Abstract
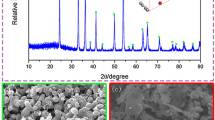
A controllable and facile process for the preparation of Nb3Sn intermetallic compound nanopowders using NbCl5 and SnCl2 vapors reduced by hydrogen has been developed. The vaporizing rates of the two chlorides are controlled by measuring their mass loss as a function of carrier gas (argon) flow rate at certain vaporization temperatures, respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicate that hydrogenous Nb3Sn products are obtained under the vaporizing rate of 0.155 g min−1 for NbCl5 and 0.036 g min−1 for SnCl2 with the hydrogen flow rate of 2100 ml min−1 at 1273 K (1000 °C). Results of semi-quantitative analysis by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) demonstrate that the atomic ratio of Nb to Sn in the as-synthesized products is 3.48:1, and the content of (Nb + Sn) is taken up to 89.61 wt pct from the total weight of the products. The products can be purified by vacuum heat treatment. Images of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) show that the products are homogenous particles with a mean diameter of 31 nm. In addition, the reaction ratio of the chlorides and the powder yield are controllable by hydrogen flow rate.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] A. Godeke: Supercond. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 19, pp. R68─R80.
[2] F. Liu, H. Liu, S. Liu, B. Liu, L. Lei, C. Chen, and Y. Wu: Fusion Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 66, pp. 208─13.
[3] E. Barzi, D. Turrioni, and A.V. Zlobin: IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., 2014, vol. 24, pp. 6000808.
[4] C. Senatore and R. Flukiger: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, vol. 102, pp. 012601.
[5] P.X. Zhang, K. Zhang, J.H. Guo, J.J. Jia, X.D. Tang, J.F. Li, J.W. Liu, S.J. Du, X.H. Liu, and Y. Feng: IEEE T. Appl. Supercond., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 4802704.
[6] I. Pong, L.R. Oberli, and L. Bottura: Supercond. Sci. Tech., 2013, vol. 26, pp. 105002.
[7] S. Ochiai and L. Osamura: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 2425─33.
[8] X. Xu, M. Sumption, X. Peng, and E.W. Collings: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, vol. 104, pp. 082602.
[9] M.J.R. Sandim, D. Stamopoulos, E. Aristomenopoulou, S. Zaefferer, D. Raabe, S. Awaji, and K. Watanabe: Physics Procedia., 2012, vol. 36, pp. 1504─09.
[10] M. López, J.A. Jiménez, K. Ramam, and R.V. Mangalaraja: J. Alloy Compd., 2014, vol. 612, pp. 215─20.
[11] R.O. Suzuki, H. Nagai, T. Oishi, and K. Ono: J. Mater. Sci., 1987, vol. 22, pp. 1999─2005.
[12] Q. Xu, C. Schwandt, and D.J. Fray: Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, vol. 160, pp. 1131─35.
[13] K.Y. Park, H.J. Kim, and Y.J. Suh: Powder Technol., 2007, vol. 172, pp. 144─48.
[14] M.T. Swihart: Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, vol. 8, pp. 127─33.
[15] J. Lu, M. Hu, Y. Tian, C. Guo, S. Guo, and Q. Liu: J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 914─18.
[16] A. Govindaraj, S.R.C. Vivekchand, and C.N.R. Rao: J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2007, vol. 7, pp. 1695─702.
[17] Y. Xing and D.E. Rosner: J. Nanopart. Res., 1999, vol. 1, pp. 277─91.
[18] T. Thurakitseree, E. Einarsson, R. Xiang, P. Zhao, S. Aikawa, S. Chiashi, J. Shiomi, and S. Maruyama: J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2012, vol. 12, pp. 370─76.
[19] D. Su, M. Ren, X.A. Li, and W. Huang: J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 6471─84.
[20] A. Kato, T. Watari, and T. Nakamatsu: J. Less Common Met., 1982, vol. 83, pp. 227─34.
[21] J.J. Hanak, K. Strater, and G.W. Cullen: RCA Rev., 1964, vol. 25, pp. 342─65.
[22] H. Yorucu and F.R. Sale: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1982, vol. 13B, pp. 625─31.
[23] Z.M. Cao, J. Zhu, H.Z. Zhu, and Z.Y. Qiao: Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2008, vol. 32, pp. 478─81. [in Chinese].
[24] S.E. Pratsinis and S. Vemury: Powder Technol., 1996, vol. 88, pp. 267─73.
[25] M. Bakhshi and B. Mobasher: Cem. Concr. Compos., 2011, vol. 33, pp. 474─84.
[26] Y. Qin and J.E. Hiller: Mater. Struct., 2014, vol. 47, pp. 351─65.
[27] A.C. Garrabrants and D.S. Kosson: Drying Technol., 2003, vol. 21, pp. 775─805.
C.Z. Chen: Non-ferrous Metal Smelting and Casting, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2003, p. 19. [in Chinese].
[29] A.V. Skripov, M.Y. Belyaev, and V.E. Arkhipov: J. Alloy Compd., 1995, vol. 229, pp. 248─53.
[30] M. Alam, W. Yang, K. Mohanarangam, G. Brooks, and Y.S. Morsi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1155─65.
[31] C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, and K.W. Eliceiri: Nat. Methods, 2012, vol. 9, pp. 671─75.
[32] Y.J. Suh, H.D. Jang, H.K. Chang, D.W. Hwang, and H.C. Kim: Mater. Res. Bull., 2005, vol. 40, pp. 2100─09.
[33] J. Zhu, K. Huang, J. Hou, and H. Zhu: T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2014, vol. 24, pp. 3987─93.
Acknowledgment
The financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC; No. 51472027) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 24, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Jiao, S., Zhang, L. et al. Facile Synthesis of Nb3Sn Via a Hydrogen Reduction Process. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 286–293 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0812-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0812-9