Abstract
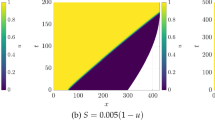
Since its conception in 1952, the Turing paradigm for pattern formation has been the subject of numerous theoretical investigations. Experimentally, this mechanism was first demonstrated in chemical reactions over 20 years ago and, more recently, several examples of biological self-organisation have also been implicated as Turing systems. One criticism of the Turing model is its lack of robustness, not only with respect to fluctuations in the initial conditions, but also with respect to the inclusion of delays in critical feedback processes such as gene expression. In this work we investigate the possibilities for Turing patterns on growing domains where the morphogens additionally regulate domain growth, incorporating delays in the feedback between signalling and domain growth, as well as gene expression. We present results for the proto-typical Schnakenberg and Gierer–Meinhardt systems: exploring the dynamics of these systems suggests a reconsideration of the basic Turing mechanism for pattern formation on morphogen-regulated growing domains as well as highlighting when feedback delays on domain growth are important for pattern formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdreeff, M., Goodrich, D. W., & Pardee, A. B. (2000). Cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. In The Holland-frei cancer medicine (5th edn.). New York: Decker.
Affolter, M., & Basler, K. (2007). The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet., 8, 663–674.
Al-Dewachi, H. S., Appleton, D. R., Watson, A. J., & Wright, N. A. (1977). Variation in the cell cycle time in the crypts of Lieberkiihn of the mouse. Virchows Arch., B Pathol., 31, 37–44.
Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Walter, P., Lewis, J., Raff, M., & Roberts, K. (2002). Molecular biology of the cell (5th edn.). New York: Garland Science.
Baker, R. E., & Maini, P. K. (2007). A mechanism for morphogen-controlled domain growth. J. Math. Biol., 54, 597–622.
Capdevila, J., & Belmonte, J. C. I. (2001). Patterning mechanisms controlling vertebrate limb development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 17, 87–132.
Chiorino, G., Metz, J. A. J., Tomasoni, D., & Ubezio, P. (2001). Desynchronization rate in cell populations: mathematical modeling and experimental data. J. Theor. Biol., 208, 185–199.
Chisholm, J. C. (1998). Analysis of the fifth cell cycle of mouse development. J. Reprod. Fertil., 84, 29–36.
Crampin, E. J., Gaffney, E. A., & Maini, P. K. (1999). Reaction and diffusion on growing domains: scenarios for robust pattern formation. Bull. Math. Biol., 61, 1093–1120.
Crampin, E. J., Hackborn, W. W., & Maini, P. K. (2002). Pattern formation in reaction–diffusion models with nonuniform domain growth. Bull. Math. Biol., 64, 747–769.
Dillon, R., & Othmer, H. G. (1999). A mathematical model for outgrowth and spatial patterning of the vertebrate limb bud. J. Theor. Biol., 197, 295–330.
Entchev, E. V., Schwabedissen, A., & Gonzalez-Gaitan, M. (2000). Gradient formation of the TGF-β homolog Dpp. Cell, 103, 981–991.
Fischer, J. A., Eun, S. H., & Doolan, B. T. (2006). Endocytosis, endosome trafficking, and the regulation of Drosophila development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 22, 181–206.
Gaffney, E. A., & Monk, N. A. M. (2006). Gene expression time delays and Turing pattern formation systems. Bull. Math. Biol., 68, 99–130.
Gierer, A., & Meinhardt, H. (1972). A theory of biological pattern formation. Kybernetik, 12, 30–39.
Gray, P., & Scott, S. K. (1983). Autocatalytic reactions in the isothermal, continuous stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci., 38, 29–43.
Jones, C. M., Armes, N., & Smith, J. C. (1996). Signalling by TGF-β family members: short-range effects of Xnr-2 and BMP-4 contrast with the long-range effects of activin. Curr. Biol., 6, 1468–1475.
Kimmel, C. B., Ballard, W. W., Kimmel, S. R., Ullmann, B., & Schilling, T. F. (1995). Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn., 203, 253–310.
Kondo, S., & Asai, R. (1995). A reaction-diffusion wave on the skin of the marine angelfish Pomacanthus. Nature, 376, 765–768.
Kondo, S., Iwashita, M., & Yamaguchi, M. (2009). How animals get their skin patterns: fish pigment pattern as a live Turing wave. Int. J. Dev. Biol., 53, 851–856.
Lewis, J. (2003). Autoinhibition with transcriptional delay: A simple mechanism for the zebrafish somitogenesis oscillator. Curr. Biol., 13, 1398–1408.
Miura, T., & Shiota, K. (2000a). Extracellular matrix environment influences chondrogenic pattern formation in limb bud micromass culture: Experimental verification of theoretical models. Anat. Rec., 258, 100–107.
Miura, T., & Shiota, K. (2000b). TGFβ2 acts as an activator molecule in a reaction–diffusion model and is involved in cell sorting phenomenon in mouse limb micromass culture. Dev. Dyn., 217, 241–249.
Mou, C., Jackson, B., Schneider, P., Overbeek, P. A., & Headon, D. J. (2006). Generation of the primary hair follicle pattern. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 9075–9080.
Murray, J. D. (1993). Mathematical biology (2nd edn.). Berlin: Springer.
Nakamasu, A., Takahashi, G., Kanbe, A., & Kondo, S. (2009). Interactions between zebrafish pigment cells responsible for the generation of Turing patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 8429–8434.
Neville, A., Matthews, P., & Byrne, H. M. (2006). Interactions between pattern formation and domain growth. Bull. Math. Biol., 68, 1975–2003.
Pardee, A. B. (1974). A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 71, 1286–1290.
Piddini, E., & Vincent, J. (2003). Modulation of developmental signals by endocytosis: different means and many ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 15, 474–481.
Ramis, J. M., Collart, C., & Smith, J. C. (2007). Xnrs and Activin regulate distinct genes during Xenopus development: Activin regulates cell division. PLoS ONE, 2, e213.
Rogulja, D., & Irvine, K. D. (2005). Regulation of cell proliferation by a morphogen gradient. Cell, 123, 449–461.
Roy, C. L., & Wrana, J. L. (2005). Clathrin- and nonclathrin-mediated endocytic regulation of cell signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 6, 112–126.
Sakuma, R., Ohnishi, Y., Meno, C., Fujii, H., Juan, H., Takeuchi, J., Ogura, T., Li, E., Miyazono, K., & Hamada, H. (2002). Inhibition of Nodal signalling by Lefty mediated through interaction with common receptors and efficient diffusion. Genes Cells, 7, 401–412.
Schnakenberg, J. (1979). Simple chemical reaction systems with limit cycle behaviour. J. Theor. Biol., 81, 389–400.
Seirin-Lee, S., & Gaffney, E. A. (2010). Aberrant behaviours of reaction diffusion self-organisation models on growing domains in the presence of gene expression time delays. Bull. Math. Biol., 72, 2161–2179.
Seirin-Lee, S., Gaffney, E. A., & Monk, N. A. M. (2010). The influence of gene expression time delays on Gierer-Meinhardt pattern formation systems. Bull. Math. Biol., 72, 2139–2160.
Shraiman, B. I. (2005). Mechanical feedback as a possible regulator of tissue growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 3318–3323.
Sick, S., Reinker, S., Timmer, J., & Schlake, T. (2006). WNT and DKK determine hair follicle spacing through a reaction–diffusion mechanism. Science, 314(5804), 1447–1450.
Solnica-Krezel, L. (2003). Vertebrate development: Taming the nodal waves. Curr. Biol., 13, R7–R9.
Sorkin, A., & von Zastrow, M. (2002). Signal transduction and endocytosis: close encounters of many kinds. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 600–614.
Tabata, T., & Takei, Y. (2004). Morphogens, their identification and regulation. Development, 131, 703–712.
Tennyson, C. N., Klamut, H. J., & Worton, R. G. (1995). The human dystrophin gene requires 16 hr to be transcribed and is cotranscriptionally spliced. Nat. Genet., 9, 184–190.
Turing, A. M. (1952). The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, 237, 37–72.
Wolfe, S. L. (1995). Introduction to cell and molecular biology. Belmont: Wadsworth.
Zetterberg, A., Larsson, O., & Wiman, K. G. (1995). What is the restriction point? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 7, 835–842.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seirin Lee, S., Gaffney, E.A. & Baker, R.E. The Dynamics of Turing Patterns for Morphogen-Regulated Growing Domains with Cellular Response Delays. Bull Math Biol 73, 2527–2551 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9634-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9634-8