Abstract
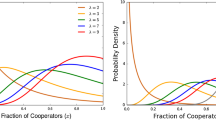
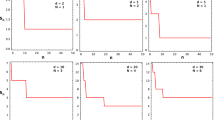
Classical replicator dynamics assumes that individuals play their games and adopt new strategies on a global level: Each player interacts with a representative sample of the population and if a strategy yields a payoff above the average, then it is expected to spread. In this article, we connect evolutionary models for infinite and finite populations: While the population itself is infinite, interactions and reproduction occurs in random groups of size N. Surprisingly, the resulting dynamics simplifies to the traditional replicator system with a slightly modified payoff matrix. The qualitative results, however, mirror the findings for finite populations, in which strategies are selected according to a probabilistic Moran process. In particular, we derive a one-third law that holds for any population size. In this way, we show that the deterministic replicator equation in an infinite population can be used to study the Moran process in a finite population and vice versa. We apply the results to three examples to shed light on the evolution of cooperation in the iterated prisoner’s dilemma, on risk aversion in coordination games and on the maintenance of dominated strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, G., & Kuperman, M. (2001). Social games in a social network. Phys. Rev. E, 63, 030901.
Antal, T., Traulsen, A., Ohtsuki, H., Tarnita, C. E., & Nowak, M. A. (2009). Mutation-selection equilibrium in games with multiple strategies. J. Theor. Biol., 258, 614–622.
Axelrod, R. (1984). The evolution of cooperation. New York: Basic Books.
Battalio, R., Samuelson, L., & Van Huyck, J. (2001). Optimization incentives and coordination failure in laboratory stag hunt games. Econometrica, 69, 749–764.
Bomze, I., & Pawlowitsch, C. (2008). One-third rules with equality: Second-order evolutionary stability conditions in finite populations. J. Theor. Biol., 254, 616–620.
Boyd, R., Gintis, H., & Bowles, S. (2010). Coordinated punishment of defectors sustains cooperation and can proliferate when rare. Science, 328, 617–620.
Brandt, H., Hauert, C., & Sigmund, K. (2006). Punishing and abstaining for public goods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 495–497.
Cooper, R. W., DeJong, D. V., Forsythe, R., & Ross, T. W. (1990). Selection criteria in coordination games: Some experimental results. Am. Econ. Rev., 80, 218–233.
Dieckmann, U., Heino, M., & Parvinen, K. (2006). The adaptive dynamics of function-valued traits. J. Theor. Biol., 241, 370–389.
Dugatkin, L. A., & Reeve, H. K. (Eds.) (1998). Game theory and animal behaviour. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Durrett, R., & Levin, S. A. (1994). Stochastic spatial models: A user’s guide to ecological applications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci., 343, 329–350.
Falster, D. S., & Westoby, M. (2003). Plant height and evolutionary games. Trends Ecol. Evol., 18, 337–343.
Fehr, E., & Gächter, S. (2000). Cooperation and punishment in public goods experiments. Am. Econ. Rev., 90, 980–994.
Friedman, D. (1996). Equilibrium in evolutionary games: Some experimental results. Econ. J., 106, 1–25.
Fudenberg, D., & Imhof, L. A. (2006). Imitation processes with small mutations. J. Econ. Theory, 131, 252–262.
Fudenberg, D., & Tirole, J. (1991). Game theory. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Geritz, S., Kisdi, E., Meszéna, G., & Metz, J. (1998). Evolutionarily singular strategies and the adaptive growth and branching of the evolutionary tree. Evol. Ecol., 12, 35–57.
Gintis, H., Bowles, S., Boyd, R. T., & Fehr, E. (Eds.) (2005). Moral sentiments and material interests—the foundations of cooperation in economic life. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Gokhale, C., & Traulsen, A. (2010). Evolutionary games in the multiverse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 5500–5504.
Harsanyi, J., & Selten, R. (1988). A general theory of equilibrium selection in games. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Hauert, C., & Doebeli, M. (2004). Spatial structure often inhibits the evolution of cooperation in the snowdrift game. Nature, 428, 643–646.
Helbing, D., & Yu, W. (2009). The outbreak of cooperation among success-driven individuals under noisy conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 3680–3685.
Hilbe, C., & Sigmund, K. (2010). Incentives and opportunism: From the carrot to the stick. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci., 277, 2427–2433.
Hofbauer, J. (1981). On the occurrence of limit cycles in the Volterra-Lotka equation. Nonlinear Anal., 5, 1003–1007.
Hofbauer, J., & Sigmund, K. (2003). Evolutionary game dynamics. Bull. Am. Math. Soc., 40, 479–519.
Hofbauer, J., & Sigmund, K. (1994). Adaptive dynamics and evolutionary stability. Appl. Math. Lett., 7, 65–70.
Hofbauer, J., & Sigmund, K. (1998). Evolutionary games and population dynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Holt, C. A., & Laury, S. K. (2002). Risk aversion and incentive effects. Am. Econ. Rev., 92, 1644–1655.
Imhof, L. A., Fudenberg, D., & Nowak, M. A. (2005). Evolutionary cycles of cooperation and defection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 10797–10800.
Kahnemann, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47, 263–291.
Lehmann, L., Keller, L., & Sumpter, D. (2007). The evolution of helping and harming on graphs: The return of inclusive fitness effect. J. Evol. Biol., 20, 2284–2295.
Lessard, S. (2005). Long-term stability from fixation probabilities in finite populations: New perspectives for ESS theory. Theor. Popul. Biol., 68, 19–27.
Lessard, S., & Ladret, V. (2007). The probability of fixation of a single mutant in an exchangeable selection model. J. Math. Biol., 54, 721–744.
Lieberman, E., Hauert, C., & Nowak, M. A. (2005). Evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Nature, 433, 312–316.
Maynard Smith, J. (1982). Evolution and the theory of games. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Maynard Smith, J. (1988). Can a mixed strategy be stable in a finite population? J. Theor. Biol., 130, 209–221.
Nakamaru, M., & Iwasa, Y. (2006). The coevolution of altruism and punishment: Role of the selfish punisher. J. Theor. Biol., 240, 475–488.
Nakamaru, M., Matsuda, H., & Iwasa, Y. (1997). The evolution of cooperation in a lattice-structured population. J. Theor. Biol., 184, 65–81.
Nakamaru, M., Nogami, H., & Iwasa, Y. (1998). Score-dependent fertility model for the evolution of cooperation in a lattice. J. Theor. Biol., 194, 101–124.
Niyogi, P. (2006). The computational nature of language learning and evolution. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Nowak, M. A., & May, R. M. (1992). Evolutionary games and spatial chaos. Nature, 359, 826–829.
Nowak, M. A., & Sigmund, K. (2004). Evolutionary dynamics of biological games. Science, 303, 793–799.
Nowak, M. A., Sasaki, A., Taylor, C., & Fudenberg, D. (2004). Emergence of cooperation and evolutionary stability in finite populations. Nature, 428, 646–650.
Nowak, M. A., Tarnita, C. E., & Antal, T. (2010). Evolutionary dynamics in structured populations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci., 365, 19–30.
Ohtsuki, H., & Nowak, M. A. (2008). Evolutionary stability on graphs. J. Theor. Biol., 251, 698–707.
Ohtsuki, H., & Nowak, M. A. (2006). The replicator equation on graphs. J. Theor. Biol., 243, 86–97.
Ohtsuki, H., Hauert, C., Lieberman, E., & Nowak, M. A. (2006). A simple rule for the evolution of cooperation on graphs and social networks. Nature, 441, 502–505.
Ohtsuki, H., Bordalo, P., & Nowak, M. A. (2007a). The one-third law of evolutionary dynamics. J. Theor. Biol., 249, 289–295.
Ohtsuki, H., Nowak, M. A., & Pacheco, J. M. (2007b). Breaking the symmetry between interaction and replacement in evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 108106.
Ohtsuki, H., Pacheco, J. M., & Nowak, M. A. (2007c). Evolutionary graph theory: Breaking the symmetry between interaction and replacement. J. Theor. Biol., 246, 681–694.
Pfeiffer, T., & Schuster, S. (2005). Game-theoretical approaches to studying the evolution of biochemical systems. Trends Biochem. Sci., 30, 20–25.
Pinker, S., Nowak, M. A., & Lee, J. J. (2008). The logic of indirect speech. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105, 833–838.
Platt, M. L., & Huettel, S. A. (2008). Risky business: The neuroeconomics of decision making under uncertainty. Nat. Neurosci., 11, 398–403.
Rand, D. G., Armao IV, J. J., Nakamaru, M., & Ohtsuki, H. (2010). Anti-social punishment can prevent the co-evolution of punishment and cooperation. J. Theor. Biol., 265, 624–632.
Roca, C. P., Cuesta, J. A., & Sánchez, A. (2006). Time scales in evolutionary dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett., 97, 158701.
Sánchez, A., & Cuesta, J. A. (2005). Altruism may arise from individual selection. J. Theor. Biol., 235, 233–240.
Santos, F., Santos, M., & Pacheco, J. (2008). Social diversity promotes the emergence of cooperation in public goods games. Nature, 454, 213–216.
Schaffer, M. E. (1988). Evolutionarily stable strategies for a finite population and a variable contest size. J. Theor. Biol., 132, 469–478.
Sigmund, K. (2010). The calculus of selfishness. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Straub, P. G. (1995). Risk dominance and coordination failures in static games. Q. Rev. Econ. Finance, 35, 339–363.
Szabó, G., & Fáth, G. (2007). Evolutionary games on graphs. Phys. Rep., 446, 97–216.
Tarnita, C., Antal, T., & Nowak, M. A. (2009). Mutation-selection equilibrium in games with mixed strategies. J. Theor. Biol., 261, 50–57.
Taylor, C., Fudenberg, D., Sasaki, A., & Nowak, M. A. (2004). Evolutionary game dynamics in finite populations. Bull. Math. Biol., 66, 1621–1644.
Taylor, P., & Jonker, L. (1978). Evolutionary stable strategies and game dynamics. Math. Biosci., 40, 145–156.
Traulsen, A., Claussen, J. C., & Hauert, C. (2005). Coevolutionary dynamics: From finite to infinite populations. Phys. Rev. Lett., 95, 238701.
Traulsen, A., Claussen, J. C., & Hauert, C. (2006). Coevolutionary dynamics in large, but finite populations. Phys. Rev. E, 74, 0119901.
Traulsen, A., Nowak, M. A., & Pacheco, J. M. (2007). Stochastic payoff evaluation increases the temperature of selection. J. Theor. Biol., 244, 349–356.
Traulsen, A., Semmann, D., Sommerfeld, R. D., Krambeck, H.-J., & Milinski, M. (2010). Human strategy updating in evolutionary games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 2962–2966.
Uchida, S., & Sigmund, K. (2010). The competition of assessment rules for indirect reciprocity. J. Theor. Biol., 263, 13–19.
Weibull, J. (1995). Evolutionary game theory. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Wild, G., & Taylor, P. D. (2004). Fitness and evolutionary stability in game theoretic models of finite populations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci., 271, 2345–2349.
Wölfing, B., & Traulsen, A. (2009). Stochastic sampling of interaction partners versus deterministic payoff assignment. J. Theor. Biol., 257, 689–695.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilbe, C. Local Replicator Dynamics: A Simple Link Between Deterministic and Stochastic Models of Evolutionary Game Theory. Bull Math Biol 73, 2068–2087 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9608-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9608-2