Abstract
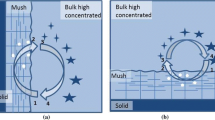
In this article, we investigate the effects of laminar natural convection on directional solidification of binary fluids with noneutectic compositions when cooled and solidified from the top. The study is performed using aqueous ammonium chloride solution as the model fluid. In the first case, the initial concentration of ammonium chloride is less than the eutectic composition, leading to an aiding of the double-diffusive convection. In this case, solidification leads to the formation of a diffused matrix of dendritic crystals (mushy region) separating the pure solid and liquid regions. The mushy interface is characterized by a waviness, which is caused by a Rayleigh-Benard type of cellular motion in the liquid region. The cellular motions, which are caused by thermal and solutal buoyancy, cease once the thickness of the liquid layer falls below a critical value. The second case leads to a unique situation, in which crystals nucleated at the top wall of the cavity detach and descend through the lighter bulk fluid and, finally, settle at the floor of the cavity. In both the aforementioned cases, the features of convective transport are visualized using a sheet of laser light scattered through neutrally buoyant glass particles seeded in the solution. Numerical simulations are also performed for the first case, and the agreement with experimental results is found to be good.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a P , a P 0 :
-
coefficients of the discretization equation
- c p :
-
specific heat
- C :
-
species composition
- D :
-
mass diffusion coefficient
- f :
-
mass fraction
- F −1 :
-
inverse of latent heat function
- g :
-
acceleration due to gravity
- h :
-
sensible enthalpy
- H(t):
-
instantaneous space-averaged liquid layer height at time t
- ΔH :
-
latent enthalpy content of a control volume
- ΔV :
-
volume of a computational cell
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- k P :
-
partition coefficient
- K :
-
permeability
- l ref :
-
diffusion length scale in the liquid
- L :
-
latent heat of fusion
- p :
-
pressure
- Pe:
-
Peclet number
- r :
-
interfacial area concentration
- R :
-
local crystal growth rate
- S :
-
source term
- T :
-
temperature
- t :
-
time
- u :
-
x component of velocity
- v :
-
y component of velocity
- u :
-
continuum velocity vector
- x, y :
-
coordinates
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity
- β T :
-
thermal expansion coefficient
- β C :
-
solutal expansion coefficient
- δ :
-
solutal boundary layer thickness
- χ :
-
volume fraction
- λ :
-
relaxation factor
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity
- ρ :
-
density
- cold:
-
cold wall
- 0, i :
-
initial
- E :
-
eutectic
- hot:
-
hot wall
- l :
-
liquid phase
- L :
-
liquidus
- m :
-
evaluated at melting point
- macro:
-
macroscopic
- n :
-
iteration level
- P :
-
related to the grid point “P”
- s :
-
solid phase
References
H.E. Huppert: J. Fluid Mech., 1990, vol. 212, pp. 209–40.
J.S. Turner, H.E. Huppert, and R.S.J. Sparks: J. Petrol., 1986, vol. 27, pp. 397–437.
G. Brandeis and C. Jaupart: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1986, vol. 77, pp. 345–61.
R.C. Kerr, A.W. Woods, M.G. Worster, and H.E. Huppert: J. Fluid Mech., 1990, vol. 216, pp. 323–42.
R.C. Kerr, A.W. Woods, M.G. Worster, and H.E. Huppert: J. Fluid Mech., 1990, vol. 217, pp. 331–48.
R.C. Kerr, A.W. Woods, M.G. Worster, and H.E. Huppert: J. Fluid Mech., 1990, vol. 218, pp. 337–54.
S.H. Davis, U. Muller, and C. Dietsche: J. Fluid Mech., 1984, vol. 144, pp. 133–51.
W.Z. Cao and D. Poulikakos: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1989, vol. 33, pp. 427–34.
T. Motegi and A. Ohno: J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1980, vol. 44, pp. 359–66.
P. Kumar, S. Chakraborty, K. Srininvasan, and P. Dutta: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 605–12.
W.D. Bennon and F.P. Incropera: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1987, vol. 30, pp. 2161–70.
V.R. Voller, A.D. Brent, and C. Prakash: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1989, vol. 34, pp. 1717–32.
D. Morvan, M.El Ganaoui, and P. Bontoux: Int J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1998, vol. 42, pp. 573–79.
M.C. Flemings: Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1974.
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and M.A. Chopra: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1661–69.
J.A. Burton, R. Prim, and W. Slichter: Theoretical. J. Chem. Phys., 1953, vol. 21, pp. 1987–91.
J. Ni, R.J. Feller, and C. Beckermann: in Modeling of Casting, Welding and Advanced Solidification Processes V, M. Rappaz, M.R. Ozgu, and K.W. Mahin, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1991, pp. 675–82.
S.V. Patankar: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere McGraw-Hill, Washington, D.C., 1980.
A.D. Brent, V.R. Voller, and K.J. Reid: Num. Heat Transfer, 1988, vol. 13, pp. 297–318.
S. Chakraborty and P. Dutta: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 562–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Srinivasan, K., Dutta, P. et al. Studies on transport phenomena during directional solidification of a noneutectic binary solution cooled from the top. Metall Mater Trans B 34, 899–909 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-003-0096-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-003-0096-8