Abstract
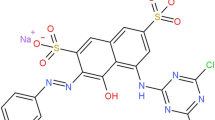
The electrocatalytic degradation of C.I. Acid Orange 3 from simulated wastewater by indirect electrochemical oxidation using an IrOx electrode was investigated. The effects of different operating parameters on the rate of dye decolorization were studied. The influences of mixing, electrolyte concentration, applied current, and initial dye concentration were examined. The change in dye concentration was followed by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, while the formation of reaction intermediates was established using high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis. Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy showed a decrease of the absorption peak at 374 nm during the electrolysis and the appearance of a new absorption maximum at 460 nm. The decolorization reaction can be followed only at 460 nm. Four intermediate products (two mono- and two dichlorinated) were detected. At the end of the study, a phytotoxicity assay was performed to determine the effectiveness of the applied method. The results showed that the applied electrochemical treatment of C.I. Acid Orange 3 leads to a decrease in phytotoxicity from 53 to 28%.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam LC, Fábián I, Suzuki K, Gordon G (1992) Hypochlorous acid decomposition in the pH 5–8 region. Inorg Chem 31:3534–3541. doi:10.1021/ic00043a011
Barrera-Díaz C, Cañizares P, Fernández FJ, Natividad R, Rodrigo MA (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: an overview of the current applications to actual industrial effluents. J Mex Chem Soc 58:256–275
Baud-Grasset F, Baud-Grasset S, Safferman SI (1993) Evaluation of the bioremediation of a contaminated soil with phytotoxicity tests. Chermosphere 26(7):1365–1374. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(93)90187-A
Brillas E (2014) A review on the degradation of organic pollutants in waters by UV photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton. J Braz Chem Soc 25:393–417. doi:10.5935/0103-5053.20130257
Brown D, Laboureur P (1983) The degradation of dyestuffs: part I. Primary biodegradation under anaerobic conditions. Chemosphere 12:397–404. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(83)90114-5
Chatwal GR (2009) Synthetic dyes. Himalaya Publishing House, Mumbai
Comninellis Ch (1994) Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim Acta 39:1857–1862. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(94)85175-1
Debordea M, von Gunten U (2008) Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment—kinetics and mechanisms: a critical review. Water Res 42:13–51. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.07.025
Devi LG, Kumar SG, Anantha Raju KS, Eraiah Rajashekhar K (2010) Photo-Fenton and photo-Fenton-like processes for the degradation of methyl orange in aqueous medium: influence of oxidation states of iron. Chem Pap 64:378–385. doi:10.2478/s11696-010-0011-0
El-Zawahry MM (1998) Decolorization of anionic dye solutions using water hyacinth derivatives. Bull Nat Res Cent (Egypt) 23:11–22
Fernando E, Keshavarz T, Kyazze G (2014) Complete degradation of the azo dye Acid Orange-7 and bioelectricity generation in an integrated microbial fuel cell, aerobic two-stage bioreactor system in continuous flow mode at ambient temperature. Bioresour Technol 156:155–162. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.036
Gassman PG, Campbell GA (1971) The mechanism of the chlorination of anilines and related aromatic amines. The involvement of nitrenium ions. J Am Chem Soc 93:2567–2569. doi:10.1021/ja00739a053
Golob V, Vinder A, Simonic M (2005) Efficiency of the coagulation/flocculation method for the treatment of dyebath effluents. Dyes Pigm 67:93–97. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.11.003
Grgur BN, Mijin DŽ (2014) A kinetics study of the methomyl electrochemical degradation in the chloride containing solutions. Appl Catal B Environ 147:429–438. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.09.028
Holčapek M, Kateřina V, Vaněrková D (2007) Effects of functional groups on the fragmentation of dyes in electrospray and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectra. Dyes Pigm 75:156–165. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.05.040
Imran M, Crowley DE, Khalid A, Hussain S, Mumtaz MW, Arshad M (2015) Microbial biotechnology for decolorization of textile wastewaters. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:73–92. doi:10.1007/s11157-014-9344-4
Iranifam M, Zarei M, Khatae AR (2011) Decolorization of C.I. Basic Yellow 28 solution using supported ZnO nanoparticles coupled with photoelectro-Fenton process. J Electroanal Chem 659:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.05.010
Kanazawa H, Onami T (2001) Mechanism of the degradation of Orange G by sodium hypochlorite. Color Technol 117:323–327. doi:10.1111/j.1478-4408.2001.tb00083.x
Khalfaoui N, Boutoumi H, Khalaf H, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical oxidation of the xanthene dye rhodamine 6G by electrochemical advanced oxidation using Pt and BDD anodes. Curr Org Chem 16:2083–2090. doi:10.2174/138527212803532459
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 49:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010
Kotiaho T, Hayward MJ, Cooks RG (1991) Direct determination of chlorination products of organic amines using membrane introduction mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 63:1794–1801. doi:10.1021/ac00017a025
Li Y, Xi D-L (2007) Quantitative structure-activity relationship study on the biodegradation of acid dyestuffs. J Environ Sci 19:800–804. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60134-X
Li J-T, Bai B, Song Y-L (2010a) Removal of acid orange 3 from aqueous solution by activated carbon adsorption. Asian J Chem 22:439–447
Li J-T, Bai B, Song Y-L (2010b) Degradation of Acid orange 3 in aqueous solution by combination of Fly ash/H2O2 and ultrasound irradiation. Indian J Chem Technol 17:198–203
Li H, Lin Y, Luo Y, Yu P, Hou L (2011) Relating organic fouling of reverse osmosis membranes to adsorption during the reclamation of secondary effluents containing methylene blue and rhodamine B. J Hazard Mater 192:490–499. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.044
Li H, Sun N, Zhang J, Liang S, Sun H (2014) Development of a matrix solid phase dispersion-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric method for multiresidue analysis of 25 synthetic colorants in meat products. Anal Methods 6:537–547. doi:10.1039/C3AY41664J
Lorimer JP, Mason TJ, Plattes M, Phull SS, Walton D (2011) Degradation of dye effluent. Pure Appl Chem 73:1957–1968
Martinez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.017
Mennear JH (1988) Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of C.I. Acid Orange 3 (CAS No. 6373-74-6) in F344/N rats and B6C3Ft mice (gavage studies), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, NTP TR 335, NIH Publication No. 89-2591, 1–156
Mijin DŽ, Avramov Ivić ML, Onjia AE, Grgur BN (2012) Decolorization of textile dye CI Basic Yellow 28 with electrochemically generated active chlorine. Chem Eng J 204–206:151–157. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.091
Mijin DŽ, Tomić VD, Grgur BN (2015) Electrochemical decolorization of CI Reactive Orange 16 dye using DSA Ti/PtOx electrode. J Serb Chem Soc 80:903–915. doi:10.2298/JSC140917107M
Mijin DŽ, Dabić DM, Mirković JM, Božić BĐ, Grgur BN (2016) Influence of microwave irradiation on hypochlorite decolorisation of synthetic dye. Zas Mater 57:63–70. doi:10.5937/ZasMat1601063M
Moehring H, Pratt D (2013) Bleaching and dyeing composition for hair. Chem Abstr 159:154601 (WO Patent 2013092904, Jun 27, 2013)
Molenda M, Lipinski N (2013) Hair dyeing compositions an anionic sugar surfactant. Chem Abstr 159:185610 (EP Patent 2,609,905, Jul 3, 2013)
Morrison RT, Boyd RN (1992) Organic chemistry, 6th edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi RR, Srikrishnaperumal T (2013) Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2099–2132. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1385-z
Pagga U, Brown D (1986) The degradation of dyes: part II. Behavior of dyes in aerobic biodegradation tests. Chemosphere 15:479–491. doi:10.12691/ijebb-2-1-6
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2003) Influence of anode material on the electrochemical oxidation of 2-naphthol part 1. Cyclic voltammetry and potential step experiments. Electrochim Acta 48:3491–3497. doi:10.1016/s0013-4686(03)00468-7
Parsa JB, Abbasi M (2012) Application of in situ electrochemically generated ozone for degradation of anthraquinone dye Reactive Blue 19. J Appl Electrochem 42:435–442. doi:10.1007/s10800-012-0417-1
Rajkumar K, Muthukumar M, Mangalaraja RV (2015) Electrochemical degradation of C.I. Reactive Orange 107 using Gadolinium (Gd3+), Neodymium (Nd3+) and Samarium (Sm3+) doped cerium oxide nanoparticles. Int J Ind Chem 6:285–295. doi:10.1007/s40090-015-0051-y
Rauf MA, Ashraf SS (2009) Fundamental principles and application of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of dyes in solution. Chem Eng J 151:10–18. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2009.02.026
Rocha JHB, Fernandes NS, Souza KR, da Silva DR, Quiroz MA, Martínez-Huitle CA (2011) Electrochemical decolourization process of textile dye in the presence of NaCl at boron doped diamond electrode. Sustain Environ Res 21:291–298
Sekizawa T, Onodera S (2010) Chemical fate and mutagenic formation potentials of phenothiazine and related compounds during water chlorination. J Toxicol Sci 35:853–862. doi:10.2131/jts.35.853
Šekuljica NŽ, Prlainović NŽ, Jakovetić SM, Grbavčić SŽ, Ognjanović ND, Knežević-Jugović ZD, Mijin DŽ (2016) Removal of anthraquinone dye by cross-linked enzyme aggregates from fresh horseradish extract. Clean Soil Air Water 44:891–900. doi:10.1002/clen.201500766
Sürme Y, Demirci OB (2014) Determination of direct violet 51 dye in water based on its decolorisation by electrochemical treatment. Chem Pap 68:1491–1497. doi:10.2478/s11696-014-0616-9
Wang JL, Xu LJ (2012) Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:251–325. doi:10.1080/10643389.2010.507698
World Health Organization (1993) occupational exposures of hairdressers and barbers and personal use of hair colourants; some hair dyes, cosmetic colourants, industrial dyestuffs and aromatic amines. In: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, vol 57, IARC Lyon, 121–125
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002
Yemashova N, Telegina A, Kotova I, Netrusov A, Kalyuzhnyi S (2004) Decolorization and partial degradation of selected azo dyes by methanogenic sludge. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 119:31–40. doi:10.1385/ABAB:119:1:31
Zhong X, Xiang L, Royer S, Valange S, Barrault J, Zhang H (2011) Degradation of C.I. Acid Orange 7 by heterogeneous Fenton oxidation in combination with ultrasonic irradiation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:970–977. doi:10.1002/jctb.2608
Zhu M-X, Lee L, Wang H-H, Wang Z (2007) Removal of an anionic dye by adsorption/precipitation processes using alkaline white mud. J Hazard Mater 149:735–741. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.037
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia under the research projects: ON172013, ON172046, and ON172007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mijin, D.Ž., Radišić, M.M., Šekuljica, N.Ž. et al. Electrochemical decolorization of C.I. Acid Orange 3 in the presence of sodium chloride at iridium oxide electrode. Chem. Pap. 71, 2173–2184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0211-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0211-y