Abstract
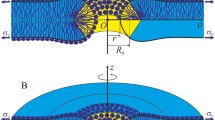
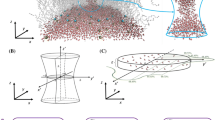
Thermally-induced fluctuations of individual phospholipids in a bilayer lipid membrane (BLM) are converted into collective motions due to the intermolecular interactions. Here, we demonstrate that transbilayer stochastic pores can be generated via collective thermal movements (CTM). Using the elastic theory of continuous media applied to smectic-A liquid crystals, we estimate the pore radius and the energetic requirements for pore appearance. Three types of thermally-induced transbilayer pores could be formed through BLMs: open and stable, open and unstable, and closed. In most of the situations, two open and stable pores with different radii could be generated. Notably, the two pores have the same generation probability. Unstable pores are possible to appear across thin bilayers that contain phospholipids with a large polar headgroup. Closed pores are present throughout the cases that we have inspected. The effects of hydrophobic thickness, polar headgroup size of phospholipids, temperature, surface tension, and elastic compression on the pore formation and pore stability have been examined as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benz, R., Frohlich, O., Lauger, P., Montal, M., 1975. Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 394, 323–334.
Boal, D.H., 2001. Mechanics of the Cell. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Bordi, F., Cametti, C., Motta, A., 2000. Ion permeation across model lipid membranes: A kinetic approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 5318–5323.
Bordi, F., Cametti, C., Naglieri, A., 1999. Ion transport in lipid bilayer membranes through aqueous pores. Coll. Surf. A 159, 231–237.
De Gennes, P.-G., 1974. The Physics of Liquid Crystals. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Engelhardt, H., Duwe, H.P., Sackmann, E., 1985. Bilayer bending elasticity measured by fourier-analysis of thermally excited surface undulations of flaccid vesicles. J. Phys. Lett. 46, L395–L400.
Farago, O., 2003. “Water-free” computer model for fluid bilayer membranes. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 596–605.
Farago, O., Santangelo, C.D., 2005. Pore formation in fluctuating membranes. J. Chem. Phys. 122, 1606–1612.
Fournier, L., Joos, B., 2003. Lattice model for the kinetics of rupture of fluid bilayer membranes. Phys. Rev. E 67, 5190–5197.
Freeman, S.A., Wang, M.A., Weaver, J.C., 1994. Theory of electroporation of planar Bilayer-membranes: Predictions of the aqueous area, change in capacitance, and pore–pore separation. Biophys. J. 67, 42–56.
Hanke, W., Schlue, W.-R., 1993. Planar Lipid Bilayers. Methods and Applications. Academic Press, London, UK.
Helfrich, W., 1973. Elastic properties of lipid Bilayers: Theory and possible experiments. Z. Naturforsch. C28, 693–703.
Helfrich, P., Jakobsson, E., 1990. Calculation of deformation energies and conformations in liquid membranes containing gramicidin channels. Biophys. J. 57, 1075–1084.
Hladky, S.B., Gruen, D.W.R., 1982. Thickness fluctuations in black lipid-membranes. Biophys. J. 38, 251–258.
Hladky, S.B., Gruen, D.W.R., 1984. Energetics of fluctuation in lipid Bilayer thickness—response. Biophys. J. 45, 645–646.
Holthuis, J.C.M., van Meer, G., Huitema, K., 2003. Lipid microdomains, lipid translocation and the organization of intracellular membrane transport (Review). Mol. Membrane Biol. 20, 231–241.
Huang, H.W., 1986. Deformation free-energy of Bilayer-membrane and its effect on gramicidin channel lifetime. Biophys. J. 50, 1061–1070.
Karatekin, E., Sandre, O., Guitouni, H., Borghi, N., Puech, P.H., Brochard-Wyart, F., 2003. Cascades of transient pores in giant vesicles: Line tension and transport. Biophys. J. 84, 1734–1749.
Kessel, A., Ben Tal, N., May, S., 2001. Interactions of cholesterol with lipid bilayers: The preferred configuration and fluctuations. Biophys. J. 81, 643–658.
Leontiadou, H., Mark, A.E., Marrink, S.J., 2004. Molecular dynamics simulations of hydrophilic pores in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 86, 2156–2164.
Litster, J.D., 1975. Stability of lipid Bilayers and red blood-cell membranes. Phys. Lett. A 53, 193–194.
Loison, C., Mareschal, M., Schmid, F., 2004. Pores in bilayer membranes of amphiphilic molecules: Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations compared with simple mesoscopic models. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 1890–1900.
Marrink, S.J., Lindahl, E., Edholm, O., Mark, A.E., 2001. Simulation of the spontaneous aggregation of phospholipids into bilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 8638–8639.
May, S., 2000. Protein-induced bilayer deformations: The lipid tilt degree of freedom. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophys. Lett. 29, 17–28.
Moroz, J.D., Nelson, P., 1997. Dynamically stabilized pores in bilayer membranes. Biophys. J. 72, 2211–2216.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., 1995. Differential length effects in a binary mixture of single-chain amphiphiles in planar monolayers: A 3-dimensional approach. Biosystems 36, 43–53.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., 1996. Global ratio of efficiency in a single chain binary mixture. J. Biol. Systems 4, 425–432.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., Victor, G., Turcu, G., 1997. Selective association of phospholipids as a clue for the passive flip-flop diffusion through bilayer lipid membranes. Biosystems 40, 263–275.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., 1998. A theoretical model for the association probabilities of saturated phospholipids from two-component bilayer lipid membranes. Acta Biotheor. 46, 347–368.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., Flonta, M.L., 1998. The hydrophobic acyl-chain effect in the lipid domains appearance through phospholipid bilayers. Theochem. J. Mol. Struct. 434, 213–227.
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., 2004. The birth, life and death of statistical pores into a bilayer membrane. In: Recent Research Developments in Biophysics. Transworld Research Network, Kerala, pp. 61–86.
Neher, E., Eibl, H., 1977. Influence of Phospholipid Polar Groups on Gramicidin Channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 464, 37-44.
Neu, J.C., Krassowska, W., 2003. Modeling postshock evolution of large electropores. Phys. Rev. E 67, 2191–2195
Neu, J.C., Smith, K.C., Krassowska, W., 2003. Electrical energy required to form large conducting pores. Bioelectrochemistry 60, 107–114.
Nielsen, C., Goulian, M., Andersen, O.S., 1998. Energetics of inclusion-induced bilayer deformations. Biophys. J. 74, 1966–1983.
Nielsen, C., Andersen, O.S., 2000. Inclusion-induced bilayer deformations: Effects of monolayer equilibrium curvature. Biophys. J. 79, 2583–2604
Partenskii, M.B., Dorman, V.L., Jordan, P.C., 1998. Membrane stability under electrical stress: A nonlocal electroelastic treatment. J. Chem. Phys. 109, 10361–10371.
Pastushenco, V.F., Chizmadzev Yu, A., Arakelyan, V.B., 1979. Electric breakdown of Bilayer lipid membranes. II. Calculation of the membrane lifetime in the steady state diffusion approximation. Bioelectrochem. Bioenergetics 6, 53–62.
Popescu, D., Margineanu, D.G., 1981. Intramembrane interactions and breakdown of lipid bilayers. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 8, 581–583.
Popescu, D., Victor, G., 1990. Association probabilities between the single chain amphiphiles into a binary mixture in planar monolayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1030, 238–250.
Popescu, D., Rucareanu, C., Victor, G., 1991. A Model for the appearance of statistical pores in membranes due to selfoscillations. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 25, 91–103.
Popescu, D., Victor, G., 1991a. Calculation of the optimal surface-area for amphiphile molecules using the hard-core method. Biophys. Chem. 39, 283–286.
Popescu, D., Victor, G., 1991b. The transversal diffusion-coefficient of phospholipid molecules through black lipid-membranes. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 25, 105–108.
Popescu, D., Rucareanu, C., 1992. Membrane selfoscillations model for the transbilayer statistical pores and flip-flop diffision. Mol. Cryst. Liquid Cryst. 25, 339–348.
Popescu, D., 1993. Association probabilities between the single-chain amphiphiles into a binary mixture in plan monolayers (II). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1152, 35–43.
Popescu, D., Movileanu, L., Victor, G., Turcu, G., 1997. Stability and instability properties of aggregation of single chain amphiphiles into binary mixtures. Bull. Math. Biol. 59, 43–61.
Popescu, D., Ion, S., Popescu, A.I., Movileanu, L., 2003. Elastic properties of bilayer lipid membranes and pore formation. In: Ti Tien, H., Ottova, A. (Eds.), Planar Lipid Bilayers (BLMs) and Their Applications. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp. 173–204.
Rawicz, W., Olbrich, K.C., McIntosh, T., Needham, D., Evans, E., 2000. Effect of chain length and unsaturation on elasticity of lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 79, 328–339.
Sackmann, E., 1995. Biological membranes: architecture and function. In: Lipowsky, R., Sackmann, E. (Eds.), Structure and Dynamics of Membranes. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 1–63.
Saulis, G., 1997. Pore disappearance in a cell after electroporation: Theoretical simulation and comparison with experiments. Biophys. J. 73, 1299–1309.
Schneider, M.B., Jenkins, J.T., Webb, W.W., 1984. Thermal fluctuations of large quasi-spherical bimolecular phospholipid-vesicles. J. Physique 45, 1457–1472.
Shillcock, J.C., Boal, D.H., 1996. Entropy-driven instability and rupture of fluid membranes. Biophys. J. 71, 317–326.
Shillcock, J.C., Seifert, U., 1998. Thermally induced proliferation of pores in a model fluid membrane. Biophys. J. 74, 1754–1766.
Sung, W., Park, P.J., 1997. Dynamics of pore growth in membranes and membrane stability. Biophys. J. 73, 1797–1804.
Sung, W.Y., Park, P.J., 1998. Transition dynamics of biological systems on mesoscopic scales: Effects of flexibility and fluctuations. Physica A 254, 62–72.
Tieleman, D.P., Leontiadou, H., Mark, A.E., Marrink, S.J., 2003. Simulation of pore formation in lipid bilayers by mechanical stress and electric fields. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 6382–6383.
Tieleman, D.P., 2004. The molecular basis of electroporation. BMC Biochem. 5, 1–12.
White, S.H., 1978. Formation of solvent-free black lipid bilayer membranes from glyceryl monooleate dispersed in squalene. Biophys. J. 23, 337–347.
Winterhalter, M., Helfrich, W., 1987. Effect of voltage on pores in membranes. Phys. Rev. A 36, 5874–5876.
Zhelev, D.V., Needham, D., 1993. Tension-stabilized pores in giant vesicles: Determination of pore-size and pore line tension. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1147, 89–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Movileanu, L., Popescu, D., Ion, S. et al. Transbilayer Pores Induced by Thickness Fluctuations. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 1231–1255 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-006-9069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-006-9069-9