Abstract
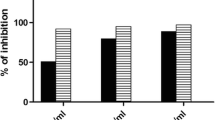
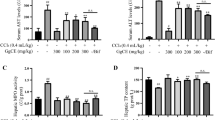
To investigate the effects of icaritin, an active ingredient extracted from Epimedium Sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.), on CCl4-induced liver injury and its possible mechanisms. Hepatocytes isolated from Sprague-Dawley male rats were treated with 3 mmol/L CCl4 for 24 h to induce acute liver cell injury, then icaritin (0.1, 1, 10, 100 μmol/L, respectively) was administrated to the cells, and estrogen receptor antagonist ICI182,780 (1 μmol/L) was co-treated with 10 μmol/L icaritin. Biochemical parameters (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD)) and cell apoptosis were detected to evaluate the injury degree. Protein expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, liver fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation were determined by western blot. Icaritin alleviated CCl4-induced liver cell injury in a concentration-dependent manner and 10 μmol/L was the optimal concentration. Icaritin (10 μmol/L) significantly reduced activities of ALT, AST in cell culture medium and MDA level of the impaired liver cells, but increased the intercellular SOD activity. The apoptotic rate of the impaired liver cells was also decreased by icaritin (10 μmol/L) treatment. Icaritin might exert antioxidative and anti-apoptotic functions via estrogen-like effect, as the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax was significantly increased, while protein expressions of L-FABP and PPAR-α were markedly increased, and this function was blocked by the estrogen receptor antagonist ICI182,780 efficiently. Icaritin may be a promising drug candidate for acute liver injury benefiting from the antioxidative and anti-apoptotic functions via estrogen-like effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Y, Gong LK, Qi XM, Li XH, Ren J (2005) Apoptosis initiated by carbon tetrachloride in mitochondria of rat primary cultured hepatocytes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26(8):969–975. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00143.x
Campbell SE, Mehan KA, Tunstall RJ, Febbraio MA, Cameron-Smith D (2003) 17beta-estradiol upregulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and lipid oxidative genes in skeletal muscle. J Mol Endocrinol 31(1):37–45
Dong H, Lu FE, Zhao L (2012) Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin J Integr Med 18(2):152–160. doi:10.1007/s11655-012-0993-2
Hong EJ, Levasseur MP, Dufour CR, Perry MC, Giguere V (2013) Loss of estrogen-related receptor alpha promotes hepatocarcinogenesis development via metabolic and inflammatory disturbances. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(44):17975–17980
Huang H, Starodub O, McIntosh A, Atshaves BP, Woldegiorgis G, Kier AB, Schroeder F (2004) Liver fatty acid-binding protein colocalizes with peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha and enhances ligand distribution to nuclei of living cells. Biochemistry 43(9):2484–2500. doi:10.1021/bi0352318
Huang J, Yuan L, Wang X, Zhang TL, Wang K (2007a) Icaritin and its glycosides enhance osteoblastic, but suppress osteoclastic, differentiation and activity in vitro. Life Sci 81(10):832–840
Huang X, Zhu D, Lou Y (2007b) A novel anticancer agent, icaritin, induced cell growth inhibition, G1 arrest and mitochondrial transmembrane potential drop in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 564(1–3):26–36
Jaeschke H (2000) Reactive oxygen and mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(7):718–724
Kaplowitz N (2001) Drug-induced liver disorders: implications for drug development and regulation. Drug Saf 24(7):483–490
Kaplowitz N (2004) Drug-induced liver injury. Clin Infect Dis 38(Suppl 2):S44–S48. doi:10.1086/381446
Lee KJ, Choi JH, Khanal T, Hwang YP, Chung YC, Jeong HG (2008) Protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Toxicology 248(1):18–24. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.03.009
Liu J, Lou YJ (2004) Determination of icariin and metabolites in rat serum by capillary zone electrophoresis: rat pharmacokinetic studies after administration of icariin. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36(2):365–370
Liu Y, Shimizu I, Omoya T, Ito S, Gu X-S, Zuo J (2002) Protective effect of estradiol on hepatocytic oxidative damage. World J Gastroenterol 8(2):363–366
Montiel-Duarte C, Ansorena E, López-Zabalza MJ, Cenarruzabeitia E, Iraburu MJ (2004) Role of reactive oxygen species, glutathione and NF-κB in apoptosis induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“Ecstasy”) on hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Pharmacol 67(6):1025–1033
Park JK, Jeong DH, Park HY, Son KH, Shin DH, Do SH, Yang HJ, Yuan DW, Hong IH, Goo MJ, Lee HR, Ki MR, Ishigami A, Jeong KS (2008) Hepatoprotective effect of Arazyme on CCl4-induced acute hepatic injury in SMP30 knock-out mice. Toxicology 246(2–3):132–142. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.01.006
Recknagel RO, Glende EA Jr, Dolak JA, Waller RL (1989) Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol Ther 43(1):139–154
Saleem TM, Chetty CM, Ramkanth S, Rajan V, Kumar KM, Gauthaman K (2010) Hepatoprotective herbs—a review. Int J Res Pharm Sci 1(1):1–5
Seglen PO (1976) Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol 13:29–83
Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR, Pillai KR, Kumar PR, Sudhakaran PR, Menon VP (2006) Influence of ferulic acid on gamma-radiation induced DNA damage, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in primary culture of isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 228(2–3):249–258
Terui K, Enosawa S, Haga S, Zhang HQ, Kuroda H, Kouchi K, Matsunaga T, Yoshida H, Engelhardt JF, Irani K, Ohnuma N, Ozaki M (2004) Stat3 confers resistance against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative injury in hepatocytes through upregulation of Mn-SOD. J Hepatol 41(6):957–965
Turrens JF (2003) Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J Physiol 552(2):335–344
Wang YK, Huang ZQ (2005) Protective effects of icariin on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by H2O2 in vitro. Pharmacol Res 52(2):174–182
Wang G, Gong Y, Anderson J, Sun D, Minuk G, Roberts MS, Burczynski FJ (2005) Antioxidative function of L-FABP in L-FABP stably transfected Chang liver cells. Hepatology 42(4):871–879. doi:10.1002/hep.20857
Wang ZQ, Weber N, Lou YJ, Proksch P (2006) Prenylflavonoids as nonsteroidal phytoestrogens and related structure-activity relationships. ChemMedChem 1(4):482–488. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200500089
Wang G, Shen H, Rajaraman G, Roberts MS, Gong Y, Jiang P, Burczynski F (2007a) Expression and antioxidant function of liver fatty acid binding protein in normal and bile-duct ligated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 560(1):61–68
Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Qi L, Lou Y (2007b) Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via estrogen-dependent pathway. Neuroscience 145(3):911–922
Wo YB, Zhu DY, Hu Y, Wang ZQ, Liu J, Lou YJ (2008) Reactive oxygen species involved in prenylflavonoids, icariin and icaritin, initiating cardiac differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem 103(5):1536–1550. doi:10.1002/jcb.21541
Zhang YW, Morita I, Zhang L, Shao G, Yao XS, Murota S (2000) Screening of anti-hypoxia/reoxygenation agents by an in vitro method. Part 2: inhibition of tyrosine kinase activation prevented hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in endothelial gap junctional intercellular communication. Planta Med 66(2):119–123. doi:10.1055/s-2000-11126
Zhang S, Lu B, Han X, Xu L, Qi Y, Yin L, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Liu K, Peng J (2013) Protection of the flavonoid fraction from Rosa laevigata Michx fruit against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 55:60–69
Zhu DY, Lou YJ (2005) Inducible effects of icariin, icaritin, and desmethylicaritin on directional differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26(4):477–485. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00076.x
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Peng Liu and Xiang Jin should be regarded as joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Jin, X., Lv, H. et al. Icaritin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury mainly because of the antioxidative function through estrogen-like effects. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 50, 899–908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-014-9792-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-014-9792-8