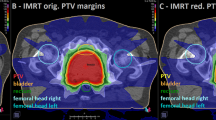
Abstract
Purpose
In this study, we compared the dose impact of the heterogeneity caused by rectal gas using two methods of treatment planning for intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT).
Materials and methods
In addition to the structure set used for the standard treatment plan, we created a structure set for evaluation for each patient. These sets were transferred to the same isocenter as the respective treatment plans for IMRT and VMAT that were to become the standard. Values were then recalculated.
Results
During the standard prostatic IMRT and VMAT treatment planning, all study participants met dose restrictions in place at our hospital. Dose restrictions were fulfilled in treatment plans for evaluation, excluding those with a clinical target volume (CTV) of V 100 % and planning target volume (PTV) of D 95 when the rectum was excluded. However, in treatment plans for evaluation, IMRT was shown to have a higher concordance rate with standard treatment plans than VMAT.
Conclusion
If rectal gas is present during either IMRT or VMAT, a dose decrease will occur in relation to CTV and PTV, suggesting that a plan does not eliminate adverse effects on organs at risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Prostate Cancer version 4.2011, http://www.nccn.org/.
Pollack A, Zagars GK, Starkschall G, Antolak JA, Lee JJ, Huang E, et al. Prostate cancer radiation dose response results of the M. D. Anderson phase III randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:1097–105.
Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Happersett L, Lee HJ, Ling CC, Burman CM, et al. Clinical experience with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2000;55:241–9.
Kuban DA, Tucker SL, Dong L, Starkschall G, Huang EH, Cheung MR, et al. Long-term results of the M. D. Anderson randomized dose-escalation trial for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:67–74.
Zelefsky MJ, Levin EJ, Hunt M, Yamada Y, Shippy AM, Jackson A, et al. Incidence of late rectal and urinary toxicities after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1124–9.
Zelefsky MJ, Crean D, Mageras GS, Lyass O, Happeresett L, Ling CC, et al. Quantification and predictors of prostate position variability in 50 patients evaluated with multiple CT scans during conformal radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 1999;50:225–34.
Wong JR, Grimm L, Uematsu M, Oren R, Cheng CW, Merrick S, et al. Image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer by CT–linear accelerator combination: prostate movements and dosimetric considerations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:561–9.
Onishi H, Kuriyama K, Komiyama T, Marino K, Araya M, Saito R, et al. Large prostate motion produced by anal contraction. Radiother Oncol. 2012;104:390–4.
Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Meeks SL, Santhanam A, Cunningham A, Levine L, et al. Observations on real-time prostate gland motion using electromagnetic tracking. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71:1084–90.
Shimizu S, Osaka Y, Shinohara N, Sazawa A, Nishioka K, Suzuki R, et al. Use of implanted markers and interportal adjustment with real-time tracking radiotherapy system to reduce intrafraction prostate motion. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:e393–9.
Boehmer D, Maingon P, Poortmans P, Baron MH, Remouchamps V, Scrase C, et al. Guidelines for primary radiotherapy of patients with prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2006;79:259–69.
Mizowaki T, Hatano K, Hiraoka M. Surveillance on interfacility differences in dose-prescription policy of intensitymodulated radiation therapy plans for prostate cancer. J Radiat Res. 2012;53:608–14.
Zelefsky MJ, Kollmeier M, Cox B, Fidaleo A, Sperling D, Pei X, et al. Improved clinical outcomes with high-dose image guided radiotherapy compared with non-IGRT for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;84:125–9.
Kupelian PA, Langen KM, Zeidan OA, Meeks SL, Willoughby TR, Wagner TH, et al. Daily variations in delivered doses in patients treated with radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:876–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
Informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
We have nothing to declare for this study.
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, M., Ikushima, H., Tominaga, M. et al. Dose impact of rectal gas on prostatic IMRT and VMAT. Jpn J Radiol 33, 723–733 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-015-0481-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-015-0481-7