Abstract
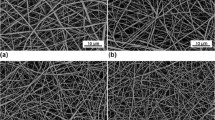
In order to investigate the in vitro biocompatibility of a novel polyurethane (PU) membrane modified by incorporation of superfine silk-fibroin powder (SFP), which was prepared for small-diameter vascular grafts, with the cultivation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), PU and SFP were mixed with the ratios of 9:1, 7:3, 5:5, 3:7 (PU:SFP) to make four composite materials. Unmodified PU and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) were added as control groups. CCK-8 assay was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of these biomaterials. Data were processed using SPSS, and P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Adherence and spreading of HUVECs on the surface of specimens was observed using direct contact cultivation. The toxicity ratings of the novel composites were grade 0–1, which is in the acceptable range. In all the experimental groups except control, SFP/PU with ratio of 1:9 had the least cytotoxicity property, and more content of SFP in the composite showed no improvement of the biocompatibility. HUVECs strongly attached to and grew on the surface of the biomaterials, and proliferated rapidly. The proliferation ability increased with increased proportion of SFP; however the cell quantity on the surface of the materials decreased when the proportion of SFP was equal to or larger than that of PU in the composite. It is concluded that this novel material has excellent cellular affinity with no cytotoxicity to HUVECs. Adding SFP gives PU better biocompatibility, while further research on optimum blend ratios is still needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouyang C, Xu H, Wang W, et al. In vivo histocompatibility evaluation of polyurethane membrane modified by superfine silk-fibroin powder. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Medical Sciences, 2009, 29(4): 508–511
Xu W L, Zhou F, Ouyang C X, et al. Small diameter polyurethane vascular graft reinforced by elastic weft-knitted tubular fabric of polyester/spandex. Fibers and Polymers, 2008, 9(1): 71–75
Liu H T, Xu W L, Zou H T, et al. Feasibility of wet spinning of silk-inspired polyurethane elastic biofiber. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(12–13): 1949–1952
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-12:2002; Biological evaluation of medical devices — Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-5:1999; Biological evaluation of medical devices — Part 5: Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity
USP XXII 24. Biological Tests/Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
Klinkert P, Post P N, Breslau P J, et al. Saphenous vein versus PTFE for above-knee femoropopliteal bypass. A review of the literature. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 2004, 27(4): 357–362
Rashid S T, Salacinski H J, Hamilton G, et al. The use of animal models in developing the discipline of cardiovascular tissue engineering: a review. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(9): 1627–1637
Abbott W M, Callow A, Moore W, et al. Evaluation and performance standards for arterial prostheses. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 1993, 17(4): 746–756
Nerem R M, Seliktar D. Vascular tissue engineering. Biomedical Engineering, 2001, 3: 225–243
Kannan R Y, Salacinski H J, Butler P E, et al. Current status of prosthetic bypass grafts: A review. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2005, 74B(1): 570–581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M.Z. and W.C.W. contributed to this paper equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Wang, WC., Liao, YG. et al. In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of silk-fibroin/polyurethane membrane with cultivation of HUVECs. Front. Mater. Sci. 8, 63–71 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0230-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0230-3