Abstract
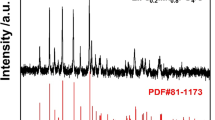
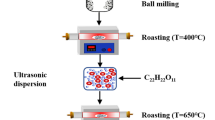
A comparison of electrochemical performance between LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C and LiMnPO4/C cathode materials was conducted in this paper. The cathode samples were synthesized by a nano-milling-assisted solid-state process using caramel as carbon sources. The prepared samples were investigated by XRD, SEM, TEM, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX), powder conductivity test (PCT), carbon-sulfur analysis, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and galvanostatic charge-discharge cycling. The results showed that LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C exhibited high specific capacity and high energy density. The initial discharge capacity of LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C was 163.6 mAh g−1 at 0.1C (1C = 160 mA g−1), compared to 112.3 mAh g−1 for LiMnPO4/C. Moreover, the Fe/Cr-substituted sample showed good cycle stability and rate performance. The capacity retention of LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C was 98.84 % over 100 charge-discharge cycles, while it was only 86.64 % for the pristine LiMnPO4/C. These results indicated that Fe/Cr substitution enhanced the electronic conductivity for the prepared sample and facilitated the Li+ diffusion in the structure. Furthermore, LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C composite presented high energy density (606 Wh kg−1) and high power density (574 W kg−1), thus suggested great potential application in lithium ion batteries (LIBs).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 144(4):1188–1194. doi:10.1149/1.1837571
Jang IC, Lim HH, Lee SB, Karthikeyan K, Aravindan V, Kang KS, Yoon WS, Cho WI, Lee YS (2010) Preparation of LiCoPO4 and LiFePO4 coated LiCoPO4 materials with improved battery performance. J Alloys Compd 497(1–2):321–324. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2010.03.055
L-e L, Liu J, Chen L, Xu H, Yang J, Qian Y (2013) Effect of different carbon sources on the electrochemical properties of rod-like LiMnPO4-C nanocomposites. RSC Advances 3(19):6847–6852. doi:10.1039/C3RA22862B
Aravindan V, Gnanaraj J, Lee Y-S, Madhavi S (2013) LiMnPO4—a next generation cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 1(11):3518–3539. doi:10.1039/C2TA01393B
Ong SP, Chevrier VL, Ceder G (2011) Comparison of small polaron migration and phase separation in olivine LiMnPO4 and LiFePO4 using hybrid density functional theory. Phys Rev B 83(7):075112. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.075112
Shang SL, Wang Y, Mei ZG, Hui XD, Liu ZK (2012) Lattice dynamics, thermodynamics, and bonding strength of lithium-ion battery materials LiMPO4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni): a comparative first-principles study. J Mater Chem 22(3):1142–1149. doi:10.1039/C1JM13547C
Oh S-M, Oh S-W, Yoon C-S, Scrosati B, Amine K, Sun Y-K (2010) High-performance carbon-LiMnPO4 nanocomposite cathode for lithium batteries. Adv Funct Mater 20(19):3260–3265. doi:10.1002/adfm.201000469
Zaghib K, Trudeau M, Guerfi A, Trottier J, Mauger A, Veillette R, Julien CM (2012) New advanced cathode material: LiMnPO4 encapsulated with LiFePO4. J Power Sources 204(0):177–181. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2011.11.085
Yoshida J, Stark M, Holzbock J, Hüsing N, Nakanishi S, Iba H, Abe H, Naito M (2013) Analysis of the size effect of LiMnPO4 particles on the battery properties by using STEM-EELS. J Power Sources 226(0):122–126. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2012.09.081
Fang H, Yi H, Hu C, Yang B, Yao Y, Ma W, Dai Y (2012) Effect of Zn doping on the performance of LiMnPO4 cathode for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 71:266–269. doi:10.1016/j.electacta. 2012.03.160
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Deng L (2012) Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiMnPO4/C via doping with Cu. Ionics 18(6):573–578. doi:10.1007/s11581-011-0655-y
Yi H, Hu C, He X, Xu H (2015) Electrochemical performance of LiMnPO4 by Fe and Zn co-doping for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 21(3):667–671. doi:10.1007/s11581-014-1238-5
Wang H, Yang Y, Liang Y, Cui L-F, Sanchez Casalongue H, Li Y, Hong G, Cui Y, Dai H (2011) LiMn1−xFexPO4 nanorods grown on graphene sheets for ultrahigh-rate-performance lithium ion batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(32):7364–7368. doi:10.1002/anie.201103163
Oh S-M, Jung H-G, Yoon CS, Myung S-T, Chen Z, Amine K, Sun Y-K (2011) Enhanced electrochemical performance of carbon–LiMn1−xFexPO4 nanocomposite cathode for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 196(16):6924–6928. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2010.11.159
Tan Z, Gao P, Cheng F, Luo H, Chen J, Zhou H, Tan S (2011) High power performance of multicomponent olivine cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Functional Materials Letters 04(03):299–303. doi:10.1142/S1793604711002111
Damen L, De Giorgio F, Monaco S, Veronesi F, Mastragostino M (2012) Synthesis and characterization of carbon-coated LiMnPO4 and LiMn1−xFexPO4 (x = 0.2, 0.3) materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 218:250–253. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2012.06.090
von Hagen R, Lorrmann H, Möller K-C, Mathur S (2012) Electrospun LiFe1−yMnyPO4/C nanofiber composites as self-supporting cathodes in Li-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 2(5):553–559. doi:10.1002/aenm.201100534
Zong J, Peng Q, Yu J, Liu X (2013) Novel precursor of Mn(PO3(OH))·3H2O for synthesizing LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode material. J Power Sources 228:214–219. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2012.11.103
Sahana MB, Vasu S, Sasikala N, Anandan S, Sepehri-Amin H, Sudakar C, Gopalan R (2014) Raman spectral signature of Mn-rich nanoscale phase segregations in carbon free LiFe1-xMnxPO4 prepared by hydrothermal technique. RSC Advances 4(110):64429–64437. doi:10.1039/C4RA11102H
Liu T, Xu J, Wu B, Xia Q, Wu X (2013) Porous LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4-C prepared by a thermal decomposition method as high performance cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. RSC Advances 3(32):13337–13341. doi:10.1039/C3RA41672K
Martha SK, Grinblat J, Haik O, Zinigrad E, Drezen T, Miners JH, Exnar I, Kay A, Markovsky B, Aurbach D (2009) LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4: an advanced cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(45):8559–8563. doi:10.1002/anie.200903587
Yamada A, Chung S-C (2001) Crystal chemistry of the olivine-type Li(Mn y Fe 1-y )PO4 and (Mn y Fe 1-y )PO4 as possible 4 V cathode materials for lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 148(8):A960. doi:10.1149/1.1385377
Yamada A, Kudo Y, Liu K-Y (2001) Phase diagram of Li x Mn y Fe 1−y PO4 (0≤x, y≤1). J ElectrochemSoc 148(10):A 1153. doi:10.1149/1.1401083
Li G, Azuma H, Tohda M (2002) Optimized LiMn y Fe1-y PO4 as the cathode for lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 149(6):A743. doi:10.1149/1.1473776
Zhang B, Wang X, Liu Z, Li H, Huang X (2010) Enhanced electrochemical performances of carbon coated mesoporous LiFe0.2Mn0.8PO4. JElectrochem. Soc 157(3):A285. doi:10.1149/1.3280230
Wang D, Ouyang C, Drézen T, Exnar I, Kay A, Kwon N-H, Gouerec P, Miners JH, Wang M, Grätzel M (2010) Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4 Via Mn-site substitution. J Electrochem Soc 157(2):A225. doi:10.1149/1.3271112
Liu J, Liu X, Huang T, Yu A (2012) Kinetics and electrochemical studies of Fe-substituted LiMnPO4. Int J Electrochem Sci 7(10):9859–9868
Shin HC, Park SB, Jang H, Chung KY, Cho WI, Kim CS, Cho BW (2008) Rate performance and structural change of Cr-doped LiFePO4/C during cycling. Electrochim Acta 53(27):7946–7951. doi:10.1016/j.electacta. 2008.06.005
Gan Y, Chen C, Liu J, Bian P, Hao H, Yu A (2015) Enhancing the performance of LiMnPO4/C composites through Cr doping. J Alloys Compd 620:350–357. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2014.09.160
Shi S, Liu L, Ouyang C, Wang D-s, Wang Z, Chen L, Huang X (2003) Enhancement of electronic conductivity of LiFePO4 by Cr doping and its identification by first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 68(19):195108. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.68.195108
Wu L, Zhong S, Lu J, Liu J, Lv F (2013) Synthesis of Cr-doped LiMnPO4/C cathode materials by sol–gel combined ball milling method and its electrochemical properties. Ionics 19(7):1061–1065. doi:10.1007/s11581-013-0919-9
Hong J, Wang F, Wang X, Graetz J (2011) LiFexMn1−xPO4: a cathode for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 196(7):3659–3663. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2010.12.045
Zhang L-L, Duan S, Peng G, Liang G, Zou F, Huang Y-H (2013) Novel synthesis of low carbon-coated Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 570:61–64. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2013.03.189
Xiang JY, Tu JP, Qiao YQ, Wang XL, Zhong J, Zhang D, Gu CD (2011) Electrochemical impedance analysis of a hierarchical CuO electrode composed of self-assembled nanoplates. J Phys Chem C 115(5):2505–2513. doi:10.1021/jp108261t
Park J, Moon WG, Kim G-P, Nam I, Park S, Kim Y, Yi J (2013) Three-dimensional aligned mesoporous carbon nanotubes filled with Co3O4 nanoparticles for Li-ion battery anode applications. Electrochim Acta 105:110–114. doi:10.1016/j.electacta. 2013.04.170
Cui Y, Zhao X, Guo R (2010) Improved electrochemical performance of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 and carbon co-coated LiFePO4 synthesized by freeze-drying process. Electrochim Acta 55(3):922–926. doi:10.1016/j.electacta. 2009.08.020
Subba Reddy CV, Chen M, Jin W, Zhu QY, Chen W, S-i M (2007) Characterization of (PVDF + LiFePO4) solid polymer electrolyte. J Appl Electrochem 37(5):637–642. doi:10.1007/s10800-007-9294-4
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the financial support with contract number 14520503100, 15ZZ095, 13PJ1407400, 21306113, and 201310-JD-B2-009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Zhang, D., Chang, C. et al. Electrochemical comparison of LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C and LiMnPO4/C cathode materials. Ionics 22, 1011–1019 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1633-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1633-6