Abstract
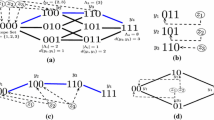
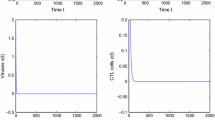
We study the global stability of a class of models for in-vivo virus dynamics that take into account the Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte immune response and display antigenic variation. This class includes a number of models that have been extensively used to model HIV dynamics. We show that models in this class are globally asymptotically stable, under mild hypothesis, by using appropriate Lyapunov functions. We also characterise the stable equilibrium points for the entire biologically relevant parameter range. As a by-product, we are able to determine what is the diversity of the persistent strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asquith, B., Bangham, C.R.M. (2003). An introduction to lymphocyte and viral dynamics: the power and limitations of mathematical analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B: Biol. Sci., 270(1525), 1651–1657.
Bocharov, G.A., Romanyukha, A.A. (1994). Mathematical-model of antiviral immune-response-iii–influenza-A Virus-infection. J. Theor. Biol., 167(4), 323–360.
Bonhoeffer, S., et al. (1997). Virus dynamics and drug therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 6971–6974.
de Leenheer, P., Smith, H.L. (2003). Virus dynamics: a global analysis. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 63, 1313–1327.
Janeway, C., et al. (2004). Immunobiology (6th ed.). New York: Garland Science.
Kooi, B., Hanegraaf, P. (2001). Bi-trophic food chain dynamics with multiple component populations. Bull. Math. Biol., 63(2), 271–299.
Kooi, B., et al. (1998). On the use of the logistic equation in models of food chains. Bull. Math. Biol., 60, 231–246.
Korobeinikov, A. (2004a). Global properties of basic virus dynamics models. Bull. Math. Biol., 66, 879–883.
Korobeinikov, A. (2004b). Lyapunov functions and global properties for SEIR and SEIS epidemic models. Math. Med. Biol., 21(2), 75–83.
Korobeinikov, A. (2009). Global asymptotic properties of virus dynamics models with dose-dependent parasite reproduction and virulence and non-linear incidence rate. Math. Med. Biol., 26, 225–239.
Korebeinikov, A., Wake, G.C. (1999). Global properties of three-dimensional predator-prey models. J. Appl. Math. Decis. Sci., 3(2), 155–162.
LaSalle, J.P. (1964). Recent advances in Liapunov stability theory. SIAM Rev., 6, 1–11.
Li, M.Y., Muldowney, J.S. (1995). Global stability for the seir model in epidemiology. Math. Biosci., 125(2), 155–164.
Marchuk, G.I., et al. (1991). Mathematical-model of antiviral immune-response. 2. Parameters identification for acute viral Hepatitis-B. J. Theor. Biol., 151(1), 41–70.
Neumann, A.U., et al. (1998). Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy. Science, 282(5386), 103–107.
Nowak, M.A., Bangham, C.R.M. (1996). Population dynamics of immune responses to persitent viruses. Science, 272, 74–79.
Nowak, M.A., May, R.M. (2000). Virus dynamics: mathematical principles of immunology and virology. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Pastore, D.H. (2005). A Dinâmica no sistema imunológico na presença de mutação. Ph.D. thesis, IMPA.
Perelson, A.S., Nelson, P.W. (1999). Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev., 41, 3–44.
Perelson, A.S., et al. (1993). Dynamics of HIV-infection of Cd4+ T-cells. Math. Biosci., 114(1), 81–125.
Perelson, A.S., et al. (1996). HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science, 271(5255), 1582–1586.
Roy, A.B., Solimano, F. (1986). Global stability of partially closed food-chains with resources. Bull. Math. Biol., 48(5–6), 455–468.
Smith, H.L. (1995). Monotone dynamical systems. Providence: AMS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors thank an anonymous referee for suggesting that an early version of Theorem 1 could be extended as presented here. MOS is partially supported by FAPERJ grants 170.382/2006 and 110.174/2009, and by CNPq grant 309616/2009-3. JPZ was supported by CNPq under grants 302161/2003-1 and 474085/2003-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souza, M.O., Zubelli, J.P. Global Stability for a Class of Virus Models with Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Immune Response and Antigenic Variation. Bull Math Biol 73, 609–625 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9543-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9543-2