMT. This research was supported by the NSFC (National Natural Science Research Foundation of China, project No. 30870138 and No. 31070158), key projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar program during the eleventh five-year plan period (2009BADA7B05), Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20123704130001) band program for scientific research innovation team in colleges and universities of Shandong province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Kovacik.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Sun, Q., Deng, Y. et al. Study on pathway and characteristics of ion secretion of salt glands of Limonium bicolor . Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2729–2741 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1644-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1644-3