Abstract
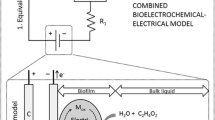
A multidimensional biofilm model is developed to simulate biofilm growth on the anode of a Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC). The biofilm is treated as a conductive material, and electrons produced during microbial growth are assumed to be transferred to the anode through a conductive biofilm matrix. Growth of Geobacter sulfurreducens is simulated using the Nernst–Monod kinetic model that was previously developed and later validated in experiments. By implementing a conduction-based biofilm model in two dimensions, we are able to explore the impact of anode density and arrangement on current production in a MFC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., & Sethian, J. (1995). A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys., 118(2), 269–277.
Alpkvist, E., & Klapper, I. (2007a). Description of mechanical response including detachment using a novel particle model of biofilm/flow interaction. Water Sci. Technol., 55(8–9), 265–273.
Alpkvist, E., & Klapper, I. (2007b). A multidimensional multispecies continuum model for heterogeneous biofilm development. Bull. Math. Biol., 69, 765–789.
Berk, R., & Canfield, J. (1964). Bioelectrochemical energy conversion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 12(1), 10.
Bond, D. R., & Lovley, D. R. (2003). Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69(3), 1548–1555.
Chambless, J. D., & Stewart, P. S. (2007). A three-dimensional computer model analysis of three hypothetical biofilm detachment mechanisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 97(6), 1573–1584.
Chopp, D. (2001). Some improvements of the fast marching method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 23, 230.
Clauwaert, P., Aelterman, P., Pham, T. H., De Schamphelaire, L., Carballa, M., Rabaey, K., & Verstraete, W. (2008). Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: The road to applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 79(6), 901–913.
Duddu, R., Bordas, S., Chopp, D. L., & Moran, B. (2008). A combined extended finite element and level set method for biofilm growth. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 74(5), 848–870.
Duddu, R., Chopp, D. L., & Moran, B. (2009). A two-dimensional continuum model of biofilm growth incorporating fluid flow and shear stress based detachment. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 103(1), 92–104.
Franks, A., Nevin, K., Jia, H., Izallalen, M., Woodard, T., & Lovley, D. (2009). Novel strategy for three-dimensional real-time imaging of microbial fuel cell communities: monitoring the inhibitory effects of proton accumulation within the anode biofilm. Energy Environ. Sci., 2(1), 113–119.
He, Z., Minteer, S., & Angenent, L. (2005). Electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39(14), 5262–5267.
Klapper, I., Rupp, C. J., Cargo, R., Purvedorj, B., & Stoodley, P. (2002). Viscoelastic fluid description of bacterial biofilm material properties. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 80(3), 289–296.
Lee, H., Torres, C., & Rittmann, B. (2009). Effects of substrate diffusion and anode potential on kinetic parameters for anode-respiring bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol., 43(19), 7571–7577.
LeVeque, R. J., & Li, Z. (1994). The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 31(4), 1019–1044.
Lide, D. R. (1990). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics (70th edn.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Logan, B., Call, D., Cheng, S., Hamelers, H., Sleutels, T., Jeremiasse, A., & Rozendal, R. (2008). Microbial electrolysis cells for high yield hydrogen gas production from organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol., 42(23), 8630–8640.
Logan, B., Cheng, S., Watson, V., & Estadt, G. (2007). Graphite fiber brush anodes for increased power production in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol., 41(9), 3341–3346.
Logan, B. E., Hamelers, B., Rozendal, R., Schroder, U., Keller, J., Freguia, S., Aelterman, P., Verstraete, W., & Rabaey, K. (2006). Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol., 40(17), 5181–5192.
Logan, B. E., & Regan, J. M. (2006a). Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol., 14(12), 512–518.
Logan, B. E., & Regan, J. M. (2006b). Microbial fuel cells-challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol., 40(17), 5172–5180.
Lovley, D. R. (2008). The microbe electric: Conversion of organic matter to electricity. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 19(6), 564–571.
Marcus, A., Torres, C., & Rittmann, B. (2010). Evaluating the impacts of migration in the biofilm anode using the model PCBIOFILM. Electrochim. Acta, 55, 6964–6972.
Marcus, A., Torres, C., & Rittmann, B. (2011). Analysis of a microbial electrochemical cell using the proton condition in biofilm (PCBIOFILM) model. Bioresour. Technol., 102(1), 253–262.
Marcus, A. K., Torres, C. I., & Rittmann, B. E. (2007). Conduction-based modeling of the biofilm anode of a microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 98(6), 1171–1182.
Merkey, B. V., Rittmann, B. E., & Chopp, D. L. (2009). Modeling how soluble microbial products (SMP) support heterotrophic bacteria in autotroph-based biofilms. J. Theor. Biol., 259(4), 670–683.
Min, B., Kim, J., Oh, S., Regan, J., & Logan, B. (2005). Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res., 39(20), 4961–4968.
Morgenroth, E., & Wilderer, P. A. (2000). Influence of detachment mechanisms on competition in biofilms. Water Res., 34(2), 417–426.
Osher, S., & Sethian, J. (1988). Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys., 79(1), 12–49.
Picioreanu, C., Kreft, J. U., Klausen, M., Haagensen, J. A. J., Tolker-Nielsen, T., & Molin, S. (2007). Microbial motility involvement in biofilm structure formation—a 3D modelling study. Water Sci. Technol., 55(8–9), 337–343.
Picioreanu, C., van Loosdrecht, M., Curtis, T., & Scott, K. (2010). Model based evaluation of the effect of pH and electrode geometry on microbial fuel cell performance. Bioelectrochemistry, 78(1), 8–24.
Picioreanu, C., van Loosdrecht, M. C., & Heijnen, J. J. (1999). Discrete-differential modelling of biofilm structure. Water Sci. Technol., 39(7), 115–122.
Picioreanu, C., van Loosdrecht, M. C., & Heijnen, J. J. (2001). Two-dimensional model of biofilm detachment caused by internal stress from liquid flow. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 72(2), 205–218.
Pozrikidis, C. (1997). Introduction to theoretical and computational fluid dynamics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Reguera, G., Nevin, K., Nicoll, J., Covalla, S., Woodard, T., & Lovley, D. (2006). Biofilm and nanowire production leads to increased current in Geobacter sulfurreducens fuel cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72(11), 7345.
Rittmann, B. E. (1982). The effect of shear stress on biofilm loss rate. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 24(2), 501–506.
Rittmann, B. E., & McCarty, P. L. (2001). Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Rittmann, B. E., Torres, C. I., & Marcus, A. K. (2008). Understanding the distinguishing features of a microbial fuel cell as a biomass-based renewable energy technology. In V. Shah (Ed.), Emerging environmental technologies (pp. 1–28). Berlin: Springer.
Smith, B. G., Vaughan, B. L., & Chopp, D. L. (2007). The eXtended Finite Element Method for boundary layer problems in biofilm growth. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci., 2(1), 35–56.
Stewart, P. (2003). Diffusion in biofilms. J. Bacteriol., 185(5), 1485.
Tender, L., Reimers, C., Stecher, H., Holmes, D., Bond, D., Lowy, D., Pilobello, K., Fertig, S., & Lovley, D. (2002). Harnessing microbially generated power on the seafloor. Nat. Biotechnol., 20(8), 821–825.
Torres, C., Krajmalnik-Brown, R., Parameswaran, P., Marcus, A., Wanger, G., Gorby, Y., & Rittmann, B. (2009). Selecting anode-respiring bacteria based on anode potential: Phylogenetic, electrochemical, and microscopic characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol., 43(24), 9519–9524.
Torres, C., Marcus, A., Lee, H., Parameswaran, P., Krajmalnik-Brown, R., & Rittmann, B. (2010). A kinetic perspective on extracellular electron transfer by anode-respiring bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 34(1), 3–17.
Torres, C., Marcus, A., Parameswaran, P., & Rittmann, B. (2008a). Kinetic experiments for evaluating the Nernst–Monod model for anode-respiring bacteria (ARB) in a biofilm anode. Environ. Sci. Technol., 42(17), 6593–6597.
Torres, C., Marcus, A., & Rittmann, B. (2008b). Proton transport inside the biofilm limits electrical current generation by anode-respiring bacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 100(5), 872–881.
Vaughan, B., Smith, B., & Chopp, D. (2010). The influence of fluid flow on modeling quorum sensing in bacterial biofilms. Bull. Math. Biol., 72, 1143–1165.
Wanner, O., Eberl, H., van Loosdrecht, M., Morgenroth, E., Noguera, D., Picioreanu, C., & Rittmann, B. (2006). Mathematical modeling of biofilms. Technical report, International Water Association.
Wanner, O., & Gujer, W. (1986). A multispecies biofilm model. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 28, 314–328.
Wäsche, S., Horn, H., & Hempel, D. C. (2002). Influence of growth conditions on biofilm development and mass transfer at the bulk/biofilm interface. Water Res., 36(19), 4775–4784.
Xavier, J., Picioreanu, C., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. (2005). A general description of detachment for multidimensional modelling of biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 91(6), 651–669.
Zhang, X.-C., & Halme, A. (1995). Modelling of a microbial fuel cell process. Biotech. Lett., 17(8), 809–814.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merkey, B.V., Chopp, D.L. The Performance of a Microbial Fuel Cell Depends Strongly on Anode Geometry: A Multidimensional Modeling Study. Bull Math Biol 74, 834–857 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9690-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9690-0