Abstract
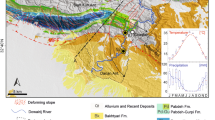
The paper describes a large-area analysis of the triggering zones of shallow landslides on a case of unsaturated layered volcanic air-fall (pyroclastic) soil deposits in Cervinara site (18 km2), Southern Italy. The physically-based model TRIGRS (Transient Rainfall Infiltration-Based Grid Regional Slope-Stability) is used, which is used with either saturated or unsaturated conditions and implemented in a GIS platform. In addition to using the TRIGRS model to simulate some recent landslides, a new simplified approach is also tested to take into account the actual layered soil stratigraphy. The consistency check of the model and of the input data is performed with reference to slope stable conditions before rainfall. The performances of the models are evaluated through the ROC curves and two other quantitative indexes taken from the literature referring to the slope failures caused by December 1999 rainstorm. Notwithstanding the simplifications and limitations of the present work, both unsaturated conditions and layered stratigraphy are outlined as key factors for the slope stability of shallow deposits of unsaturated coarse-grained soils subjected to short heavy rainfall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvioli M, Guzzetti F, Rossi M (2014) Scaling properties of rainfall-induced landslides predicted by a physically based model. Geomorphology 213: 38–47. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph. 2013.12.039
Autorità di Bacino Liri-Garigliano e Volturno (2012). Personal Communication.
Baum RL, Savage WZ, Godt JW (2002) TRIGRS–A Fortran program for transient rainfall infiltration and grid-based regional slope-stability analysis, Open-file report 02-424, p.35, U.S. Geological Survey. Available online at: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2002/ofr-02-424/(Accessed on 14 July 2015)
Baum RL, Savage WZ, Godt JW (2008) TRIGRS -A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid-Based Regional Slope-Stability Analysis, Version 2. 0. U. S. Geological Survey. Available online at: http://pubs.usgs. gov/of/2008/1159/downloads/pdf/OF08-1159.pdf (Accessed on 14 July 2015).
Cascini L, Cuomo S, De Santis A (2011a) Numerical modelling of the December 1999 Cervinara flow-like mass movements (Southern Italy). In: Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction and Assessment, Padua, Italy, 14-17 June 2011. Italian Journal of Engineering Geology and Environment: 635–644. DOI: 10.4408/IJEGE.2011-03.B-069.
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Della Sala M (2011b) Spatial and temporal occurrence of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of flow type: A case of Sarno-Quindici, Italy. Geomorphology 126(1-2): 148–158. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.10.038
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Guida D (2008a) Typical source areas of May 1998 flow-like mass movements in the Campania region, Southern Italy. Engineering Geology 96: 107–125. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.10.003
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M (2008b) The role played by mountain tracks on rainfall-induced shallow landslides: a case study. In: Proceedings of iEMSs, Barcelona, Spain, 7-10 July 2008, ISBN: 978-84-7653-074-0, pp. 1484–1491.
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Fernández-Merodo JA (2008c) Geomechanical modelling of triggering mechanisms for rainfall-induced triangular shallow landslides of the flow-type. In: Proceedings of iEMSs, Barcelona, Spain, 7-10 July 2008, ISBN: 978-84-7653-074-0, pp. 1516–1523.
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M (2013) Inception of debris avalanches: remarks on geomechanical modelling. Landslides 10(6): 701–711. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-012-0366-0
Cascini L, Sorbino G, Cuomo S (2005) Flow-like mass movements in pyroclastic soils: remarks on the modelling of triggering mechanisms. Italian Geotechnical Journal 4: 11–31.
Cascini L, Sorbino G, Cuomo S, Ferlisi S (2014) Seasonal effects of rainfall on the shallow pyroclastic deposits of the Campania region (southern Italy). Landslides 11(5): 779–792. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-013-0395-3
Cervi F, Berti M, Borgatti L, et al. (2010) Comparing predictive capability of statistical and deterministic methods for landslides susceptibility mapping: a case study in the northern Apennines (Reggio Emilia Province, Italy). Landslides 7(4): 433–444. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-010-0207-y
Cuomo S (2014) New advances and challenges for numerical modeling of landslides of the flow type. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 9: 91–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeps.2014.06.004
Cuomo S, Della Sala M (2015) Large-area analysis of soil erosion and landslides induced by rainfall: a case of unsaturated shallow deposits, Journal of Mountain Science. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-014-3242-7
Cuomo S, Della Sala M, Novità A (2015) Physically based modelling of soil erosion induced by rainfall in small mountain basins. Geomorphology 243: 106–115. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.04.019
Cuomo S, Della Sala M, Capuano C, et al. (2014) Analisi su area vasta dell’innesco di frane superficiali e fenomeni erosivi indotti da pioggia. In: Proceedings of XXV Convegno Nazionale di Geotecnica–AGI Roma–, held in Baveno, Italy, 4-6 June 2014. ISBN 978-88-97517-05-4, 471-478.
Cuomo S, Foresta V (2015) Penetration tests in shallow layered unsaturated pyroclastic soil deposits of Southern Italy. In: Proceedings of “Soil Mechanichs 2015–Panamerican Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering”, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15-18 November 2015, D. Manzanal and A.O. Sfriso (Eds.) ISBN: 978-1-61499-600-2: 454–461. DOI: 10.3233/978-1-61499-603-3-454
Damiano E, Olivares L, Picarelli L (2012) Steep-slope monitoring in unsaturated pyroclastic soils. Engineering Geology 137-138: 1–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.03.002
De Vita P, Napolitano E, Godt JW, et al. (2013) Deterministic estimation of hydrological thresholds for shallow landslide initiation and slope stability models: case study from the Somma-Vesuvius area of southern Italy. Landslides 10 (6): 713–728. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-012-0348-2
Dietrich WE, Montgomery DR (1998) Shalstab: a digital terrain model for mapping shallow landslide potential. Available online at: http://socrates.berkeley.edu/~geomorph/shalstab/(Accessed on 14 July 2015)
Fiorillo F, Guadagno FM, Aquino S, et al. (2001) The December 1999 Cervinara landslides: further debris flows in the pyroclastic deposits of Campania (Southern Italy). Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 60(3): 171–184. DOI: 10.1007/s100640000093
Fiorillo F, Wilson RC (2004) Rainfall induced debris flows in pyroclastic deposits, Campania Southern Italy. Engineering Geology 75: 263–289. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.014
Godt JW, Baum RL, Savage WZ, et al. (2008) Transient deterministic shallow landslide modeling: requirements for susceptibility and hazard assessments in a GIS framework. Engineering Geology 102: 214–226. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo. 2008.03.019
Haneberg JW, (2004) A rational probabilistic method for spatially distributed landslide hazard assessment. Environmental & Engineering Geoscience 10: 27–43. DOI: 10.2113/10.1.27
Iverson RM (2000) Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resources Research 36(7): 1897–1910. DOI: 10.1029/2000WR900090
Mergili M, Marchesini I, Alvioli M, et al. (2014a) A strategy for gis-based 3-d slope stability modelling over large areas. Geoscientific Model Developement 7: 5407–5445. DOI: 10.5194/gmdd-7-5407-2014
Mergili M, Marchesini I, Rossi M, et al. (2014b) Spatially distributed three-dimensional slope stability modelling in a raster GIS. Geomorphology 206: 178–195. DOI: 10.1016/j. geomorph.2013.10.008
Montrasio L, Valentino R, Losi GL (2011) Towards a real-time susceptibility assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslides on a regional scale Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 11: 1927–1947. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-11-1927-2011
Raia S, Alvioli M, Rossi M, et al. (2014) Improving predictive power of physically based rainfall-induced shallow landslide models: a probabilistic approach. Geoscientific Model Developement 7: 495–514. DOI: 10.5194/gmdd-6-1367-2013
Richards LA (1931) Capillary conductions of liquids through porous mediums. Journal of Applied Physics 1: 318–333. DOI: 10.1063/1.1745010
Salciarini D, Tamagnini C, Conversini P, et al. (2012) Spatially distributed rainfall thresholds for the initiation of shallow landslides. Natural Hazards 61: 229–245. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-011-9739-2
Savage WZ, Godt JW, Baum RL (2003) A model for spatially and temporally distributed shallow landslide initiation by rainfall infiltration. in press. In: Proceedings of 3rd Int. Conf. on Debris Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment, Davos, Switzerland, 10-12 September 2003. pp 179–187.
Savage WZ, Godt JW, Baum RL (2004) Modeling timedependent areal slope stability. In: Landslides–Evaluation and Stabilization. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Landslides. Lacerda WA, Erlich M, Fontoura SAB, Sayao ASF, (Eds.), held in Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, Vol 1, 23–36.
Sorbino G, Sica C, Cascini L (2010) Susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides source areas using physically based models. Natural Hazards 53: 313–332. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-009-9431-y
Sorbino G, Sica C, Cascini L, et al. (2007) On the forecasting of flowslides triggering areas using physically based models. In: Proceedings of First North American Landslide Conference, Vail, Colorado (USA), held on 3-8 June 2007. Schaefer, Schuster, Turner eds, AEG Special Publication 23, ISBN: 978-0-975-4295-3-2. pp 305–315.
Srivastava R, Yeh J (1991) Analytical solutions for onedimensional, transient infiltration toward the water table in homogeneous and layered soils. Water Resources Research 27(5): 753–762. DOI: 10.1029/90WR02772
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8024-0319
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3618-2910
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuomo, S., Iervolino, A. Investigating the role of stratigraphy in large-area physically-based analysis of December 1999 Cervinara shallow landslides. J. Mt. Sci. 13, 104–115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3261-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3261-4