Abstract
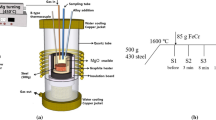
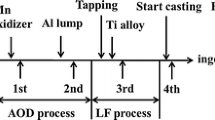
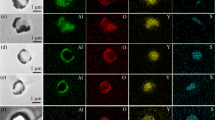
In this article, the addition of dispersoid titanium oxide inclusions into liquid steel, the effect of additions on the inclusions found in the steel and on grain refinement, and acicular ferrite formation were studied. Different TiO2-containing materials and addition procedures into liquid steel were tested in experimental heats to obtain inclusions that promote grain refinement and acicular ferrite formation in C-Mn-Cr steel. Different additives with metallic Ti and TiO2 were added into the steel melt just before casting or into the mold during casting to create Ti-containing inclusions. The aluminum content in steel was lowered by an addition of iron oxide. The samples taken from steel melts and ingots were studied with a scanning electron microscope to find inclusions and to analyze them. Thermodynamic calculations showed that the Al content should be low (<50 ppm) to obtain Ti oxide dominating inclusions, whereas Al2O3 were formed at higher Al contents. When TiO2 was added late before casting, the oxide inclusions were Ti oxides and were mixed with Ti, Al, and Mn oxides. Small inclusions around 1 μm were detected in the samples with TiO x or TiN as the main component. It could be concluded that the additions resulted in a clearly higher number and in a smaller size of TiO x inclusions than just by adding metallic Ti. Selected samples were brought for subsequent hot rolling and heat-treatment experiments to find out the grain-refining effect and the eventual formation of acicular ferrite. Grain refinement was observed clearly, but the presence of acicular ferrite could not be confirmed definitely.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.J. Jackson: Iron Steel, 1972, p. 163.
G. Tither and Z. Shouhua: HSLA Steel: Processing, Properties and Applications, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Warrendale, PA, 1992, p. 3.
C. Zener: J. Appl. Phys., 1949, vol. 20, pp. 950-53.
B.L. Bramfitt: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1987-95.
H. Suito, H. Ohta, and S. Morioka: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 840-46.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, IOM Communications Ltd., London, UK, 2001, pp. 237-76.
J.S. Byun, J.H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, and D.N. Lee: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1593-1606
S. Aihara, G. Shgesato, M. Sugyama, and F. Lemori: Nippon Steel Technical Report, no. 91, 2005, pp. 43-48.
J.-H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, S.H. Chung, J.-D. Shim, and D.N. Lee: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 2751-60.
J.-H. Shim, J.-S. Byun, Y.W. Cho, Y.J. Oh, J.-D. Shim, and D.N. Lee: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 49-54.
J.-H. Shim, Y.J. Oh, J.Y. Suh, Y.W. Cho, J.-D. Shim, J.S. Byun, and D.N. Lee: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 2115-22.
T.-K. Lee, H.J. Kim, B.Y. Kang, and S.K. Hwang: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 1260-68.
D.S. Sarma, A.V. Karasev, and P.G. Jönsson: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 1063-74.
P. Krauklis, F.J. Barbaro, and K.E. Easterling: Proc. Int. Conf. on Martensitic Transformations, Montery Institute for Advanced Studies, Montery, CA, 1992, p. 439.
J.L. Lee and Y.T. Pan: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 1027-33.
J.L. Lee: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 3291-98.
G. Thewlis: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 110-25.
D. Lou and L. Holappa: Microstructure and Property Control of Steels with Inclusions, SINTEF Materials Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2001.
Ø. Grong, L. Kolbeisen, C. van der Eijk, and G. Tranell: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 824-31.
C. Van Der Eijk, O. Grong, F. Haakonsen, L. Kolbeinsen, and G. Tranell: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 1046-50.
H.-H. Jin, J.-H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, and H.-C. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1111-13.
H. Goto, K. Miyazawa, W. Yamada, and K. Tanaka: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 708-14
N. Kikuchi, S. Nabeshima, Y. Kishimoto, T. Matsushita, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 1255-64.
N. Kikuchi, S. Nabeshima, Y. Kishimoto, Y. Ishiguro, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 4, pp. 1036-45.
N. Kikuchi, S. Nabeshima, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol.48, pp. 934-43.
J.M. Gregg and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 739-48.
S. Hossein Nedjad and A. Farzaneh: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 937-40.
C.W. Bale, P. Chartrand, S.A. Degterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, R. Ben Mahfoud, J. Melanqon, A.D. Pelton, and S. Petersen: CALPHAD, 2002, vol. 26, pp. 189-228.
F. Ruby-Mayer, J. Lehmann, and H. Gaye: Scand. J. Metall., 2000, vol. 29, pp. 206-12.
I.-H. Jung, G. Eriksson, P. Wu, and A. Pelton: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 1290-97.
H. Matsuura, C. Wang, G. Wen, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 1265-74.
M. Mizumo, I. Tanaka, and H. Adachi: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 1637-45.
J.M. Gregg and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 3321-30.
X. Zhuo, X. Wang, W. Wang, and H.-G. Lee: J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 2007, vol. 14, pp. 14-21.
J.L. Lee and Y.T. Pan: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1399-408.
Acknowledgments
The work was carried out with a financial grant from the Research Fund for Coal and Steel of the European Community, which is gratefully acknowledged. Rautaruukki Raahe Steelworks are indebted for chemical analyses of steel samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 30, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiviö, M., Holappa, L. & Iung, T. Addition of Dispersoid Titanium Oxide Inclusions in Steel and Their Influence on Grain Refinement. Metall Mater Trans B 41, 1194–1204 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9416-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9416-y