Abstract
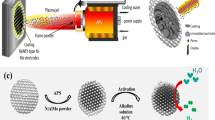
High velocity oxy-fuel process was used to prepare nickel electrode coatings for hydrogen production by alkaline water electrolysis. To further increase the active surface area of the electrodes, pyramidal fin arrays with two different sizes were deposited on the top surface of the electrodes using mesh screen masks. The surface microstructure, topology and roughness of the coatings were studied using scanning electron microscope, optical microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Steady-state polarization curves were used to evaluate the electrocatalytic activity of the electrodes. The performance of the electrodes coated using mesh outperformed the electrode deposited without using mesh. In addition, the electrode that was coated using the coarse mesh was characterized with the highest activity with the exchange current density and overpotential values of 9.3 × 10−3 A/cm2 and −306 mV, respectively. Formation of different roughness levels due to the combination of normal and off-normal impact of the coating particles on the surface of the fins was identified as the main factor for the increased activity of this electrode toward the hydrogen evolution reaction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ursua, L.M. Gandia, and P. Sanchis, Hydrogen Production from Water Electrolysis: Current Status and Future Trends, Proc. IEEE, 2012, 100(2), p 410-426
W. Hu, Electrocatalytic Properties of New Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution in Alkaline Water Electrolysis, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2000, 25(2), p 111-118
D.L. Stojić, M.P. Marčeta, S.P. Sovilj, and Š.S. Miljanić, Hydrogen Generation from Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving, J. Power Sources, 2003, 118(1), p 315-319
K. Zeng and D. Zhang, Recent Progress in Alkaline Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production and Applications, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2010, 36(3), p 307-326
C. Fan, D. Piron, A. Sleb, and P. Paradis, Study of Electrodeposited Nickel-Molybdenum, Nickel-Tungsten, Cobalt-Molybdenum, and Cobalt-Tungsten as Hydrogen Electrodes in Alkaline Water Electrolysis, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, 141(2), p 382-387
H. Suffredini, J. Cerne, F. Crnkovic, S. Machado, and L. Avaca, Recent Developments in Electrode Materials for Water Electrolysis, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2000, 25(5), p 415-423
M. Janjua and R. Le Roy, Electrocatalyst Performance in Industrial Water Electrolysers, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 1985, 10(1), p 11-19
B. Conway and G. Jerkiewicz, Relation of Energies and Coverages of Underpotential and Overpotential Deposited H at Pt and other Metals to the ‘Volcano Curve’ for Cathodic H2 Evolution Kinetics, Electrochim. Acta, 2000, 45(25), p 4075-4083
I. Herraiz-Cardona, E. Ortega, J.G. Antón, and V. Pérez-Herranz, Assessment of the Roughness Factor Effect and the Intrinsic Catalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ni-Based Electrodeposits, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(16), p 9428-9438
F. Crnkovic, S. Machado, and L. Avaca, Electrochemical and Morphological Studies of Electrodeposited Ni–Fe–Mo–Zn Alloys Tailored for Water Electrolysis, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(3), p 249-254
B. Łosiewicz, A. Budniok, E. Rówiński, E. Łągiewka, and A. Lasia, The Structure, Morphology and Electrochemical Impedance Study of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on the Modified Nickel Electrodes, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(2), p 145-157
M. Aghasibeig, M. Mousavi, F.B. Ettouill, C. Moreau, R. Wuthrich, and A. Dolatabadi, Electrocatalytically Active Nickel-Based Electrode Coatings Formed by Atmospheric and Suspension Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2014, 23(1-2), p 220-226
M. Aghasibeig, R. Wuthrich, C. Moreau, and A. Dolatabadi, Electrocatalytic Behaviour of Nickel Coatings Formed by APS and SPS Processes, International Thermal Spray Conference and Exposition, ASM International, 2014, p 739-744
I. Herraiz-Cardona, E. Ortega, L. Vázquez-Gómez, and V. Pérez-Herranz, Double-Template Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Porous Nickel Electrodes for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(3), p 2147-2156
L. Birry and A. Lasia, Studies of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Raney Nickel-Molybdenum Electrodes, J. Appl. Electrochem., 2004, 34(7), p 735-749
A. Kellenberger, N. Vaszilcsin, W. Brandl, and N. Duteanu, Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Skeleton Nickel and Nickel–Titanium Electrodes Obtained by Thermal Arc Spraying Technique, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(15), p 3258-3265
M. Aghasibeig, H. Monajatizadeh, P. Bocher, A. Dolatabadi, R. Wuthrich, and C. Moreau, Cold Spray as a Novel Method for Development of Nickel Electrode Coatings for Hydrogen Production, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(1), p 227-238
M. Aghasibeig, C. Moreau, A. Dolatabadi, and R. Wuthrich, Fabrication of Nickel Electrode Coatings by Combination of Atmospheric and Suspension Plasma Spray Processes, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 285, p 68-76
M. Oksa, E. Turunen, T. Suhonen, T. Varis, and S.P. Hannula, Optimization and Characterization of High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Sprayed Coatings: Techniques, Materials, and Applications, Coatings, 2011, 1(1), p 17-52
C. Lyphout, P. Nylén, and L. Östergren, Relationships Between Process Parameters, Microstructure, and Adhesion Strength of HVOF Sprayed IN718 Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2011, 20(1-2), p 76-82
M. Aghasibeig, A. Dolatabadi, R. Wuthrich, and C. Moreau, Three-dimensional Electrode Coatings for Hydrogen Production Fabricated by Combined Atmospheric and Suspension Plasma Spray, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 291, p 348-355
M. Li and P.D. Christofides, Modeling and Control of High-velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF) Thermal Spray: A Tutorial Review, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(5-6), p 753-768
Y. Cormier, P. Dupuis, B. Jodoin, and A. Corbeil, Net Shape Fins for Compact Heat Exchanger Produced by Cold Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 22(7), p 1210-1221
Y. Cormier, P. Dupuis, B. Jodoin, and A. Corbeil, Pyramidal Fin Arrays Performance Using Streamwise Anisotropic Materials by Cold Spray Additive Manufacturing, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25(1), p 170-182
W. Tillmann, I. Baumann, P. Hollingsworth, and I.-A. Laemmerhirt, Influence of the Spray Angle on the Properties of HVOF Sprayed WC–Co Coatings Using (−10+ 2 μm) Fine Powders, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 22(2-3), p 272-279
Š. Houdková, M. Kašparová, and F. Zahálka, The Influence of Spraying Angle on Properties of HVOF Sprayed Hardmetal Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(5), p 893-901
C. Li, W. Li, Y. Wang, and H. Fukanuma, Effect of Spray Angle on Deposition Characteristics in Cold Spraying, Thermal Spray 2003: Advancing the Science & Applying the Technology, ASM International, USA, p 5-8
P. Fauchais, A. Vardelle, M. Vardelle, and M. Fukumoto, Knowledge Concerning Splat Formation: An Invited Review, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2004, 13(3), p 337-360
H. Hagi, Diffusion Coefficient of Hydrogen in Iron Without Trapping by Dislocations and Impurities, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1994, 35(2), p 112-117
S.M. Myers, M. Baskes, H. Birnbaum, J.W. Corbett, G. DeLeo, S. Estreicher, E.E. Haller, P. Jena, N.M. Johnson, and R. Kirchheim, Hydrogen Interactions with Defects in Crystalline Solids, Rev. Mod. Phys., 1992, 64(2), p 559
B. Łosiewicz, A. Budniok, E. Rówiński, E. Łągiewka, and A. Lasia, Effect of Heat-treatment on the Mechanism and Kinetics of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ni–P+ TiO2 + Ti Electrodes, J. Appl. Electrochem., 2004, 34(5), p 507-516
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgement is given to Dr. Fadhel Ben Ettouil for his assistance with the HVOF coating process. We wish to thank Mr. John Gavita at Olympus Corporation for providing access to the confocal laser scanning microscopy. This work was financially supported by Fonds de recherche du Québec (FQRNT), Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and Canada Research Chairs program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghasibeig, M., Moreau, C., Dolatabadi, A. et al. Engineered Three-Dimensional Electrodes by HVOF Process for Hydrogen Production. J Therm Spray Tech 25, 1561–1569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0458-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0458-9