Abstract
Background
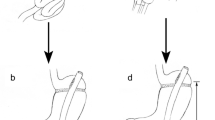
Of patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), 15–35% of patients fail to achieve “adequate” weight loss or regain significant weight. Multiple solutions have been proposed, but not well studied. We report our experience with limb distalization with lengthening the biliopancreatic (BP) limb and shortening the common channel (CC).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed data from patients undergoing laparoscopic limb distalization for excess weight loss (EWL) <50% or BMI >35 kg/m2 after RYGB from 2012 to 2017. The BP limb was lengthened and CC was shortened to 100–200 cm. Perioperative outcomes such as morbidity, weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, comorbidity remission, and operative details were analyzed.
Results
Twenty-two patients were included. The mean BMI prior to RYGB was 54.1 ± 8.5 kg/m2 and 43.0 ± 5.5 kg/m2 prior to limb distalization. The mean follow-up was 18.3 ± 12.9 months with a mean BMI change, %EWL, and %TWL (total weight loss) of 11.8 ± 7.4 kg/m2, 62.3 ± 32.4%, and 25.4 ± 14.4%, respectively. The total mean BMI change, %EWL, and %TWL from RYGB was 22.2 ± 9.9 kg/m2, 77.8 ± 23.6%, and 40.2 ± 13.3%, respectively. Of patients with persistent comorbidities, remission rates of diabetes, hypertension, and gastroesophageal reflux disease were 100%, 17%, and 38%, respectively. The mean operative time was 132.6 ± 54.4 min and mean hospital stay was 2.2 ± 1.3 days. Overall morbidity was 27.3%. Three patients (13.6%) developed nutritional deficiencies requiring reversal surgery.
Conclusion
In patients with inadequate weight loss or weight regain after RYGB, limb distalization with lengthening of the BP limb is an effective procedure for additional weight loss and further improvement of comorbidities. Nutritional complications are a risk, but can be minimized with close follow-up and patient compliance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):641–51.
Wittgrove AC, Clark GW. Laparoscopic gastric bypass, Roux-en-Y- 500 patients: technique and results, with 3-60 month follow-up. Obes Surg. 2000;10(3):233–9.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
Higa K, Ho T, Tercero F, et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(4):516–25.
Rawlins ML, Teel D, Hedgcorth K, et al. Revision of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass to distal bypass for failed weight loss. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(1):45–9.
Stefanidis D, Kuwada TS, Gersin KS. The importance of the length of the limbs for gastric bypass patients--an evidence-based review. Obes Surg. 2011;21(1):119–24.
Parikh M, Heacock L, Gagner M. Laparoscopic “gastrojejunal sleeve reduction” as a revision procedure for weight loss failure after roux-en-y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2011;21(5):650–4.
Hamdi A, Julien C, Brown P, et al. Midterm outcomes of revisional surgery for gastric pouch and gastrojejunal anastomotic enlargement in patients with weight regain after gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2014;24(8):1386–90.
Tran DD, Nwokeabia ID, Purnell S, et al. Revision of Roux-En-Y gastric bypass for weight regain: a systematic review of techniques and outcomes. Obes Surg. 2016;26(7):1627–34.
Aminian A, Corcelles R, Daigle CR, et al. Critical appraisal of salvage banding for weight loss failure after gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11(3):607–11.
Thompson CC, Chand B, Chen YK, et al. Endoscopic suturing for transoral outlet reduction increases weight loss after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):129–137.e3.
Iannelli A, Schneck AS, Hébuterne X, et al. Gastric pouch resizing for Roux-en-Y gastric bypass failure in patients with a dilated pouch. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(2):260–7.
Bessler M, Daud A, Digiorgi MF, et al. Adjustable gastric banding as revisional bariatric procedure after failed gastric bypass--intermediate results. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6(1):31–5.
Odstrcil EA, Martinez JG, Santa ana CA, et al. The contribution of malabsorption to the reduction in net energy absorption after long-limb Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92(4):704–13.
Keshishian A, Zahriya K, Hartoonian T, et al. Duodenal switch is a safe operation for patients who have failed other bariatric operations. Obes Surg. 2004;14(9):1187–92.
Hernández-martínez J, Calvo-ros MÁ. Gastric by-pass with fixed 230-cm-long common limb and variable alimentary and biliopancreatic limbs in morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2011;21(12):1879–86.
Mahawar KK, Kumar P, Parmar C, et al. Small bowel limb lengths and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a systematic review. Obes Surg. 2016;26(3):660–71.
Brethauer SA, Kothari S, Sudan R, et al. Systematic review on reoperative bariatric surgery: American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Revision Task Force. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10(5):952–72.
Parikh M, Pomp A, Gagner M. Laparoscopic conversion of failed gastric bypass to duodenal switch: technical considerations and preliminary outcomes. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2007;3(6):611–8.
Buchwald H, Kellogg TA, Leslie DB, et al. Duodenal switch operative mortality and morbidity are not impacted by body mass index. Ann Surg. 2008;248(4):541–8.
Søvik TT, Taha O, Aasheim ET, et al. Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic duodenal switch for superobesity. Br J Surg. 2010;97(2):160–6.
Ghiassi S, Higa K, Chang S, et al. Conversion of standard Roux-en-Y gastric bypass to distal bypass for weight loss failure and metabolic syndrome: 3-year follow-up and evolution of technique to reduce nutritional complications. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14(5):554–61.
Himpens J, Coromina L, Verbrugghe A, et al. Outcomes of revisional procedures for insufficient weight loss or weight regain after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2012;22(11):1746–54.
Dapri G, Cadière GB, Himpens J. Laparoscopic conversion of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass to distal gastric bypass for weight regain. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2011;21(1):19–23.
Sugerman HJ, Kellum JM, Demaria EJ. Conversion of proximal to distal gastric bypass for failed gastric bypass for superobesity. J Gastrointest Surg. 1997;1(6):517–24.
Kellum JM, Chikunguwo SM, Maher JW, et al. Long-term results of malabsorptive distal Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in superobese patients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(2):189–93.
Brolin RE, Cody RP. Adding malabsorption for weight loss failure after gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(11):1924–6.
Srikanth MS, Oh KH, Fox SR. Revision to malabsorptive Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (MRNYGBP) provides long-term (10 years) durable weight loss in patients with failed anatomically intact gastric restrictive operations: long-term effectiveness of a malabsorptive Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in salvaging patients with poor weight loss or complications following gastroplasty and adjustable gastric bands. Obes Surg. 2011;21(7):825–31.
Parrott J, Frank L, Rabena R, et al. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Integrated Health Nutritional Guidelines for the surgical weight loss patient 2016 update: micronutrients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(5):727–41.
Svanevik M, Risstad H, Hofsø D, et al. Perioperative outcomes of proximal and distal gastric bypass in patients with BMI ranged 50-60 kg/m(2)--a double-blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Obes Surg. 2015;25(10):1788–95.
Fobi MA, Lee H, Igwe D, et al. Revision of failed gastric bypass to distal Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a review of 65 cases. Obes Surg. 2001;11(2):190–5.
Sethi M, Chau E, Youn A, et al. Long-term outcomes after biliopancreatic diversion with and without duodenal switch: 2-, 5-, and 10-year data. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(9):1697–705.
Thurnheer M, Bisang P, Ernst B, et al. A novel distal very long Roux-en Y gastric bypass (DVLRYGB) as a primary bariatric procedure--complication rates, weight loss, and nutritional/metabolic changes in the first 355 patients. Obes Surg. 2012;22(9):1427–36.
Madan AK, Harper JL, Tichansky DS. Techniques of laparoscopic gastric bypass: on-line survey of American Society for Bariatric Surgery practicing surgeons. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4(2):166–72.
Christou NV, Look D, Maclean LD. Weight gain after short- and long-limb gastric bypass in patients followed for longer than 10 years. Ann Surg. 2006;244(5):734–40.
Müller MK, Räder S, Wildi S, et al. Long-term follow-up of proximal versus distal laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Br J Surg. 2008;95(11):1375–9.
Nergaard BJ, Leifsson BG, Hedenbro J, et al. Gastric bypass with long alimentary limb or long pancreato-biliary limb--long-term results on weight loss, resolution of co-morbidities and metabolic parameters. Obes Surg. 2014;24(10):1595–602.
Homan J, Boerboom A, Aarts E, et al. A longer biliopancreatic limb in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass improves weight loss in the first years after surgery: results of a randomized controlled trial. Obes Surg. 2018;28:3744–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3421-7. [Epub ahead of print].
Gazer B, Rosin D, Bar-zakai B, et al. Accuracy and inter-operator variability of small bowel length measurement at laparoscopy. Surg Endosc. 2017;31(11):4697–704.
Isreb S, Hildreth AJ, Mahawar K, et al. Laparoscopic instruments marking improve length measurement precision. World J Laparosc Surg. 2009;2(3):57–60.
Funding
This study was made possible by grant support from the Foundation for Surgical Fellowships (FSF) for Reuben D Shin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Author 6 is an editor of Obesity Surgery.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, R.D., Goldberg, M.B., Shafran, A.S. et al. Revision of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass with Limb Distalization for Inadequate Weight Loss or Weight Regain. OBES SURG 29, 811–818 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-03635-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-03635-0