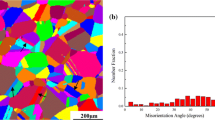
Abstract
The work prepared a typical Ni-17Mo-7Cr (wt.%)-based superalloy and investigated the effect of aging time on microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloy subjected to simulated heat-affected zone (HAZ) thermal treatment. After aging, many fine MoC particles are precipitated at the grain boundaries as well as in the grains. Regions with lamellar-like structures become larger, and many fine MoC particles are produced around them. The microstructural degradation caused by aging has limited influence on the alloy’s high-temperature (800 °C) mechanical properties. After exposure to the HAZ simulation, the alloy can still maintain excellent mechanical properties when aged at 800 °C for different time, similar to the alloy that did not undergo the HAZ simulation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Pfenninger and J. Keirstead, Renewables, Nuclear, or Fossil fuels? Scenarios for Great Britain’s Power System Considering Costs, Emissions and Energy Security, Appl. Energy, 2015, 152, p 83–93
F.Y. Ouyang, C.H. Chang, and J.J. Kai, Long-term Corrosion Behaviors of Hastelloy N and Hastelloy B3 in Moisture-containing Molten FLiNaK Salt Environments, J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, 446, p 81–89
Z.F. Xu, L. Jiang, J.S. Dong, Z.J. Li, and X.T. Zhou, The Effect of Silicon on Precipitation and Decomposition Behaviors of M6C Carbide in a Ni-Mo-Cr Superalloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 620, p 197–203
X.L. Li, S.M. He, X.T. Zhou, Y. Zou, Z.J. Li, A.G. Li, and X.H. Yu, Effects of Rare Earth Yttrium on Microstructure and Properties of Ni-16Mo-7Cr-4Fe Nickel-based Superalloy, Mater. Charact., 2014, 95, p 171–179
M. Hashim, K.E.S.R. Babu, M. Duraiselvam, and H. Natu, Improvement of Wear Resistance of Hastelloy C276 through Laser Surface Melting, Mater. Des., 2013, 46, p 546–551
B.N. Du, J.X. Yang, C.Y. Cui, and X.F. Sun, Effects of Grain Size on the High-cycle Fatigue Behavior of IN792 Superalloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 65, p 57–64
F.H. Latief and K. Kakehi, Influence of Thermal Exposure on the Creep Properties of an Aluminized Ni-based Single Crystal Superalloy in Different Surface Orientations, Mater. Des., 2014, 56, p 816–821
Y.M. He, J.G. Yang, C.J. Qin, S.J. Chen, and Z.L. Gao, Characterization of the Ni-Mo-Cr Superalloy Subjected to Simulated Heat-affected Zone Thermal Cycle Treatment, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 643, p 7–16
H.E. McCoy, Studies of the Carbon Distribution in Hastelloy N, ORNL, 1966, p. 21.
R.B. Briggs, Molten-salt Reaction Program Semiannual Progress Report, ORNL, 1965, p. 95.
Y.M. He, J.G. Yang, S.J. Chen, Z. Li, and Z.L. Gao, Effect of High-Temperature Aging on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ni-Mo-Cr Based Superalloy Subjected to Simulated Heat-Affected Zone Thermal Cycle, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 660, p 266–275
R.E. Gehlbach and H.E. McCoy, Phase Instability in Hastelloy N, ORNL, 1968, p. 347.
O.A. Ojo and M.C. Chaturvedi, On the Role of Liquated γ’ Precipitates in Weld Heat Affected Zone Micro-fissuring of a Nickel-based Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 403, p 77–86
D. Tytko, P.P. Choi, J. Klower, A. Kostka, G. Inden, and D. Raabe, Microstructural Evolution of a Ni-based Superalloy (617B) at 700 °C Studied by Electron Microscopy and Atom Probe Tomography, Acta Mater., 2012, 60, p 1731–1740
R. Hu, G.H. Bai, J.S. Li, J.Q. Zhang, T.B. Zhang, and H.Z. Fu, Precipitation Behavior of Grain Boundary M23C6 and its Effect on Tensile Properties of Ni-Cr-W Based Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 548, p 83–88
W.D. Callister, Materials Science and Engineering—an Introduction, Seventh edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2007.
H. Li, S. Xia, B.X. Zhou, and W.Q. Liu, C-Cr Segregation at Grain Boundary before the Carbide Nucleation in Alloy 690, Mater. Charact., 2012, 66, p 68–74
I.S. Kim, B.G. Choi, H.U. Hong, J. Do, and C.Y. Jo, Influence of Thermal Exposure on the Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Wrought Ni-base Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 593, p 55–63
C.T. Sims, N.S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel, The Superalloys, Wiley, New York, 1972
L.J. Huang, L. Geng, and H.X. Peng, Microstructurally Inhomogeneous Composites: Is a Homogeneous Reinforcement Distribution Optimal?, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2015, 71, p 93–168
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51405439 and 51475426) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant Nos. LY17E050019 and LQ16E060004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Yang, J., Chen, S. et al. Aging Time-Microstructure-Mechanical Property Correlation of a Ni-17Mo-7Cr-Based Superalloy Subjected to Simulated Heat-Affected Zone Thermal Treatment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 4556–4566 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2866-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2866-5