Abstract
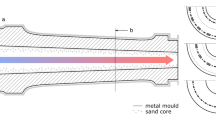
The objective of the present study was to investigate the inhomogeneity of microstructure and damping capacity of a FC25 disc-brake rotor made of gray cast iron (GCI) and their interrelationship. The rotor had inhomogeneous microstructure due to different cooling rates caused by the position of inlets in a mold during casting. The volume fraction and size of graphite decreased with increasing cooling rate. A maximum deviation of the volume fraction of graphite within the rotor was approximately 2 pct, whereas that of the total perimeter of graphite per unit area was approximately 33 pct. Damping capacities measured at the first vibrational mode of both the real rotor and cantilever specimens, which were taken from four different regions within the rotor, depended on the location within the rotor. This result indicates that the damping capacity of the rotor is influenced by the inhomogeneous microstructure; particularly, the damping capacity was proportional to the total perimeter of graphite per unit area. Therefore, it was concluded that the damping of the GCI rotor used in the present study occurs primarily by the viscous or plastic flow at the interphase boundaries between the pearlite matrix and graphite particles at least at the frequencies of below 1140 Hz.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.M. Kinkaid, O.M. O’Reilly, and P. Papadopoulos: J. Sound Vib., 2003, vol. 267, pp. 105-166.
R.D. Adams: J. Sound Vib., 1972, vol. 23, pp. 199-216.
Y.-K. Lee, J.-H. Jun, and C.-S. Choi: Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 35, pp. 825-830.
Y. Sutou, T. Omori, N. Koeda, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 438-440, pp. 743-746.
M.-H. Tsai, M.-S. Chen, L.-H. Lin, M.-H. Lin, C.-Z. Wu, K.-L. Ou, and C.-H. Yu: J. Alloys Compds., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 813-819.
M.H. Cho, S.J. Kim, R.H. Basch, J.W. Fash, and H. Jang: Tribol. Int., 2003, vol. 36, pp. 537-545.
A. Visnapuu, R.W. Nash, and P.C. Turner: Report No. RI9068, United States Bureau of Mines, Washington DC, USA, January 1987.
T. Murakami, T. Inoue, H. Shimura, M. Nakano, and S. Sasaki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 432, pp. 113-119.
K. Sugimoto: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1978, vol. 35, pp. 31-44.
J. Zhang, R.J. Perez, C.R. Wong, and E.J. Lavernia: Mater. Sci. Eng. R., 1994, vol. 13, pp. 325-389.
S.A. Golovin, V.A. Kuzmenko, G.D. Petrushin, N.N. Pis’mennyi, and I.I. Renne: Strength Mater, 1980, vol. 12, pp. 360–63.
P. Millet, R. Schaller, and W. Benoit: J. Phys. Col., 1983, vol. 44, pp. C9-511-C9-515.
P. Millet, R. Schaller, and W. Benoit: J. Phys. Col., 1981, vol. 42, pp. C5-929-C5-934.
P. Millet, R. Schaller, and W. Benoit: J. Phys. Col., 1985, vol. 46, pp. C10-405-C10-408.
P. Delavignette and S. Amelinckx: J. Nucl. Mater., 1962, vol. 5, pp. 17-66.
G. Qi, G. Zhang, and X. Pu: SAE international, Warrendale, PA, September 2013, DOI:10.4271/2013-01-2031.
J. Lee, H. Park, S. Kim, and J. Han: SAE international, Warrendale, PA, September 2009, DOI:10.4271/2009-01-3030.
L. Wang and T. Ge: Phys. Status Solidi., 1988, vol. 105, pp. 447-453.
S.S. Rao: Mechanical vibrations, 5th ed. (Korean version), Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 2010, pp. 165–67.
P. Trucano and R. Chen: Nature, 1975, vol. 258, pp. 136-137.
Y. X. Zhao and I.L. Spain: Phys. Rev. B, 1989, vol. 40, pp. 993-997.
J. Hemanth and K.V.S. Rao: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1999, vol. 8, pp. 417-423.
G.L. Rivera, R.E. Boeri, and J.A. Sikora: Scripta Mater., 2004, vol. 50, pp. 331-335.
N. Ridley: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15, pp. 1019-1036.
A.M. Elwazri, P. Wanjara, and S. Yue: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 404, pp. 91-98.
I.G. Ritchie and Z.L. Pan: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22, pp. 607-616.
J.N. Wei, H.F. Cheng, Y.F. Zhang, F.S. Han, Z.C. Zhou, and J.P. Shui: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. A325, pp. 444-453.
S.-H. Baik: Nucl. Eng. Des. 2000, vol. 198, pp. 241-252.
A.K. Jena and M.C. Chaturvedi: Phase Transformation in Materials, 1st ed., Prentice Hall, New Jersey, USA, 1995, pp. 184-186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 10, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Han, J., Lee, SJ. et al. Inhomogeneity of Microstructure and Damping Capacity of a FC25 Disc-Brake Rotor and Their Interrelationship. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 3933–3942 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3580-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3580-x