Abstract
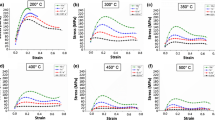
In order to improve the understanding of the hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) behaviors of large-scaled AZ80 magnesium alloy fabricated by semi-continuous casting, compression tests were carried out in the temperature range from 250 to 400 °C and strain rate range from 0.001 to 0.1 s−1 on a Gleeble 1500 thermo-mechanical machine. The effects of the temperature and strain rate on the hot deformation behavior have been expressed by means of the conventional hyperbolic sine equation, and the influence of the strain has been incorporated in the equation by considering its effect on different material constants for large-scaled AZ80 magnesium alloy. In addition, the DRX behavior has been discussed. The result shows that the deformation temperature and strain rate exerted remarkable influences on the flow stress. The constitutive equation of large-scaled AZ80 magnesium alloy for hot deformation at steady-state stage (ɛ = 0.5) was \( \dot{\upvarepsilon } = 1.394 \times 10^{12} [\sinh (0.018\upsigma )]^{5.043} \exp ( - 169.610/RT). \) The true stress-true strain curves predicted by the extracted model were in good agreement with the experimental results, thereby confirming the validity of the developed constitutive relation. The DRX kinetic model of large-scaled AZ80 magnesium alloy was established as X d = 1 − exp[−0.95((ɛ − ɛc)/ɛ*)2.4904]. The rate of DRX increases with increasing deformation temperature, and high temperature is beneficial for achieving complete DRX in the large-scaled AZ80 magnesium alloy.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.L. Ma, K. Zhang, X.G. Li, Y.J. Li, G.L. Shi, and J.W. Yuan, Influence of Solution and Aging on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Complex Deformed WE93 Alloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 51, p 73–78
X.S. Xia, Q. Chen, J.P. Li, D.Y. Shu, C.K. Hu, S.H. Huang, and Z.D. Zhao, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior of As-Extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 610, p 203–211
Y. Xue, Z.M. Zhang, G. Lu, Z.P. Xie, Y.B. Yang, and Y. Cui, Study on Flow Stress Model and Processing Map of Homogenized Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy During Thermomechanical Processes, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, doi:10.1007/s11665-014-1324-x
X.S. Xia, Q. Chen, K. Zhang, Z.D. Zhao, M.L. Ma, X.G. Li, and Y.J. Li, Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of Coarse-Grained Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 587, p 283–290
T. Zhong, K.P. Rao, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, and M. Gupta, Processing Maps, Microstructure Evolution and Deformation Mechanisms of Extruded AZ31-DMD During Hot Uniaxial Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 773–781
Y.C. Lin and M.S. Chen, Study of Microstructural Evolution During Static Recrystallization in a Low Alloy Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44, p 835–842
J. Liu and Z.S. Cui, Hot Forging Process Design and Parameters Determination of Magnesium Alloy AZ31B Spur Bevel Gear, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 5871–5880
Y.C. Lin, L.T. Li, and Y.C. Xia, A New Method to Predict the Metadynamic Recrystallization Behaviors in 2124 Aluminum Alloy, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2011, 50, p 2038–2043
P. Changizian, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and A.A. Roostaei, The High Temperature Flow Behavior Modeling of AZ81 Magnesium Alloy Considering Strain Effects, Mater. Des., 2012, 39, p 384–389
D.H. Yu, Modeling High-Temperature Tensile Deformation Behavior of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy Considering Strain Effects, Mater. Des., 2013, 51, p 323–330
L. Wang, F. Liu, Q. Zuo, and C.F. Chen, Prediction of Flow Stress for N08028 Alloy Under Hot Working Conditions, Mater. Des., 2013, 47, p 737–745
B. Meng, M. Wan, X.D. Wu, Y.K. Zhou, and C. Chang, Constitutive Modeling for High-Temperature Tensile Deformation Behavior of Pure Molybdenum Considering Strain Effects, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2014, 45, p 41–47
J. Cai, F.G. Li, T.Y. Liu, B. Chen, and M. He, Constitutive Equations for Elevated Temperature Flow Stress of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Considering the Effect of Strain, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 1144–1151
J. Luo, M.Q. Li, and W.X. Yu, Prediction of Flow Stress in Isothermal Compression of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Using Fuzzy Neural Network, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 3078–3083
J. Li, F.G. Li, J. Cai, R.T. Wang, Z.W. Yuan, and F.M. Xue, Flow Behavior Modeling of the 7050 Aluminum Alloy at Elevated Temperatures Considering the Compensation of Strain, Mater. Des., 2012, 42, p 369–377
H. Mirzadeh and A. Najafizadeh, Flow Stress Prediction at Hot Working Conditions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 1160–1164
N. Haghdadi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and H.R. Abedi, The Flow Behavior Modeling of Cast A356 Aluminum Alloy at Elevated Temperatures Considering the Effect of Strain, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 535, p 252–257
M.L. Ma, K. Zhang, X.G. Li, Y.J. Li, and K. Zhang, Hot Deformation Behavior of Rare Earth Magnesium Alloy Without Pre-homogenization Treatment, Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2008, 18, p 132–139
W.F. Zhang, W. Sha, W. Yan, W. Wang, Y.Y. Shan, and K. Yang, Constitutive Modeling, Microstructure Evolution and Processing Map for a Nitride-Strengthened Heat-Resistant Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23, p 3043–3050
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon, Effect of Strain-Rate upon the Plastic Flow of Steel, J. Appl. Phys., 1944, 15, p 22–27
Y.C. Lin, Y.C. Xia, X.M. Chen, and M.S. Chen, Constitutive Descriptions for Hot Compressed 2124-T851 Aluminum Alloy over a Wide Range of Temperature and Strain Rate, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, 50, p 227–233
H. Zhou, Q.D. Wang, B. Ye, and W. Guo, Hot Deformation and Processing Maps of As-Extruded Mg-9.8Gd-2.7Y-0.4Zr Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 576, p 101–107
H.Y. Wu, J.C. Yang, F.J. Zhu, and H.C. Liu, Hot Deformation Characteristics of As-Cast and Homogenized AZ61 Mg Alloys Under Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 550, p 273–278
C. Manuel, M.B. Jesús, R. Ignacio, P. Félix, and A. Oscar, The Effect of Heterogeneous Deformation on the Hot Deformation of WE54 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 58, p 30–35
S. Mandal, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, and K.P.N. Murthy, Artificial Neural Network Modeling to Evaluate and Predict the Deformation Behavior of Stainless Steel Type AISI, 304L During Hot Torsion, Appl. Soft Comput., 2009, 9, p 237–244
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, Y.J. Wang, X.Q. An, L.P. Zhong, A.T. Tang, and F.S. Pan, Dynamic recrystallization Behavior and Hot Workability of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr-0.9Y Alloy by Using Hot Compression Test, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 357–365
S.I. Kim and Y.C. Yoo, Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of AISI, 304 Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 311, p 108–113
F. Chen, Z.S. Cui, and S.J. Chen, Recrystallization of 30Cr2Ni4MoV Ultrasuper-Critical Rotor Steel During Hot Deformation. Part I: Dynamic Recrystallization, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 5073–5080
E.I. Poliak and J.J. Jonas, A One-Parameter Approach to Determining the Critical Conditions for the Initiation of Dynamic Recrystallization, Acta Mater., 1996, 44, p 127–136
H.Z. Li, H.J. Wang, Z. Li, C.M. Liu, and H.T. Liu, Flow Behavior and Processing Map of As-Cast Mg-10Gd-48Y-2Zn-0.6Zr alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 528, p 154–160
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Chong Qing Science and Technology talent training plan under Grant No. cstc2014kjrc-qnrc50004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Xia, X. Modeling High Temperature Deformation Behavior of Large-Scaled Mg-Al-Zn Magnesium Alloy Fabricated by Semi-continuous Casting. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 3539–3548 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1640-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1640-9