Summary
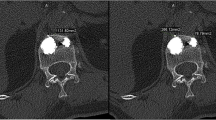
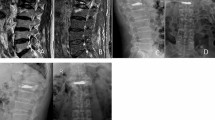
The clinical effects of two different methods–high-viscosity cement percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) and low-viscosity cement percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP) in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) were investigated. From June 2010 to August 2013, 98 cases of OVCFs were included in our study. Forty-six patients underwent high-viscosity PVP and 52 patients underwent low-viscosity PKP. The occurrence of cement leakage was observed. Pain relief and functional activity were evaluated using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), respectively. Restoration of the vertebral body height and angle of kyphosis were assessed by comparing preoperative and postoperative measurements of the anterior heights, middle heights and the kyphotic angle of the fractured vertebra. Nine out of the 54 vertebra bodies and 11 out of the 60 vertebra bodies were observed to have cement leakage in the high-viscosity PVP and low-viscosity PKP groups, respectively. The rate of cement leakage, correction of anterior vertebral height and kyphotic angles showed no significant differences between the two groups (P>0.05). Low-viscosity PKP had significant advantage in terms of the restoration of middle vertebral height as compared with the high-viscosity PVP (P<0.05). Both groups showed significant improvements in pain relief and functional capacity status after surgery (P<0.05). It was concluded that high-viscosity PVP and low-viscosity PKP have similar clinical effects in terms of the rate of cement leakage, restoration of the anterior vertebral body height, changes of kyphotic angles, functional activity, and pain relief. Low-viscosity PKP is better than high-viscosity PVP in restoring the height of the middle vertebra.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi X, Lu H, Tian F, et al. Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2014, 134(1): 21–30
Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, et al. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: Technical aspects. Am J Neuroradiol, 1997, 18(10): 1897–1904
Young C, Munk PL, Heran MK, et al. Treatment of severe vertebral body compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty. Skeletal Radiol, 2011, 40(12): 1531–1536
Baumann C, Fuchs H, Kiwit J, et al. Complications in percutaneous vertebroplasty associated with puncture or cement leakage. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2007, 30(2): 161–168
Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2001, 26(14): 1511–1515
Grohs JG, Matzner M, Trieb K, et al. Minimal invasive stabilization of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective nonrandomized comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech, 2005, 18(3): 238–242
Phillips FM, Todd Wetzel F, Lieberman I, et al. An in vivo3 comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2002, 27(19): 2173–2178
Gangi A, Guth S, Imbert JP, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indications, technique, and results. Radiographics, 2003, 23(2): e10
Yeom JS, Kim WJ, Choy WS, et al. Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2003, 85(1): 83–89
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2000, 25(8): 923–928
Baroud G, Crookshank M, Bohner M. High-viscosity cement significantly enhances uniformity of cement filling in vertebroplasty: an experimental model and study on cement leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2006, 31(22): 2562–2568
Loeffel M, Ferguson SJ, Nolte L-P, et al. Vertebroplasty: experimental characterization of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement spreading as a function of viscosity, bone porosity, and flow rate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2008, 33(12): 1352–1359
Gstöttner M, Angerer A, Rosiek R, et al. Quantitative volumetry of cement leakage in viscosity-controlled vertebroplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech, 2012, 25(5): E150–154
Schlaich C, Minne HW, Bruckner T, et al. Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int, 1998, 8(3): 261–267
Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2006, 31(17): 1983–2001
Shah RV. Sacral kyphoplasty for the treatment of painful sacral insufficiency fractures and metastases. Spine J, 2012, 12(2): 113–120
Santiago FR, Abela AP, Alvarez LG, et al. Pain and functional outcome after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. A comparative study. Eur J Radiol, 2010, 75(2): e108–e113
Yan D, Duan L, Li J, et al. Comparative study of percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2011, 131(5): 645–650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by Development Center for Medical Science and Technology, National Health and Family Planning Commission of China (No. W2012ZT15).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, K., Liu, Y., Peng, H. et al. A comparative study of high-viscosity cement percutaneous vertebroplasty vs. low-viscosity cement percutaneous kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 36, 389–394 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1597-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1597-4