Abstract
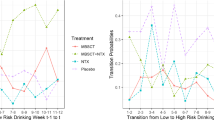
We use dynamical systems modeling to help understand how selected intra-personal factors interact to form mechanisms of behavior change in problem drinkers. Our modeling effort illustrates the iterative process of modeling using an individual’s clinical data. Due to the lack of previous work in modeling behavior change in individual patients, we build our preliminary model relying on our understandings of the psychological relationships among the variables. This model is refined and the psychological understanding is then enhanced through the iterative modeling process. Our results suggest that this is a promising direction in research in alcohol use disorders as well as other behavioral sciences.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks HT, Bekele-Maxwell K, Everett RA, Stephenson L, Kuerbis A, Shao S, Morgenstern J (2017) Dynamic modeling of behavior change in problem drinkers at the cohort level, In preparation
Banks HT, Catenacci J, Hu S (2016) Use of difference-based methods to explore statistical and mathematical model discrepancy in inverse problems. J Inverse Ill posed Probl 24:413–433
Banks HT, Hu S, Thompson WC (2014) Modeling and inverse problems in the presence of uncertainty. CRC Press, New York
Banks HT, Rehm KL, Sutton KL, Davis C, Hail L, Kuerbis A, Morgenstern J (2014) Dynamic modeling of behavior change. Q Appl Math 72:209–251
Banks HT, Tran HT (2009) Mathematical and experimental modeling of physical and biological processes. CRC Press, New York
Bisconti TL, Bergeman CS, Boker SM (2004) Emotional well-being in recently bereaved widows: a dynamical systems approach. J Gerontol Psychol Sci 59B:158–167
Boker SM, Laurenceau J-P (2006) Dynamical systems modeling: an application to the regulation of intimacy and disclosure in marriage. In: Walls TA, Schafer JL (eds) Models for intensive longitudinal data. Oxford University Press Inc, New York, pp 195–218
Boker SM, Molenar PCM, Nesselroade JR (2009) Issues in intraindividual variability: individual differences in equilibria and dynamics over multiple time scales. Psychol Aging 24:858–862
Centers for disease control and prevention, alcohol use and your health (2016). http://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/alcohol-use.htm
Chow S-M, Ram N, Boker SM, Fujita F, Clore G (2005) Emotion as a thermostat: representing emotion regulation using a damped oscillator model. Am Psychol Assoc 5:208–225
Likert R (1932) A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Arch Psychol 22:55
McLellan AT, Carise D, Kleber HD (2003) Can the national addiction treatment infrastructure support the public’s demand for quality care? J Subst Abus Treat 25:117–121
Molenaar PCM, Campbell CG (2009) The new person-specific paradigm in psychology. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 18:112–117
Montpetit MA, Bergeman CS, Deboeck PR, Tiberio SS, Boker SM (2010) Resilience-as-process: negative affect, stress, and coupled dynamical systems. Psychol Aging 25:631–640
Morgenstern J, Kuerbis AN, Chen AC, Kahler CW, Bux DA Jr, Kranzler HR (2012) A randomized clinical trial of naltrexone and behavioral therapy for problem drinking men who have sex with men. J Consult Clin Psychol 80:863–875
Morgenstern J, Kuerbis A, Houser J, Muench F, Shao S, Treloar H (2016) Within-person associations between daily motivation and self-efficacy and drinking among problem drinkers in treatment. Psychol Addict Behav 30:630–638
Moss HB, Chen CM, Yi H-Y (2007) Subtypes of alcohol dependence in a nationally representative sample. Drug Alcohol Depend 91:149–158
National institute for alcohol abuse and alcoholism, alcohol facts and statistics (2016). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/alcohol-facts-and-statistics
National institutes for health, all of us research program (2017). https://www.nih.gov/research-training/allofus-research-program
Newell KM, Molenaar PCM (1998) Applications of nonlinear dynamics to developmental process modeling. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc, New Jersey
Sacks J, Gonzales KR, Bouchery EE, Tomedi LE, Brewer RD (2010) national and state costs of excessive alcohol consumption. Am J Prev Med 49(2015):e73–e79
Sánchez F, Wang X, Castillo-Chávez C, Gorman DM, Gruenewald PJ (2007) Drinking as an epidemic—a simple mathematical model with recovery and relapse. In: Witkiewitz K, Marlatt GA (eds) Therapist’s guide to evidence-based relapse prevention. Elsevier Inc., San Diego, pp 353–368
Seber GAF, Wild CJ (2003) Nonlinear regression. Wiley, Hoboken
Stahre M, Roeber J, Kanny D, Brewer RD, Zhang X (2014) Contribution of excessive alcohol consumption to deaths and years of potential life lost in the United States. Prev Chronic Dis 11(11):130293. doi:10.5888/pcd11.130293
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism under Grant number 1R01AA022714-01A1, in part by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant number AFOSR FA9550-15-1-0298, and in part by the National Science foundation under NSF Undergraduate Biomathematics Grant number DBI-1129214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banks, H.T., Bekele-Maxwell, K., Everett, R.A. et al. Dynamic Modeling of Problem Drinkers Undergoing Behavioral Treatment. Bull Math Biol 79, 1254–1273 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-017-0282-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-017-0282-5