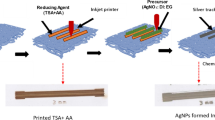
Abstract
The synthesis of silver nanoparticles for silver ink formation has attracted broad interest in the electronic part printing and semiconductor chip industry due to the extraordinary electrical and mechanical properties of these materials. The preparation of silver nanoparticles through a physical or chemical reduction process is the most common methodology applied to obtain nanoparticles with the required size, shape and surface morphology. The chemical solution or solvent carrier applied for silver ink formulation must be applied simultaneously with the direct writing technique to produce the desired adherence, viscosity, and reliable performance. This review paper discusses the details concerning the past and recent advancement of the synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles and silver ink formation. A review on the advantages of various sintering techniques, which aim to achieve the electrical and mechanical properties of the required printed structure, is also included. A brief summary concerning the recent challenges and improvement approaches is presented at the end of this review.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.Z. Cao, Nanostructures and Nanomaterials, Imperial College Press, London, 2004
K. Chang, Tiny is Beautiful: Translating “Nano” into Practical, The New York Times, 2005
R. Das, S.S. Nath, D. Chakdar, G. Gope, and R. Bhattacharjee, Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization, J. Nanotechnol., 2009, doi:10.2240/azojono0129
J.F. Dijksman, P.C. Duineveld, M.J.J. Hack, A. Pierik, J. Rensen, J.-E. Rubingh, I. Schram, and M.M. Vernhout, Precision Ink Jet Printing of Polymer Light Emitting Displays, J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, p 511–522
H. Kobayashi, S. Kanbe, and S. Seki, A Novel RGB Multicolor Light-Emitting Polymer Display, Synth. Met., 2000, 111, p 125–128
Y. Yoshioka and G.E. Jabbour, Desktop Inkjet Printer as a Tool to Print Conducting Polymers, Synth. Met, 2006, 156, p 779–783
K.E. Paul, W.S. Wong, S.E. Ready, and R.A. Street, Additive Jet Printing of Polymer Thin-Film Transistor, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83, p 2070–2702
D.C. Huang, F. Liao, S. Molesa, D. Redinger, and V. Subramanian, Plastic Compatible Low Resistance Printable Gold Nanoparticle Conductors for Flexible Electronics, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(7), p G412–G417
B. Chen, T. Cui, Y. Liu, and K. Varahramyan, All Polymer RC Filter Circuits Fabricated with Inkjet Printing Technology, Solid-State Electron, 2003, 47, p 841–847
C.N. Hoth, S.A. Choulis, P. Schilinsky, and C.J. Brabec, High Photovoltaic Performance of Inkjet Printed Polymer: Fullerene Blends, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, p 3973
E. Tekin, P.J. Smith, and U.S. Schubert, Inkjet Printing as a Deposition and Patterning Tool for Polymers and Inorganic Particles, Soft Matter, 2008, 4, p 703–713
K.S. Chou and C.Y. Ren, Synthesis of Nanosized Silver Particles by Chemical, Reduction Method, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2000, 64, p 241–246
K.K. Caswell, C.M. Bender, and C.J. Murphy, Seedless, Surfactantless Wet Chemical Synthesis of Silver Nanowires, Nano Lett., 2003, 3, p 667–669
Z.S. Pillai and P.V. Kamat, What Factors Control the Size and Shape of Silver Nanoparticles in the Citrate Ion Reduction Method, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, p 945–995
I. Pastoriza-Santos and L.M. Liz-Marzan, Synthesis of Silver Nanoprisms in DMF, Nano Lett., 2002, 2, p 903–905
L.K. Kurihara, G.M. Chow, and P.E. Schoen, Nanocrystalline Metallic Powders and Films Produced by the Polyol Method, NanaShuchued Mater., 1995, 5, p 607–613
I. Sondi, D.V. Goia, and E. Matijevic, Preparation of Highly Concentrated Stable Dispersions of Uniform Silver Nanoparticles, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, 260, p 75–81
Y. Yin, Z.Y. Li, Z. Zhong, B. Gates, Y. Xia, and S. Venkateswaran, Synthesis and Characterization of Stable Aqueous Dispersions of Silver Nanoparticles through the Tollens Process, J. Mater. Chem., 2002, 12, p 522–527
Y. Sun and Y. Xia, Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles, Science, 2002, 298, p 2176–2179
S. Komarneni, D. Li, B. Newalkar, H. Katsuki, and A.S. Bhalla, Microwave-Polyol Process for Pt and Ag Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2002, 18, p 5959–5962
F. Fieret, J.P. Lagier, and M. Figlarz, Preparing Monodisperse Metal Powders in Micrometer and Submicrometer Sizes by the Poyol Process, MRS Bull., 1989, 14(12), p 29–34
S. Puvvada, S. Baral, G.M. Chow, S.B. Qudri, and B.R. Ratna, Synthesis of Palladium Metal Nanoparticles in the Bicontinuous Cubic Phase of Glycerol Monooleate, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, p 2135–2136
D.G. Duff, A. Baiker, I. Gamson, and P.P. Edwards, A new hydrosol of gold clusters. A. A comparison of some different measurement techniques, Langmuir, 1993, 9, p 2310–2317
S. Ayyappan, R. Srinivasa Gopalan, G.N. Subbanna, and C.N.R. Rao, Nanoparticles of Ag, Au, Pd, and Cu Produced by Alcohol Reduction of the Salts, J. Mater. Res., 1997, 12(2), p 398–401
I. Washio, Y. Xiong, Y. Yin, and Y. Xia, Reduction by the End Groups of Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone): A New and Versatile Route to the Kinetically Controlled Synthesis of Ag Triangular Nanoplates, Adv. Mater, 2006, 18, p 1745–1749
A. Gautam, P. Tripathy, and S. Ram, Microstructure, Topology and X-ray Diffraction in Ag-Metal Reinforced Polymer of Polyvinyl Alcohol of Thin Laminates, J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41, p 3007–3016
R. Janardhanan, M. Karuppaiah, N. Hebalkar, and T.N. Rao, Synthesis and Surface Chemistry of Nano Silver Particles, Polyhedron, 2009, 28(12), p 2522–2530
J. Steinfeld, Ed., Laser-Induced Chemical Processes, Plenum Press, New York, 1981
B. Braren, J.J. Dubowski, and D.P. Norton, Ed., Laser Ablation in Material Processing: Fundamental and Applications, MRS Symposium Proceedings, Pittsburgh, 1993
D. Bauerle, Laser Processing and Chemistry, 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1996
J.C. Miller, R.F. Haglund, Eds., Laser Ablation and Desorption, Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences, Academic Press, San Diego, 1998
J. Neddersen, G. Chumanov, and T.M. Cotton, Laser Ablation of Metals: A New Method for Preparing SERS Active Colloids, Appl. Spectrosc., 1993, 47, p 1959–2177
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, and H. Sawabe, Formation and Size Control of Silver Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Solution, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, p 9111–9117
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, and H. Sawabe, Structure and Stability of Silver Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution Produced by Laser Ablation, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, p 8333–8337
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, and H. Sawabe, Formation of Gold Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Solution of Surfactant, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, p 5114–5120
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, and T. Kondow, Dissociation and Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles Under Laser Irradiation, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, p 9050–9056
S. Kim, W. S. Lee, J. Lee, I. Park, Direct Micro/Nano Metal Patterning Based on Two-Step Transfer Printing of Ionic Metal Nano-Ink. Nanotechnology, 2012, 23. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/28/285301
W.W. Wits, A. Sridhar, Inkjet Printing of 3D Metallic Silver Complex Microstructures. International Conference on Competitive Manufacturing, 2010
P.J. Smith, D.-Y. Shin, J.E. Stringer, N. Reis, and B. Derby, Direct Ink-Jet Printing and Low Temperature Conversion of Conductive Silver Patterns, J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(13), p 4153–4158
A.L. Dearden, P.J. Smith, D.-Y. Shin, N. Reis, B. Derby, and P. O’Brien, A Low Curing Temperature Silver Ink for Use in Ink-Jet Printing and Subsequent Production of Conductive Tracks, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2004, 26, p 315–318
A. Sridhar, J. Reiding, H. Adelaar, F. Achterhoek, D.J. Van Dijk, and R. Akkerman, Inkjet-Printing- and Electroless-Plating Based Fabrication of RF Circuit Structures on High-Frequency Substrates, J. Micromech. Microeng., 2009, 19, p 085020
Zheng.Chun. Liu, Su. Yi, and Kody. Varahramyan, Inkjet-Printed Silver Conductors Using Silver Nitrate Ink and Their Electrical Contacts with Conducting Polymers, Thin Solid Films, 2005, 478(1–2), p 275–279
J. Perelaer, C.E. Hendriks, A.W.M. de Laat, and U.S. Schubert, One-Step Inkjet Printing of Conductive Silver Tracks on Polymer Substrates, Nanotechnology, 2009, 20, p 165303
S. Brett Walker, and J.A. Lewis, Reactive Silver Inks for Patterning High-Conductivity Features at Mild Temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 134, p 1419–1421
C.J. Curtis, D.L. Schulz, A. Miedaner, J. Alleman, T. Rivkin, J.D. Perkin, and D.S. Ginley, Spray and Inkjet Printing of Hybrid Nanoparticle-Metal-Organic Inks for Ag and Cu Metallizations. Mater. Res. Proc., 2001, 676, p 861
D.S. Ginley, C.J. Curtis, A. Miedaner, M.F.A.M. Van Hest, T. Kaydanova, Metal Inks. Patent Number: US20080003364A1, 2008
P. Buffat and J.-P. Borel, Size Effect on the Melting Temperature of Gold Particle, Phys. Rev. A, 1976, 13, p 2287–2298
G.L. Allen, R.A. Bayles, W.W. Gile, and W.A. Jesser, Small Particle Melting of Pure Metals, Thin Solid Films, 1986, 144, p 297–308
W.H. Qi and M.P. Wang, Size Effect on the Cohesive Energy of Nanoparticle, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2002, 21, p 1743
K.K. Nanda, S.N. Sahu, and S.N. Behera, Liquid-Drop Model for the Size-Dependent Melting of Low-Dimensional Systems, Phys. Rev. A, 2002, 66, p 013208
J. Sun and S.L. Simon, The Melting Behavior of Aluminum Nanoparticles, Thermochim. Acta, 2007, 463, p 32
M.-S. Elpidio, G.-P. Jesús, N.-T. María, Q.-G. Cristina, C.-J. Martha, L.-S. Francisco, G.-H. Jesús, and R. Facundo, Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Albumin as a Reducing Agent, Mater. Sci. Appl., 2011, 2, p 578–581
A.J. Lovinger, Development of Electrical Conduction in Silver-Filled Epoxy Adhesives, J. Adhes., 1979, 10, p 1–15
J.R. Greer and R.A. Street, Thermal Cure Effects on Electrical Performance of Nanoparticle Silver Inks, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 6345–6349
J. Perelaer, A.W.M. de Laat, C.E. Hendriks, U.S. Schubert, Inkjet-Printed Silver Tracks: Low Temperature Curing and Thermal Stability Investigation. J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18, p. 3209–3215
H. Wijshoff, The Dynamics of the Piezo Inkjet Printhead Operation, Phys. Rep., 2010, 491, p 77–177
K.-S. Chou, K.-C. Huang, and H.-H. Lee, Fabrication and Sintering Effect on the Morphologies and Conductivity of Nano-Ag Particle Films by the Spin Coating Method, Nanotechnology, 2005, 16, p 779–784
K. Yamasaki, K. Maekawa, T. Niizeki, M. Mita, Y. Matsuba, N. Terada, H. Saito, Temperature Soak Reliability of Laser-Sintered Ag Pads for Wire Bonding. 13th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, 2011
K. Maekawa, K. Yamasaki, T. Niizeki, M. Mita, Y. Matsuba, N. Terada, H. Saito, High-Speed Laser Plating on Cu Lead Frame Using Ag Nanoparticles, Electronic Components and Technology Conference, 2010
G. Xie, O. Ohashi, N. Yamaguchi, and A. Wang, Effect of Surface Oxide Films on the Properties of Pulse Electric-Current Sintered Metal Powders, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34A, p 2655–2661
Z. Radivojevic, K. Andersson, K. Hashizume, M. Heino, M. Mantysalo, P. Mansikkamaki, Y. Matsuba, N. Terada, Optimised Curing of Silver Ink Jet Based Printed Traces, Proceedings of 12th Intl. Workshop on Thermal investigations of ICs, 2006, p. 133-138, ISBN 2-916187-04-9
J. Perelaer, B.-J. de Gans, and U.S. Schubert, Ink-Jet Printing and Microwave Sintering of Conductive Silver Tracks, Adv. Mater., 2006, 18, p 2101–2104
H.-S. Kim, S.R. Dhage, D.-E. Shim, and H.T. Hahn, Intense Pulsed Light Sintering of Copper Nanoink for Printed Electronics, Appl. Phys. A, 2009, 97, p 791–798
I. Reinhold, C.E. Hendriks, R. Eckardt, J.M. Kranenburg, J. Perelaer, R.R. Baumann, and U.S. Schubert, Argon Plasma Sintering of Inkjet Printed Silver Tracks on Polymer Substrates, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, p 3384–3388
M.J. Renn, WO Patent Number: 2007/070868 A2, 2007
L.H. Liang, C.M. Shen, S.X. Du, W.M. Liu, X.C. Xie, and H.J. Gao, Increase in Thermal Stability Induced by Organic Coatings on Nanoparticles, Phys. Rev B., 2004, 70, p 205419
J.F. Mei, Formulation and Processing of Conductive Inks for Inkjet Printing of Electrical Components, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, 2004
S. Magdassi, M. Grouchko, and A. Kamyshny, Conductive Inkjet Inks for Plastic Electronics: Air Stable Copper Nanoparticles and Room Temperature Sintering. NIP25 and Digital Fabrication, Tech. Progr. Proc., 2009, 2009, p 611–613
R.J. Jouet, J.R. Carney, R.H. Granholm, H.W. Sandusky, and A.D. Warren, Preparation and Reactivity Analysis of Novel Perfluoroalkyl Coated Aluminium Nanocomposites, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22, p 422–429
M. Grouchko, A. Kamyshny, and S. Magdassi, Formation of Air-Stable Copper-Silver Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Inkjet Printing, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, p 3057–3062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, C.Y., Cheong, C.F., Mandeep, J.S. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Inks: Review on the Past and Recent Technology Roadmaps. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 3541–3550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1166-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1166-6