Abstract
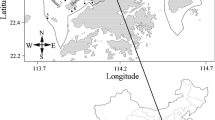
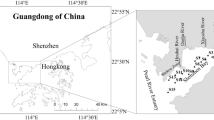
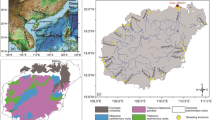
This article investigates the variations of contamination levels of heavy metals such as copper, lead, chromium, cadmium, zinc, arsenic, and mercury over time in surface sediments of the Changjiang River Estuary (CRE), Yellow River Estuary (YRE), Pearl River Estuary (PRE), and their adjacent coastal areas in China. The contamination factor (CF), pollution load index (PLI), and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) are used to evaluate the quality of the surface sediments in the study areas. The results showed that the CRE, YRE, and their adjacent coastal areas were at a low risk of contamination in terms of heavy metals, while the PRE and its adjacent coastal area were at a moderate level. By comparison, the concentrations of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the YRE and its adjacent coastal area were relatively lower than those in the CRE, PRE, and their adjacent coastal areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastami K D, Bagheri H, Haghparast S, Soltani F, Hamzehpoor A, Bastami M D (2012). Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Gorgan Bay, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull, 64(12): 2877–2884
Caccia V G, Millero F J, Palanques A (2003). The distribution of trace metals in Florida Bay sediments. Mar Pollut Bull, 46(11): 1420–1433
Chabukdhara M, Nema A K (2012). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hindon River sediments: a chemometric and geochemical approach. Chemosphere, 87(8): 945–953
Chakraborty P, Ramteke D, Chakraborty S, Nagender Nath B (2014). Changes in metal contamination levels in estuarine sediments around India—An assessment. Mar Pollut Bull, 78(1–2): 15–25
Chen F R, Yang Y Q, Zhang D R, Zhang L (2006). Heavy metals associated with reduced sulfur in sediments from different deposition environments in the Pearl River estuary, China. Environ Geochem Health, 28(3): 265–272
Chen S, Yan S, Liu Z (2009). Characteristics of surface sediment distribution in the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent waters. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 18(2): 152–156 (in Chinese)
Cooke J A, Andrews S M, Johnson M S (1990). Lead, zinc, cadmium and fluoride in small mammals from contaminated grass-land established on fluorspar tailings. Water Air Soil Pollut, 51(1–2): 43–54
Dai S B, Lu X X (2014). Sediment load change in the Yangtze River (Changjiang): a review. Geomorphology, 215: 60–73
Deniseger J, Erickson J, Austin A, Roch M, Clark M J R (1990). The effects of decreasing heavy metal concentrations on the biota of Buttle Lake, Vancouver Island, British Columbia. Water Res, 24(4): 403–416
Dong A, Zhai S, Yu Z, Han D (2010). Evaluation on potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Yangtze estuary and its adjacent coastal area. Mark Sci, 34(3): 69–75 (in Chinese)
Gan H, Liang K, Zhen Z (2010). Background values, contamination assessment and zoning of heavy metals in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Earth and Environmental, 38(3): 344–350 (in Chinese)
Gaur V K, Gupta S K, Pandey S D, Gopal K, Misra V (2005). Distribution of heavy metals in sediment and water of River Gomti. Environ Monit Assess, 102(1–3): 419–433
Hakanson L (1980). Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res, 14(8): 975–1001
He S, Song J, Li X, Liu Z (2011). Distribution, source of heavy metals in the surface sediments and sediment quality of the Changjiang Estuarine and its adjacent regions. Mark Sci, 35(5): 4–9 (in Chinese)
Hu B Q, Cui R Y, Li J, Wei H L, Zhao J T, Bai F L, Song W Y, Ding X (2013). Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Changhua River Estuary and adjacent shelf (Hainan Island). Mar Pollut Bull, 76(1–2): 400–405
Huang H, Ping X, Li L, Liao Y, Shen X (2011). Concentrations and assessment of heavy metals in seawater, sediments and aquatic organisms at Yangtze River estuary in spring and summer. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(5): 898–903 (in Chinese)
Huang H, Yue Y, Wang X, Wang L (2004). Pollution of heavy metals in surface sediments from Haihe River (Jiangsu section) and its assessment of potential ecological risk. Environmental Pollution & Control, 26(3): 207–231 (in Chinese)
Huang X, Liang K, Liu X (2006). The distribution and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in the Pearl River Estuary. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 3(5): 27–36 (in Chinese)
Ip C C M, Li X D, Zhang G, Wai O W H, Li Y S (2007). Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environ Pollut, 147(2): 311–323
Kalnejais L, Martin W R, Bothner M H (2010). The release of dissolved nutrients and metals from coastal sediments due to resuspension. Mar Chem, 121(1–4): 224–235
Larrose A, Coynel A, Schäfer J, Blanc G, Massé L, Maneux E (2010). Assessing the current state of the Gironde Estuary by mapping priority contaminant distribution and risk potential in surface sediment. Appl Geochem, 25(12): 1912–1923
Li X D, Wai OWH, Li Y S, Coles B J, RamseyMH, Thornton L (2000). Heavy metal distribution in sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary, South China. Appl Geochem, 15(5): 567–581
Li X Q, Gan Y Q, Zhou A G, Liu Y D (2015). Relationship between water discharge and sulfate sources of the Yangtze River inferred from seasonal variations of sulfur and oxygen isotopic compositions. J Geochem Explor, 153: 30–39
Lim D I, Choi J W, Shin H H, Jeong D H, Jung H S (2013). Toxicological impact assessment of heavy metal contamination on macrobenthic communities in southern coastal sediments of Korea. Mar Pollut Bull, 73(1): 362–368
Liu F, Yan W, Wang W, Gu S, Chen Z (2002). Pollution of heavy metals in the Pearl River Estuary and its assessment of potential ecological risk. Marine Environmental Science, 21(3): 34–38 (in Chinese)
Loska K, Wiechula D (2003). Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere, 51(8): 723–733
Luo X, Chen S, Mai B, Fu J, Ceng Y (2006). The pollution of Pearl River Delta waters by the tracing domestic sewage of linear alkylbenzenes (LABs). China Environ Sci, 26(4): 414–417 (in Chinese)
Ma H, Chen J, Cui Y, Zhao J, Yang F (2011). Environmental quality assessment of water body and surface sediment in the sea area of Jiaozhou Bay wetland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(10): 2749–2756 (in Chinese)
Ma Y, Li T J, Gao Q Z (2014). Background values and contamination of heavy metals in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 34(3): 712–719
Morelli G, Gasparon M (2014). Metal contamination of estuarine intertidal sediments of Moreton Bay, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull, 89(1–2): 435–443
Müller G (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geochem J, 2(3): 108–118
Qiao S, Shi X, Bai Y, Xiong L, Zhu A, Liu Y, Fang X (2011). Distribution of organic carbon, nitrogen in suspended and surface sediments and their controlling factors off the Huanghe (Yellow River) mouth and the nearby Bohai sea. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 29(2): 354–362 (in Chinese)
Ren H, Li G, Cui L, He L (2014). Phases and periodic changes of water discharge and sediment load from the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea during 1950–2011. Acta Geogr Sin, 69(5): 619–631 (in Chinese)
Saulnier I, Mucci A (2000). Trace metal remobilization following the resuspension of estuarine sediments: Saguenay Fjord, Canada. Appl Geochem, 15(2): 191–210
Simpson S L, Batley G E (2007). Predicting metal toxicity in sediments: a critique of current approaches. Integr Environ Assess Manag, 3(1): 18–31
Singh K P, Mohan D, Singh V K, Malik A (2005). Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments-atributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol (Amst), 312(1–4): 14–27
Sun Z G, Mou X J, Tong C, Wang C Y, Xie Z L, Song H L, Sun WG, Lv Y C (2015). Spatial variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in intertidal zone of the Yellow River estuary, China. Catena, 126: 43–52
Tang A, Liu R H, Ling M, Xu L Q, Wang J Y (2010). Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of soluble heavy metals in the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent sea. Procedia Environ Sci, 2: 1193–1198
Tomlinson D C, Wilson J G, Harris C R, Jeffrey D W (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Meersunters, 33(1–4): 566–575
Varol M (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater, 195: 355–364
Varol M, Sen B (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. Catena, 92: 1–10
Wang H T, Wang J W, Liu R M, Yu W W, Shen Z Y (2015). Spatial variation, environmental risk and biological hazard assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Mar Pollut Bull, 93(1–2): 250–258
Wang J W, Liu R M, Zhang P P, Yu W W, Shen Z Y, Feng C H (2014). Spatial variation, environmental assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull, 87(1–2): 364–373
Wang P, Zhai S, Xu S (2008). Pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent area after the first-stage water storage of the three gorges projects. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 28(4): 19–26 (in Chinese)
Wu B, Song J, Li X (2013). Environmental characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yellow River Estuary. Environ Sci, 34(4): 1324–1332 (in Chinese)
Wu X, Liu R, Qin J, Sun P, Gao Z, Jia Y (2007). Study on the variance character of heavy metals contents in sediments in Yellow River Estuary. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 69–74 (in Chinese)
Wu Z J, Zhou H Y, Ren D Z, Gao H, Li J T (2015). Processes controlling the seasonal and spatial variations in sulfate profiles in the pore water of the sediments surrounding Qi’ao Island, Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Cont Shelf Res, 98: 26–35
Xiao Z (2012). Characteristic and transport trend of surface sediments in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent sea area. Marine Science Bulletin, 31(5): 481–488 (in Chinese)
Xing Y (2007). Comparative studies on the magnetic properties of surface sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary and the Yellow River Estuary. M.E. Thesis, East China Normal University, China (in Chinese)
Xu X G, Guo H H, Chen X L, Lin H P, Du Q L (2002). A multi-scale study on land use and land cover quality change: the case of the Yellow River Delta in China. GeoJournal, 56(3): 177–183
Yang B, Cao L, Liu S, Zhang G (2015). Biogeochemistry of bulk organic matter and biogenic elements in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent sea. Mar Pollut Bull, 96(1–2): 471–484
Yang S L, Milliman J D, Li P, Xu K (2011). 50, 000 dams later: erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Global Planet Change, 75(1–2): 14–20
Ye F, Huang X P, Zhang D W, Tian L, Zeng Y Y (2012). Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China: implications for sources and historical changes. J Environ Sci (China), 24(4): 579–588
Zhang L, Chen F, Yin K, Lu Y, Yang Y, Zhang D (2010). The characteristics and sources of surface sediments in the Pearl River Estuary and its adjacent shelves. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(1): 98–103 (in Chinese)
Zhang X (2013). Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of heavy metals in the Yangtze River Estuary, the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent sea. M.E. Thesis, Ocean University of China (in Chinese)
Zhang Y (2010). Hydrodynamics and waste water transportation of Yangtze River Estuary affected by Three Gorges project. M.E. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology (in Chinese)
Zheng L, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Zhou C, Qu L (2014). Enrichment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the dumping areas in Bohai sea and assessment of their potential ecological risk. Marine Science Bulletin, 33(3): 342–348 (in Chinese)
Zhou H Y, Peng X T, Pan J M (2004). Distribution, source and enrichment of some chemical elements in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Cont Shelf Res, 24(16): 1857–1875
Zhu H, Ruan R, Chen G, Gu Y (2011). Influence of Three Gorges Reservoir operation on water source safety in Yangtze River Estuary. China Water & Wastewater, 27(8): 34–36 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of Tianjin with Spill Oil Accident from Penglai Oil field 19-3 Compensation (No. 19-3BC2014-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Li, D. & Song, G. Assessment of heavy metal levels in surface sediments of estuaries and adjacent coastal areas in China. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 85–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0569-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0569-0