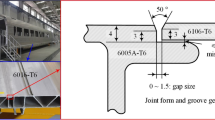
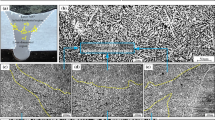
Abstract
A7N01P-T4 aluminum alloy is widely used in some important welded components of high-speed trains. The hybrid laser-metal inert gas (MIG) welding process was studied to solve problems associated with the MIG welding process, such as low welding efficiency, high residual stress and deformation, and serious loss of strength. A high-speed camera, a voltage and current collection system, and NI DAQ were used to acquire arc profiles, welding voltage, and welding current simultaneously. Thermal cycle tests were carried out. Residual stresses induced by the welding process and fatigue strength of the joint were investigated. Large-size fatigue specimens were used in fatigue tests. The results show that the energy of the hybrid welding process is focused, and the power density of hybrid welding process is intense. The heat input per unit of the hybrid welding process is only half of that of the MIG welding process. Compared with the MIG welded joint, the overall residual stress level of the hybrid-welded joint is lower. The peak longitudinal stress of the hybrid-welded joint is reduced by 20 pct. The fatigue strength of hybrid joints is 14 pct higher than that of MIG-welded joints. Narrow weld and HAZ, weak softening behavior, and low residual stress level are the causes of the improvement of fatigue strength.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Gou, M. Zhang, H. Chen, J. Chen, P. Li, and Y.P. Yang: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 85, pp. 309-17.
J.M. Sun, X.Z. Liu, Y.G. Tong, and D. Deng: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 63, pp. 519-30.
S.H. Yan, Y. Nie, Z.T. Zhu, H. Chen, G.Q. Gou, J.P. Yu, and G.G. Wang: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, vol. 298, pp. 12-8.
S.H. Yan, H. Chen, Z.T. Zhu, and G.Q. Gou: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 61, pp. 160-7.
P. Colegrove, C. Ikeagu, A. Thistlethwaite, S. Williams, T. Nagy, W. Suder, A. Steuwer, and T. Pirling: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2009, vol. 14, pp. 717-25.
M.N. James, P.J. Webster, D.J. Hughes, Z. Chen, N. Ratel, S.P. Ting, G. Bruno, and A. Steuwer: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 427, pp. 16-26.
W. Liang, H. Murakawa, and D. Deng: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 67, pp. 303-12.
M.N. James, D.J. Hughes, D.G. Hattingh, G. Mills, and P.J. Webster: Int. J. Fatigue, 2009, vol. 31, pp. 28-40.
H.S. Bang, H.S. Bang, Y.C. Kim, and S.M. Joo: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 49, pp. 217-21.
N.S. Ma, L.Q. Li, H. Huang, S. Chang, and H. Murakawa: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 220, pp. 36-45.
C. Morgenstern, C.M. Sonsino, A. Hobbacher, and F. Sorbo: Int. J. Fatigue, 2006, vol. 28, pp. 881-90.
F. Lefebvre and I. Sinclair: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 407, pp. 265-72.
B. Hu and I.M. Richardson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 459, pp. 94-100.
C. Zhang, M. Gao, G. Li, C. Chen, and X.Y. Zeng: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2013, vol. 18, pp. 703-10.
Wang, H. Chen, Z. Zhu, P. Qiu, and Y. Cui: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016.
A.L. Biro, B.F. Chenelle, and D.A. Lados: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 1622-37.
G. Pouget and A.P. Reynolds: Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, vol. 30, pp. 463-72.
L. Fratini, S. Pasta, and A.P. Reynolds: Int. J. Fatigue, 2009, vol. 31, pp. 495-500.
G. Bussu and P.E. Irving: Int. J. Fatigue, 2003, vol. 25, pp. 77-88.
C.D.M. Liljedahl, O. Zanellato, M.E. Fitzpatrick, J. Lin, and L. Edwards: Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, vol. 32, pp. 735-43.
M.B. Prime, T. Gnaupel-Herold, J.A. Baumann, R.J. Lederich, D.M. Bowden, and R.J. Sebring: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 4013-21.
S. Ganguly, V. Stelmukh, L. Edwards, and M.E. Fitzpatrick: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 491, pp. 248-57.
C.D.M. Liljedahl, J. Brouard, O. Zanellato, J. Lin, M.L. Tan, S. Ganguly, P.E. Irving, M.E. Fitzpatrick, X. Zhang, and L. Edwards: Int. J. Fatigue, 2009, vol. 31, pp. 1081-8.
Y.E. Ma, P. Staron, T. Fischer, and P.E. Irving: Int. J. Fatigue, 2011, vol. 33, pp. 1417-25.
B. Ribic, T.A. Palmer, and T. DebRoy: Int. Mater. Rev., 2009, vol. 54, pp. 223-44.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy. 2nd ed., Wiley, New York, NY, 2003, pp. 13-126.
H.S. Bang, H.S. Bang, Y.C. Kim, and I.H. Oh: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 2328-33.
X. Zhang, B. Liu, Y. Liu, H. Li, and H. Li: Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2007, vol. 17, pp. 1561-6.
S.K. Khanna, X. Long, W.D. Porter, H. Wang, C.K. Liu, M. Radovic, and E. Lara-Curzio: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2005, vol. 10, pp. 82-7.
K. Deplus, A. Simar, W. Van Haver, and B. de Meester: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Techol., 2011, vol. 56, pp. 493-504.
A. Bastier, M.H. Maitournam, F. Roger, and K. Dang Van: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 200, pp. 25-37.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2014CB660807).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 2, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Chen, H., Qiu, P. et al. Residual Stress and Fatigue Strength of Hybrid Laser-MIG-Welded A7N01P-T4. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 591–601 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0782-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0782-y