Abstract
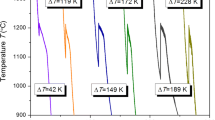
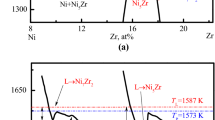
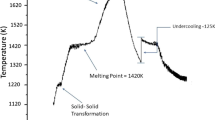
Both Ni-36 wt pct Sb and Ni-52.8 wt pct Sb eutectic alloys were highly undercooled and rapidly solidified with the glass-fluxing method and drop-tube technique. Bulk samples of Ni-36 pct Sb and Ni-52.8 pct Sb eutectic alloys were undercooled by up to 225 K (0.16 T E ) and 218 K (0.16 T E ), respectively, with the glass-fluxing method. A transition from lamellar eutectic to anomalous eutectic was revealed beyond a critical undercooling ΔT 1*, which was complete at an undercooling of ΔT 2*. For Ni-36 pct Sb, ΔT 1*≈60 K and ΔT 2*≈218 K; for Ni-52.8 pct Sb, ΔT 1*≈40 K and ΔT 2*≈139 K. Under a drop-tube containerless solidification condition, the eutectic microstructures of these two eutectic alloys also exhibit such a “lamellar eutectic-anomalous eutectic” morphology transition. Meanwhile, a kind of spherical anomalous eutectic grain was found in a Ni-36 pct Sb eutectic alloy processed by the drop-tube technique, which was ascribed to the good spatial symmetry of the temperature field and concentration field caused by a reduced gravity condition during free fall. During the rapid solidification of a Ni-52.8 pct Sb eutectic alloy, surface nucleation dominates the nucleation event, even when the undercooling is relatively large. Theoretical calculations on the basis of the current eutectic growth and dendritic growth models reveal that γ-Ni5Sb2 dendritic growth displaces eutectic growth at large undercoolings in these two eutectic alloys. The tendency of independent nucleation of the two eutectic phases and their cooperative dendrite growth are responsible for the lamellar eutectic-anomalous eutectic microstructural transition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Goetzinger, M. Barth, and D.M. Herlach: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 1647–55.
M. Leonhardt, W. Löser, and H.G. Lindenkreuz: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 2961–68.
B. Wei, D.M. Herlach, B. Feuerbacher, and F. Sommer: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 1801–09.
S. Walder and P.L. Ryder: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 4007–13.
R. Abbaschian and M.D. Lipschutz: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, vols. A226–A228, pp. 13–21.
A.L. Greer: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A178, pp. 113–20.
T.Z. Kattamis and M.C. Flemings: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1449–57.
T.J. Piccone, Y. Wu, Y. Shiohara, and M.C. Flemings: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 925–32.
S. Walder and P.L. Ryder: J. Appl. Phys., 1993, vol. 74 (10), pp. 6100–05.
C.D. Cao, W.J. Xie, and B. Wei: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. A283, pp. 86–93.
W.H. Hofmeister, N.D. Evans, R.J. Bayuzick, and M.B. Robinson: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 1421–28.
R. Jansen and P.R. Sahm: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. A65, pp. 199–212.
K.A. Jackson and J.D. Hunt: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 1129–35.
R. Trivedi, P. Magnin, and W. Kurz: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 971–80.
W. Kurz and R. Trivedi: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 3051–57.
B. Wei, G.C. Yang, and Y.H. Zhou: Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 1249–58.
C. Dong and B. Wei: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1996, vol. 15, pp. 970–73.
T. Lyman: Metals Handbook, vol. 8, Metallography Structures and Phase Diagrams, 8th ed., ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1973, p. 325.
N. Wang, C.D. Cao, and B. Wei: Adv. Space Res., 1990, vol. 24 (10), pp. 1257–62.
N. Wang and B. Wei: J. Alloys Compounds, 2000, vol. 302, pp. 274–80.
J. Lipton, W. Kurz, and R. Trivedi: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 957–64.
W.J. Boettinger, S.R. Coriell, and R. Trivedi: Proc. 4th Conf. on Rapid Solidification Processing: Principles and Technologies, R. Mehrabian and P.A. Parrish, eds., Claitors, Baton Rouge, LA, 1987, p. 13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X.J., Wei, B. Microstructural characteristics of Ni-Sb eutectic alloys under substantial undercooling and containerless solidification conditions. Metall Mater Trans A 33, 1221–1228 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0223-1
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0223-1