Abstract
Aim
This study investigates the effects of surgery on collagen turnover in patients affected by Crohn’s disease (CD).
Methods
Fifteen patients affected by active CD, assessed according to the Crohn’s disease activity index, and confirmed by histology, with different pharmacological treatments, were enrolled in the study. N-Terminal propeptide of type III collagen was assessed on peripheral blood before and 6 months after surgery, as an index of collagen turnover. A control group of 15 healthy age- and sex-matched subjects was also studied.
Results
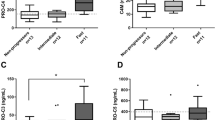
In CD patients peripheral N-terminal propeptide of type III collagen serum levels were significantly higher than in controls before surgery (5.0 ± 1.8 vs 2.7 ± 0.7 μg/l, respectively; p = 0.0001). Six months after these values were significantly reduced (from 5.0 ± 1.8 to 3.1 ± 0.8 μg/l; p = 0.003). Independently on the pretreatment regimen and the duration of the disease, an improvement in the patients’ symptoms was observed.
Conclusions
The surgical resection of the affected intestinal segment in CD patients seems to be able to break down the collagen synthesis processes. Peripheral N-terminal propeptide of type III collagen could be seen as an additive marker to clinical and endoscopic observations after surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 1998;115(1):182–205.
Knigge KL. Inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Cornerstone 2002;4(4):49–60.
Zheng CQ, Hu GZ, Zeng ZS, Lin LJ, Gu GG. Progress in searching for susceptibility gene for inflammatory bowel disease by positional cloning. World J Gastroenterol 2003;9(8):1646–56.
Tamboli CP, Cortot A, Colombel JF. What are the major arguments in favour of the genetic susceptibility for inflammatory bowel disease? Eur J Gastoenterol Hepatol 2003;15(6):587–92.
Hugot JP. Genetic origin of IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2004;10(S1):S11–5.
Devani M, Cugno M, Vecchi M, Ferrero S, Di Berardino F, Avesani EC, de Franchis R, Colman RW. Kallikrein–kinin system activation in Crohn’s disease: differences in intestinal and systemic markers. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97(8):2026–32.
Krishnan A, Korzenik JR. Inflammatory bowel disease and environmental influences. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2002;31(1):21–39.
Isaacs KL, Lewis JD, Sandborn WJ, Sands BE, Targan SR. State of the art: IBD therapy and clinical trials in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2005;11(Suppl 1):S3–12.
Halfvarson J, Jess T, Magnuson A, Montgomery SM, Orholm M, Tysk C, Binder V, Jarnerot G. Environmental factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a co-twin control study of a Swedish–Danish twin population. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2006;12(10):925–33.
Ciulla M, Cioffi U, De Simone M, Contessini-Avesani E. TGF-beta1 and collagen metabolism in IBD patients. Med Sci Monit 2002;8(12):LE55–6.
Hendrickson BA, Gokhale R, Cho JH. Clinical aspects and pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002;15(1):79–94.
Chutkan RK. Inflammatory bowel disease. Prim Care 2001;28(3):539–56.
Pucilowska JB, McNaughton KK, Mohapatra NK, Hoyt EC, Zimmermann EM, Sartor RB, Lund PK. IGF-I and procollagen alpha1(I) are coexpressed in a subset of mesenchymal cells in active Crohn’s disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;279(6):G1307–22.
Kjeldsen J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB, Junker P. Seromarkers of collagen I and III metabolism in active Crohn’s disease. Relation to disease activity and response to therapy. Gut 1995;37(6):805–10.
Kjeldsen J, Rasmussen M, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB, Kronborg O, Junker P. Collagen metabolites in the peripheral and splanchnic circulation of patients with Crohn disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2001;36(11):1193–7.
Silvennoinen J, Risteli L, Karttunen T, Risteli J. Increased degradation of type I collagen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1996;38(2):223–8.
Stallmach A, Schuppan D, Riese HH, Matthes H, Riecken EO. Increased collagen type III synthesis by fibroblasts isolated from strictures of patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 1992;102(6):1920–9.
Hahn EG, Schuppan D. Ethanol and fibrinogenesis in the liver. In Seitz HK, Kommerell B, ed. Alcohol-related disease in gastroenterology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1985, pp 124–53.
Uscanga L, Kennedy RH, Choux R, Druguet M, Grimaud JA, Sarles H. Sequential connective matrix changes in experimental acute pancreatitis. An immunohistochemical and biochemical assessment in the rat. Int J Pancreatol 1987;2(1):33–45.
Cantin AM, Boileau R, Begin R. Increased procollagen III aminoterminal peptide-related antigens and fibroblast growth signals in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1988;137(3):572–8.
Querejeta R, Varo N, Lopez B, Larman M, Artinano E, Etayo JC, Martinez Ubago JL, Gutierrez-Stampa M, Emparanza JI, Gil MJ, Monreal I, Mindan JP, Diez J. Serum carboxy-terminal propeptide of procollagen type I is a marker of myocardial fibrosis in hypertensive heart disease. Circulation 2000;101(14):1729–35.
Sartorio A, Arosio M, Conti A, Ferrero S, Porretti S, Faglia G. Long-term monitoring of rec-GH treatment by serial determination of serum aminoterminal propeptide of type III procollagen in children and adults with GH deficiency. J Endocrinol Invest 1999;22(3):169–75.
De Simone M, Cioffi U, Contessini-Avesani E, Oreggia B, Paliotti R, Pierini A, Bolla G, Oggiano E, Ferrero S, Magrini F, Ciulla MM. Elevated serum procollagen type III peptide in splanchnic and peripheral circulation of patients with inflammatory bowel disease submitted to surgery. BMC Gastroenterol 2004;4(4):29.
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology 1976;70(3):439–44.
Longobardi T, Jacobs P, Bernstein CN. Work losses related to inflammatory bowel disease in the United States: results from the National Health Interview Survey. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98(5):1064–72.
Stange EF, Travis SP, Vermeire S, Beglinger C, Kupcinkas L, Geboes K, Barakauskiene A, Villanacci V, Von Herbay A, Warren BF, Gasche C, Tilg H, Schreiber SW, Scholmerich J, Reinisch W, European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation. European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: definitions and diagnosis. Gut 2006;55(1):i1–15.
Russell RK, Satsangi J. IBD: a family affair. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2004;18(3):525–39.
Marks DJ, Harbord MW, MacAllister R, Rahman FZ, Young J, Al-Lazikani B, Lees W, Novelli M, Bloom S, Segal AW. Defective acute inflammation in Crohn’s disease: a clinical investigation. Lancet 2006;367(9511):668–78.
Caprilli R, Gassull MA, Escher JC, Moser G, Munkholm P, Forbes A, Hommes DW, Lochs H, Angelucci E, Cocco A, Vucelic B, Hildebrand H, Kolacek S, Riis L, Lukas M, de Franchis R, Hamilton M, Jantschek G, Michetti P, O’Morain C, Anwar MM, Freitas JL, Mouzas IA, Baert F, Mitchell R, Hawkey CJ; European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation. European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: special situations. Gut 2006;55(1):i36–58.
Dubinsky MC, Seidman EG. Diagnostic markers of inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2000;16(4):337–42.
Colombel JF, Solem CA, Sandborn WJ, Booya F, Loftus EV Jr, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Bodily KD, Fletcher JG. Quantitative measurement and visual assessment of ileal Crohn’s disease activity by computed tomography enterography: correlation with endoscopic severity and C reactive protein. Gut 2006;55(11):1561–7.
Cioffi U, Ciulla MM, De Simone M, Paliotti R, Pierini A, Magrini F, Botti F, Contessini-Avesani E. Effects of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases on left ventricular structure and function: a study protocol. BMC Public Health 2002;10(2):9.
Sartorio A, Conti A, Ferrero S, Giambona S, Re T, Passini E, Ambrosi B. Evaluation of markers of bone and collagen turnover in patients with active and preclinical Cushing’s syndrome and in patients with adrenal incidentaloma. Eur J Endocrinol 1998;138(2):146–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Simone, M., Ciulla, M.M., Cioffi, U. et al. Effects of Surgery on Peripheral N-Terminal Propeptide of Type III Procollagen in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. J Gastrointest Surg 11, 1361–1364 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0233-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0233-9