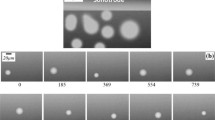
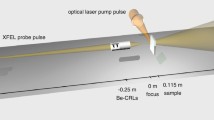
Abstract
The highly dynamic behavior of ultrasonic bubble implosion in liquid metal, the multiphase liquid metal flow containing bubbles and particles, and the interaction between ultrasonic waves and semisolid phases during solidification of metal were studied in situ using the complementary ultrafast and high-speed synchrotron X-ray imaging facilities housed, respectively, at the Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, US, and Diamond Light Source, UK. Real-time ultrafast X-ray imaging of 135,780 frames per second revealed that ultrasonic bubble implosion in a liquid Bi-8 wt pctZn alloy can occur in a single wave period (30 kHz), and the effective region affected by the shockwave at implosion was 3.5 times the original bubble diameter. Furthermore, ultrasound bubbles in liquid metal move faster than the primary particles, and the velocity of bubbles is 70 ~ 100 pct higher than that of the primary particles present in the same locations close to the sonotrode. Ultrasound waves can very effectively create a strong swirling flow in a semisolid melt in less than one second. The energetic flow can detach solid particles from the liquid–solid interface and redistribute them back into the bulk liquid very effectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. L. Roderick and R. Truell: J. Appl. Phys., 1952, vol. 23, pp. 267-79.
K. S. Suslick, D. J. Casadonte, M. L. Green and M. E. Thompson: Ultrasonics, 1987, vol. 25, pp. 56-59.
K. S. Suslick, S. Choe, A. A. Cichowlas and M. W. Grinstaff: Nature, 1991, vol. 353, pp. 414-16.
J.D. Achenbach and O.K. Parikh: Rev. Prog. Q., Springer US, 1991, pp. 1837–44.
H. R. Mayer, H. Lipowsky, M. Papakyriacou, R. Rösch, A. Stich and S. Stanzl-Tschegg: Fatigue Fract. Eng. M., 1999, vol. 22, pp. 591-99.
D. G. Shchukin, E. Skorb, V. Belova and H. Möhwald: Adv. Mater., 2011, vol. 23, pp. 1922-34.
J.Campbell: Int.Mater. Rev., 1981, vol. 26, pp. 77-108.
G. I. Eskin and D. G. Eskin: Ultrasonic Treatment of Light Alloy Melts, 2nd ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, US, 2015.
W. Lauterborn and T. Kurz: Rep. Prog. Phys., 2010, vol. 73, pp. 1-88.
K. S. Suslick and D. J. Flannigan: Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 659-83.
M. L. Calvisi, O. Lindau, J. R. Blake and A. J. Szeri: Phys. Fluids, 2007, vol. 19, pp. 101-15.
D. J. Flannigan and K. S. Suslick: Nature, 2005, vol. 434, pp. 52-55.
K. S. Suslick, D. A. Hammerton and R. E. Cline: J. Am..Chem.Soc., 1986, vol. 108, pp. 5641-42.
C. D. Ohl and R. Ikink: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, vol. 90, pp. 21-24.
W. Lauterborn and C. D. Ohl: Ultrason. Sonochem., 1997, vol. 4, pp. 65-75.
T. L. Lee, J. C. Khong, K. Fezzaa and J. Mi: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2013, vol. 765, pp. 190-94.
H. Huang, D. Shu, Y. Fu, J. Wang and B. Sun: Ultrason. Sonochem., 2014, vol. 21, pp. 1275-78.
J. Mi, D. Tan, and T.L. Lee: Metall. and Mater. Trans. B, 2014 (Open Access published online 11 Dec 2014), DOI: 10.1007/s11663-014-0256-z.
X. Jian, H. Xu, T. T. Meek and Q. Han: Mater. Lett., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 190-93.
M. Qian and A. Ramirez: J. Appl.Phys., 2009, vol. 105, pp. 81-86.
M. K. Aghayani and B. Niroumand: J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 114-22.
H. Chen, Z. Li, Z. Wu and Z. Zhang: J. Alloys Compd., 2005, vol. 394, pp. 282-85.
O. V. Abramov: Ultrasonics, 1987, vol. 25, pp. 73-82.
T. V. Atamanenko, D. G. Eskin, L. Zhang and L. Katgerman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 2056-66.
R. Hickling: Nature, 1965, vol. 206, pp. 915-17.
J. D. Hunt and K. A. Jackson: J. Appl. Phys., 1966, vol. 37, pp. 254-57.
B. Chalmers: Liquids: Structures, Properties, Solidlnteractions, 1st ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 1965.
G.M. Swallowe, J.E. Field, C.S. Rees, and A. Duckworth: Acta Mater., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 961–67.
R. Chow, R. Blindt, R. Chivers and M. Povey: Ultrasonics, 2005, vol. 43, pp. 227-30.
D. Shu, B. Sun, J. Mi and P.S. Grant: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 3755-66.
Y. Wang, X. Liu, K.S. Im, W. K. Lee, J. Wang, K. Fezzaa, D. S. Hung and J. R. Winkelman: Nat. Phys., 2008, vol. 4, pp. 305-09.
K. Fezzaa, Y. Wang: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, vol. 100, pp. 13-16.
R. Boll, D. Anielski, C. Bostedt, J. Bozek, L. Christensen, R. Coffee, S. De, P. Decleva, S. Epp, B. Erk, L. Foucar, F. Krasniqi, J. Küpper, A. Rouzée, B. Rudek, A. Rudenko, S. Schorb, H. Stapelfeldt, M. Stener, S. Stern, S. Techert, S. Trippel, M. Vrakking, J. Ullrich, and D. Rolles: Phys. Rev. A, 2013, vol. 88, no. 6, pp. 1402-1406.
D. Milathianaki, S. Boutet, G. J. Williams, A. Higginbotham, D. Ratner, A. E. Gleason, M. Messerschmidt, M. M. Seibert, D. C. Swift, P. Hering, J. Robinson, W. E. White, and J. S. Wark: Science, 2013, vol. 342, pp. 220-23.
T. B. Massalski, and H. Okamoto: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed., Materials Park, ASM International, 1990.
J. Vizdal, M. H. Braga, A. Kroupa, K. W. Richter, D. Soares, L. F. Malheiros, and J. Ferreira: Calphad, 2007,vol. 31, pp. 438-48.
M. Drakopoulos: http://www.diamond.ac.uk/Beamlines/Engineering-and-Environment/I12/applications.html.
R.C. Gonzalez, R.E. Woods and S.L. Eddins: Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, 2nd ed., Gatesmark, LLC, 2009.
Y. A. Hassan and R. E. Canaan: Exp. Fluids, 1991, vol. 12, pp. 49-60.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the U.K. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (Grant No. EP/L019965/1), The Royal Society Industry Fellowship (for J Mi), and the Hull University & Chinese Scholarship Council (Hull-CSC) PhD Studentship (for D. Tan). The awards of the synchrotron X-ray beam time (EE8542-1) by the Diamond Light Source, UK, and the synchrotron X-ray beam time (GUP 23649 and GUP 26170) by the Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, US are also gratefully acknowledged. Use of the Advanced Photon Source, an Office of Science User Facility operated for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory, was supported by the U.S. DOE under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Special thanks also go to Julia Malle of Glass Workshop in the Department of Chemistry, University of Hull, who has assisted on making the special quartz tube containers used in the in situ synchrotron X-ray imaging studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 15, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, D., Lee, T.L., Khong, J.C. et al. High-Speed Synchrotron X-ray Imaging Studies of the Ultrasound Shockwave and Enhanced Flow during Metal Solidification Processes. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 2851–2861 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2872-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2872-x