Background
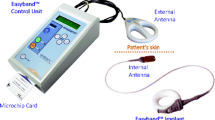
It has already been demonstrated that laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) is a safe and effective alternative to other permanent bariatric surgery techniques. Although clinical complications have been managed through improvements in surgical techniques, port-related complications and adjustment process inefficiencies have persisted. To reduce and manage these issues, a new type of gastric band has been developed which uses telemetric technology to eliminate the use of hydraulic ports and simplify the overall gastric band adjustment procedure.
Methods
From June 2005 to October 2005, 37 patients were implanted in two German academic centers with the Easyband® telemetrically adjustable gastric band (Endoart S.A., Lausanne, Switzerland), using standard gastric banding laparoscopic technique. Prospective data was collected and analyzed for a minimum of 6 months on all morbidly obese patients who underwent laparoscopic telemetrically adjustable gastric banding.
Results
Data on 37 patients was analyzed.The mean percent excess weight loss was 10.2% at 1 month, 21.6% at 3 months, and 29.4% at 6 months. In 12 hypertensive patients, the systolic blood pressure decreased from 143 ± 24 mmHg at baseline to 131 ± 10 mmHg after 6 months. Diastolic pressure did not change significantly. In all 5 patients with diagnosed type 2 diabetes, the fasting blood glucose normalized after 6 months (135 mg/dl at baseline, 81 mg/dl at month 6).
Conclusion
These early results of the new telemetrically adjustable gastric banding device indicate clinical safety and efficacy comparable to that achieved by other commercially available gastric bands. Additional multi-center studies with long-term followup are recommended to confirm the benefits of telemetrically adjustable gastric banding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf AM. What is the economic case for treating obesity? Obes Res 1998; 6 (Suppl 1): 2S–7S.
Wolf AM, Colditz GA. Current estimates of the economic cost of obesity in the United States. Obes Res 1998; 6: 97–106.
Belachew M, Legrand MJ, Vincent V. History of Lap-Band: from dream to reality. Obes Surg 2001; 11: 297–302.
Fielding GA, Allen JW. A step-by-step guide to placement of the LAP-BAND adjustable gastric banding system. Am J Surg 2002; 184 (6B): 26S–30S.
Weiner RA. [Gastric banding: surgical and technical aspects]. Chirurg 2005; 76: 678–88.
Weiner RA, Korenkov M, Matzig E et al. Initial clinical experience with telemetrically adjustable gastric banding. Surg Technol Int 2006; 15: 63–69.
Korenkov M, Sauerland S, Yucel N et al. Port function after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc 2003; 17: 1068–71.
O’Brien P. Invited commentary: port and tubing complications. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 366.
Susmallian S, Ezri T, Elis M et al. Access-port complications after laparoscopic gastric banding. Obes Surg 2003; 13: 128–31.
Weiner R, Blanco-Engert R, Weiner S et al. Outcome after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding- 8 years experience. Obes Surg 2003; 13: 427–34.
Kim TH, Daud A, Ude AO et al. Early U.S. outcomes of laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc 2006; 20: 202–9.
Ponce J, Paynter S, Fromm R. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: 1,014 consecutive cases. J Am Coll Surg 2005; 201: 529–35.
Dolan K, Bryant R, Fielding G. Treating diabetes in the morbidly obese by laparoscopic gastric banding. Obes Surg 2003; 13: 439–43.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE. Changes in comorbidities and improvements in quality of life after LAP-BAND placement. Am J Surg 2002; 184 (6B): 51S–54S.
Sarker S, Herold K, Creech S et al. Early and late complications following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Am Surg 2004; 70: 146–9; discussion 149–50.
DeMaria EJ. Laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding: complications. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 2003; 13: 271–7.
Chapman AE, Kiroff G, Game P et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: a systematic literature review. Surgery 2004; 135: 326–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiner, R.A., Korenkov, M., Matzig, E. et al. Early Results with a New Telemetrically Adjustable Gastric Banding. OBES SURG 17, 717–721 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9132-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9132-0