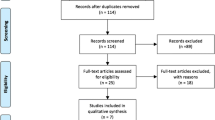
Summary
The rs10954213 polymorphism and the haplotype diversity in interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) play a special role in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) but with inconclusive results. We conducted a meta-analysis integrating case-control and haplotype variant studies in multiple ethnic populations to clearly discern the effect of these two variants on SLE. Eleven studies on the relation between rs10954213 polymorpisms in IRF5 and SLE were included and we selected a random effect model to calculate the pooled odds ratios (ORs) and the corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI). A total of 6982 cases and 8077 controls were involved in the meta-analysis. The pooled results indicated that A allele was significantly associated with increased risk of SLE as compared with the IRF5 rs10954213 G allele (A vs. G, P<0.00001) in all subjects. The same pattern of the results was also obtained in the European, African American, and Latin American. Asian population had a much lower prevalence of the A allele (49.1%) than any other population studied, and Europeans had the highest frequency of the IRF5 rs10954213 A allele (62.1%). The significant association of increased SLE risk and TCA haplotype was indicated in the contrast of TCA vs. TTA as the pooled OR was 2.14 (P=0.002). The same result was also found in the contrast of TCA vs. TTG as the pooled OR was 1.45 (P=0.004). This meta-analysis suggests that the A allele of rs10954213 and TCA haplotype (rs2004640-rs2070197-rs10954213) in IRF5 is associated with the increased risk of SLE in different ethnic groups, and its prevalence is ethnicity dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, et al. Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science, 2001,294(5546):1540–1543
Ronnblom L, Alm GV. A pivotal role for the natural interferon alpha-producing cells (plasmacytoid dendritic cells) in the pathogenesis of lupus. J Exp Med, 2001,194(12):F59–63
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003,100(5): 2610–2615
Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM. Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol, 2006,28(2):119–130
Obermoser G, Pascual V. The interferon-alpha signature of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 2010,19(9): 1012–1019
Crow MK. Interferon pathway activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep, 2005,7(6): 463–468
Petri M, Singh S, Tesfasyone H, et al. Longitudinal expression of type I interferon responsive genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 2009,18(11): 980–989
Banchereau J, Pascual V. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity, 2006,25(3):383–392
Kawasaki M, Fujishiro M, Yamaguchi A, et al. Possible role of the JAK/STAT pathways in the regulation of T cell-interferon related genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 2011,20(12):1231–1239
Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet, 2006,38(5):550–555
Graham RR, Kyogoku C, Sigurdsson S, et al. Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007,104(16):6758–6763
Ferreiro-Neira I, Calaza M, Alonso-Perez E, et al. Opposed independent effects and epistasis in the complex association of IRF5 to SLE. Genes Immun, 2007,8(5): 429–438
Kawasaki A, Kyogoku C, Ohashi J, et al. Association of IRF5 polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population: support for a crucial role of intron 1 polymorphisms. Arthritis Rheum, 2008,58(3): 826–834
Kelly JA, Kelley JM, Kaufman KM, et al. Interferon regulatory factor-5 is genetically associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in African Americans. Genes Immun, 2008,9(3):187–194
Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, et al. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol, 2001,19:623–655
Vuong MT, Gunnarsson I, Lundberg S, et al. Genetic risk factors in lupus nephritis and IgA nephropathy-no support of an overlap. PLoS One, 2010,5(5):e10559
Song WQ, Li HH, Chen HB, et al. Relationship between polymorphism sites of IRF5, TLR-9 and SLE patients in Shandong Han population. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2009,89(43):3038–3042
Löfgren SE, Yin H, Delgado-Vega AM, et al. Promoter insertion/deletion in the IRF5 gene is highly associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in distinct populations, but exerts a modest effect on gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Rheumatol, 2010,37(3):574–578
Hellquist A, Jarvinen TM, Koskenmies S, et al. Evidence for genetic association and interaction between the TYK2 and IRF5 genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol, 2009,36(8):1631–1638
Sigurdsson S, Goring HH, Kristjansdottir G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the genetic variants of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) reveals a novel 5 bp length polymorphism as strong risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet, 2008,17(6): 872–881
Reddy MV, Velazquez-Cruz R, Baca V, et al. Genetic association of IRF5 with SLE in Mexicans: higher frequency of the risk haplotype and its homozygozity than Europeans. Hum Genet, 2007,121(6):721–727
Kozyrev SV, Lewen S, Reddy PM, et al. Structural insertion/deletion variation in IRF5 is associated with a risk haplotype and defines the precise IRF5 isoforms expressed in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum, 2007,56(4):1234–1241
Siu HO, Yang W, Lau CS, et al. Association of a haplotype of IRF5 gene with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese. J Rheumatol, 2008,35(2): 360–362
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med, 2002,21(11):1539–1558
Zintzaras E, Chatzoulis DZ, Karabatsas CH, et al. The relationship between C677T methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism and retinopathy in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Hum Genet, 2005,50(6): 267–275
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ, 1997,315(7109):629–634
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomised clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials, 1996,17(1):1–12
Liu K, Liu J, Huang Y, et al. Alpha-adducin Gly460Trp polymorphism and hypertension risk: a meta-analysis of 22 studies including 14303 cases and 15961 controls. PLoS One, 2010,5(9):e13057
Hu W, Ren H. A meta-analysis of the association of IRF5 polymorphism with systemiclupus erythematosus. Int J Immunogenet, 2011,38(5): 411–417
Barnes BJ, Richards J, Mancl M, et al. Global and distinct targets of IRF-5 and IRF-7 during innate response to viral infection. J Biol Chem, 2004,279(43):45 194–45 207
Honda K, Yanai H, Takaoka A, et al. Regulation of the type I IFN induction: a current view. Int Immunol, 2005,17(11):1367–1378
Takaoka A, Yanai H, Kondo S, et al. Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature, 2005,434(7030):243–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
This study was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents from the Ministry of Education of China (No. NCET-09-0390).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Hf., An, Xj., Yang, Y. et al. Association of rs10954213 polymorphisms and haplotype diversity in interferon regulatory factor 5 with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 15–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1064-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1064-4