Abstract
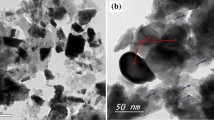
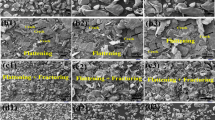
In the present work, mechanical milling technique using a high-energy ball mill was employed for preparing of nanoscaled WC grains powders with an average grain size of 7 nm in diameters of WC. The present study demonstrates a successful consolidation process achieved at 1250 °C for sintering of ball-milled WC powders into full dense bulk buttons (above 99.6%), using SPS technique. The as-consolidated WC bulk nanocrystalline buttons revealed high hardness value (~24 GPa) with low elastic modulus (~332 GPa). Moreover, they possessed a high fracture toughness (15 MPa m1/2) that has never been reported for pure WC.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.X. Yan, M. Cai, and P.K. Shen, Nanosized tungsten carbide synthesized by a novel route at low temperature for high performance electrocatalysis, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, p 1646. doi:10.1038/srep01646
M.S. El-Eskandarany, Mechanical Alloying: Nanotechnology, Materials Science and Powder Metallurgy, 2nd ed., Elsevier Inc., Oxford, 2015
M.S. El-Eskandarany, Fabrication of nanocrystalline WC and nanocomposite refractory materials at room temperature, J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 296, p 175–182
V. Richter and M. Ruthendorf, On hardness and toughness of ultrafine and nanocrystalline hard materials, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 1999, 17, p 141–152
M.S. El-Eskandarany et al., Synthesis of full-density nanocrystalline tungsten carbide by reduction of tungstic oxide at room temperature, Met. Trans., 1996, 27 A, p 4210–4213
S. Grasso et al., Low-temperature spark plasma sintering of pure nano WC powder, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2013, doi:10.1111/jace.12365
B. Huang, L.D. Chen, and Q. Bais, Bulk ultrafine binderless WC prepared by spark plasma sintering, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54, p 441–445
A.S. Kurlov and A.I. Gusev, Tungsten Carbides: Structure, Properties and Application in Hardmetals, 1st ed., Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2013
A.S. Kurlov et al., Microstructure of nanocrystalline WC powders and WC-Co hard alloys, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2011, 27, p 165–172
Z.Z. Fang, X. Wang, T. Ryu, K.S. Hwang, and H.Y. Sohn, Synthesis, sintering, and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline cemented tungsten carbide: a review, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2009, 27, p 288–299
M.S. El-Eskandarany, A.A. El-Mahdy, H.A. Ahmed, and A.A. Amer, Synthesis and characterizations of ball-milled nanocrystalline WC and nanocomposite WC-Co powders and subsequent consolidations, J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 312, p 315–325
R.K. Enneti, Synthesis of nanocrystalline tungsten and tungsten carbide powders in a single step via thermal plasma technique, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2015, 53, p 111–116
Y. Xun and F.A. Mohamed, Refining efficiency and capability of top-down synthesis of nanocrystalline materials, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 527, p 5446–5452
Y. Kanemitsu, T. Nishimura, H. Yoshino, K. Takao, and Y. Masumoto, Effect of hot isostatic pressing on binderless cemented carbide, Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 1982, 1, p 66–68
G. Maizza, S. Grasso, Y. Sakka, T. Noda, and O. Ohashi, Relation between microstructure, properties and spark plasma sintering (SPS) parameters of pure ultrafine WC powder, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2007, 8, p 644–654
M. Tokita, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Method, Systems, and Applications, Handbook of Advanced Ceramics, 1st ed., Elsevier Inc., Oxford, 2015
M.S. El-Eskandarany, Fabrication and characterizations of new nanocomposite WC/Al2O3 materials by room temperature ball milling and subsequent consolidation, J. Alloys Compd., 2005, 391, p 228–235
H.J. Fecht, Nanostructure formation by mechanical attrition, Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, 6, p 33–42
M. Tokita, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Method, Systems, and Applications, Handbook of Advanced Ceramics, Elsevier Inc., Oxford, 2013
B.R. Lawn, A.G. Evans, and D.B. Marshall, Elastic/plastic indentation damage in ceramics: the median/radial crack system, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1980, 63, p 574–581
G.R. Anstis, P. Chantikul, B.R. Lawn, and D.B. Marshall, Techniques for measuring reacture toughness I, direct crack measurements, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1981, 64, p 533–538
H. Gleiter, Nanostructured materials: basic concepts and microstructured, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, p 1–29
Y. Zhou, U. Erb, K.T. Aust, and G. Palumbo, The effects of triple junctions and grain boundaries on hardness and Young modulus in nanostructured Ni–P, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48, p 825–830
F. Wang, X.-Q. Feng, S.-W. Yu, and C.-W. Nan, Interface effects on effective elastic moduli of nanocrystalline materials, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 363, p 1–8
X. Qing and G. Xingming, The scale effect on the yield strength of nanocrystalline materials, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2006, 43, p 7793–7799
Acknowledgments
The financial support received by the Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Program-Energy and Building Research Center, Kuwait Institute for scientific Research is highly appreciated. We would like to express our deepest gratitude to the Kuwait Government for purchasing the equipment used in the present work, using the budget dedicated for the project led by the first author (P-KISR-06-04) of Establishing Nanotechnology Center in KISR is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherif El-Eskandarany, M., Al-Hazza, A. & Al-Hajji, L.A. HRTEM and Nanoindentation Studies of Bulk WC Nanocrystalline Materials Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering of Ball-Milled Powders. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 124–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2443-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2443-3