Abstract
Background
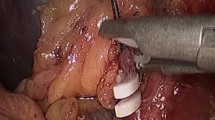
Laparoscopic partial splenectomy (LPS) is a surgical option for splenic masses, with the goal of reducing postoperative complications while preserving splenic function.
Methods
Thirty-seven patients who underwent laparoscopic splenectomy for tumorous lesions of the spleen at two affiliated hospitals were enrolled. Among them, 22 patients underwent laparoscopic total splenectomy (LTS) and 15 patients underwent LPS.
Results
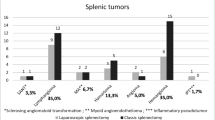
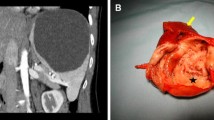
The tumorous lesions of the spleen in both groups, in order of decreasing frequency, consisted of epithelial cysts, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas, abscesses, metastatic tumors, and hamartomas. All procedures were completed by laparoscopy, and the pathologic lesions in the spleen were completely removed in both groups. There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of the operative time (LTS 151.5 ± 98.5 min, LPS 168.6 ± 46.8 min, p = 0.483), intraoperative blood loss (LTS 337.3 ± 188.4 ml, LPS 422.6 ± 187.4 ml, p = 0.185), and transfusion rate (LTS 3/22 [13.6 %], LPS 3/15 [20.0 %], p = 0.606). However, there were significant differences in postoperative complications such as pleural effusion (LTS 9/22 [40.9 %], LPS 0/15 [0 %], p = 0.005), splenic vein thrombosis (LTS 10/22 [45.5 %], LPS 0/15 [0 %], p = 0.002), and postoperative hospital stay (LTS 5.4 ± 1.8 days, LPS 4.2 ± 0.8 days, p = 0.027).
Conclusions
LPS is a feasible, safe surgical procedure in patients with tumorous lesions of the spleen, and it represents an effective approach to reduce postoperative hospital stay and complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OPSS:
-
Overwhelming postsplenectomy sepsis
- LPS:
-
Laparoscopic partial splenectomy
- LTS:
-
Laparoscopic total splenectomy
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ASA class:
-
American Society of Anesthesiologist class
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
- PSVT:
-
Portal or splenic vein thrombosis
References
Wang X, Li Y, Crook N, Peng B, Niu T. Laparoscopic splenectomy: a surgeon’s experience of 302 patients with analysis of postoperative complications. Surg Endosc 2013;27:3564-3571.
Slater BJ, Chan FP, Davis K, Dutta S. Institutional experience with laparoscopic partial splenectomy for hereditary spherocytosis. J Pediatr Surg 2010;45:1682-1686.
Bhandarkar DS, Katara AN, Mittal G, Shah R, Udwadia TE. Prevention and management of complications of laparoscopic splenectomy. Indian J Surg 2011;73:324-330.
Mouttalib S, Rice HE, Snyder D, Levens JS, Reiter A, Soler P, Rothman JA, Thornburg CD. Evaluation of partial and total splenectomy in children with sickle cell disease using an Internet-based registry. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2012;59:100-104.
Buesing KL, Tracy ET, Kiernan C, Pastor AC, Cassidy LD, Scott JP, Ware RE, Davidoff AM, Rescorla FJ, Langer JC, Rice HE, Oldham KT. Partial splenectomy for hereditary spherocytosis: a multi-institutional review. J Pediatr Surg 2011;46:178-183.
Héry G, Becmeur F, Méfat L, Kalfa D, Lutz P, Lutz L, Guys JM, de Lagausie P. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy: indications and results of a multicenter retrospective study. Surg Endosc 2008;22:45-49.
Dutta S, Price VE, Blanchette V, Langer JC. A laparoscopic approach to partial splenectomy for children with hereditary spherocytosis. Surg Endosc 2006;20:1719-1724.
Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Takiguchi S, Yasui M, Danno K, Fujie Y, Kitani K, Seki Y, Hata T, Shingai T, Takemasa I, Ikenaga M, Yamamoto H, Ohue M, Monden M. Total splenic vein thrombosis after laparoscopic splenectomy: a possible candidate for treatment. Am J Surg 2007;193:21-25.
Uranüs S, Pfeifer J, Schauer C, Kronberger L, Rabl H, Ranftl G, Hauser H, Bahadori K. Laparoscopic partial splenic resection. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1995;5:133-136.
Smith ST, Scott DJ, Burdick JS, Rege RV, Jones DB. Laparoscopic marsupialization and hemisplenectomy for splenic cysts. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 2001;11:243-249.
Fan H, Zhang D, Zhao X, Pan F, Jin ZK. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy for large splenic epidermoid cyst. Chin Med J (Engl) 2011;124:1751-1753.
Szczepanik AB, Meissner AJ. Partial splenectomy in the management of nonparasitic splenic cysts. World J Surg 2009;33:852-856.
Krauth MT, Lechner K, Neugebauer EA, Pabinger I. The postoperative splenic/portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy and its prevention—an unresolved issue. Haematologica 2008;93:1227-1232.
Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Takiguchi S, Kubota M, Ikenaga M, Yamamoto H, Fujiwara Y, Ohue M, Yasuda T, Imamura H, Tatsuta M, Yano M, Furukawa H, Monden M. High incidence of thrombosis of the portal venous system after laparoscopic splenectomy: a prospective study with contrast-enhanced CT scan. Ann Surg 2005;241:208-216.
Rattner DW, Ellman L, Warshaw AL. Portal vein thrombosis after elective splenectomy. An underappreciated, potentially lethal syndrome. Arch Surg 1993;128:565-569; discussion 569-570.
Svensson M, Wirén M, Kimby E, Hägglund H. Portal vein thrombosis is a common complication following splenectomy in patients with malignant haematological diseases. Eur J Haematol 2006;77:203-209.
Breitenstein S, Scholz T, Schäfer M, Decurtins M, Clavien PA. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 2007;204:179-181.
Wu HM, Kortbeek JB. Management of splenic pseudocysts following trauma: a retrospective case series. Am J Surg 2006;191:631-634.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Funding
There was no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Lee, J.S., Yoon, Y.C. et al. Role of Laparoscopic Partial Splenectomy for Tumorous Lesions of the Spleen. J Gastrointest Surg 19, 1052–1058 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2812-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2812-5