Abstract
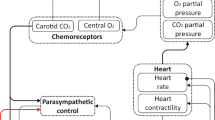
This work describes a comprehensive mathematical model of the human respiratory control system which incorporates the central mechanisms for predicting sleep-induced changes in chemical regulation of ventilation. The model integrates four individual compartments for gas storage and exchange, namely alveolar air, pulmonary blood, tissue capillary blood, body tissues, and gas transport between them. An essential mechanism in the carbon dioxide transport is its dissociation into bicarbonate and acid, where a buffering mechanism through hemoglobin is used to prevent harmfully low pH levels. In the current model, we assume high oxygen levels and consider intracellular hydrogen ion concentration as the principal respiratory control variable. The resulting system of delayed differential equations is solved numerically. With an appropriate choice of key parameters, such as velocity of blood flow and gain of a non-linear controller function, the model provides steady-state results consistent with our experimental observations measured in subjects across sleep onset. Dynamic predictions from the model give new insights into the behaviour of the system in subjects with different buffering capacities and suggest novel hypotheses for future experimental and clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aittokallio, J., Virkki, A., Aittokallio, T., Saaresranta, T., Polo-Kantola, P., Polo, O., in press. Non-invasive respiratory monitoring during wakefulness and sleep in pre- and postmenopausal women. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. Available online 31 May 2005 (doi:10.1016/j.resp.2005.03.012).
Aittokallio, T., Gyllenberg, M., Polo, O., 2002. Adjustment of the human respiratory system to increased upper airway resistance during sleep. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 3–28.
Batzel, J., Tran, H., 2000a. Stability of the human respiratory control system I. Analysis of a two-dimensional delay state-space model. Math. Biol. 41, 45–79.
Batzel, J., Tran, H., 2000b. Stability of the human respiratory control system II. Analysis of a three-dimensional delay state-space model. Math. Biol. 41, 80–102.
Batzel, J.J., Timischl-Teschl, S., Kappel, F., 2005. A cardiovascular-respiratory control system model including state delay with application to congestive heart failure in humans. J. Math. Biol. 50(3), 293–335.
Batzel, J.J., Tran, H.T., 2000c. Modeling instability in the control system for human respiration: applications to infant non-REM sleep. Appl. Math. Comput. 110(1), 1–51.
Browne, H.A.K., Adams, L., Simonds, A., Morrell, M.J., 2003. Ageing does not influence the sleep-related decrease in the hypercapnic ventilatory response. Eur. Respir. J. 21(3), 523–529.
Carley, D.W., Shannon, D.C., 1988a. A minimal mathematical model of human periodic breathing. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 1400–1409.
Carley, D.W., Shannon, D.C., 1988b. Relative stability of human respiration during progressive hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 1389–1399.
Caruana-Montaldo, B., Gleeson, K., Zwillich, C.W., 2000. The control of breathing in clinical practice. Chest 117(1), 205–225.
Chiari, L., Avanzolini, G., Ursino, M., 1997. A comprehensive simulator of the human respiratory system: Validation with experimental and simulated data. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 25, 985–999.
Clark, J.S., Votteri, B., Ariagno, R.L., Cheung, P., Eichhorn, J.H., Fallat, R.J., Lee, S.E., Newth, C.J.L., Rotman, H., Sue, D.Y., 1992. Noninvasive assessment of blood gases. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145, 220–232.
Cleave, J.P., Levine, M.R., Fleming, P.J., 1984. The control of ventilation: A theoretical analysis of the response to transient disturbances. J. Theor. Biol. 108, 261–283.
Cleave, J.P., Levine, M.R., Fleming, P.J., Long, A.M., 1986. Hopf bifurcations and the stability of the respiratory control system. J. Theor. Biol. 119, 299–318.
Colrain, I.M., Trinder, J., Fraser, G., Wilson, G.V., 1987. Ventilation during sleep onset. J. Appl. Physiol. 63(5), 2067–74.
den Aardweg, J.G.V., Karemaker, J.M., 2002. Influence of chemoreflexes on respiratory variability in healthy subjects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 165, 1041–1947.
Despopulous, A., Silbernagl, S., 2003. Color Atlas of Physiology, 5th edn. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York, NY, USA.
ElHefnawy, A., Saidel, G.M., Bruce, E.N., Cherniack, N.S., 1990. Stability analysis of CO2 control of ventilation. J. Appl. Physiol. 69, 498–503.
Erdi, P., Toth, J., 1989. Mathematical Models of Chemical Reactions. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Fowler, A., Kalamangalam, G., 2000. The role of the central chemoreceptor in causing periodic breathing. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 17(2), 147–167.
Fowler, A.C., Kalamangalam, G.P., 1993. A mathematical analysis of the grodins model of respiratory control. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 10, 249–280.
Grodins, F.S., Buell, J., Bart, A.J., 1967. Mathematical analysis and digital simulation of the respiratory control system. J. Appl. Physiol. 22(2), 260–276.
Guglielmi, N., Hairer, E., 2000. Users' guide for the code radar5. Technical report, University of Geneve, Department of Mathematics.
Guglielmi, N., L'Aquila, Hairer, E., 2001. Implementing radau iia methods for stiff delay differential equations. Computing 67, 1–12.
Janssens, J.P., Perrin, E., Bennani, I., de Muralt, B., Titelion, V., Picaud, C., 2001. Is continuous transcutaneous monitoring of P CO 2 (TcCO2) over 8 h reliable in adults? Respir. Med. 95, 331–335.
Javaheri, S., 1999. A mechanism of central sleep apnea in patients with heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 341(13), 949–954.
Khoo, M.C.K., 1990. A model-based evaluation of the single-breath CO2 ventilatory response test. J. Appl. Physiol. 68(1), 393–399.
Khoo, M.C.K., 2000. Determinants of ventilatory instability and variability. Respir. Physiol. 122(2-3), 168–182.
Khoo, M.C.K., Gottschalk, A., Pack, A.I., 1991. Sleep-induced periodic breathing and apnea: A theoretical study. J. Appl. Physiol. 70(5), 2014–2024.
Khoo, M.C.K., Kronauer, R.E., Strohl, K.P., Slutsky, A.S., 1982. Factors inducing periodic breathing in humans: A general model. J. Appl. Physiol. 53, 644–659.
Kirby, T.P., Wraith, P.K., Cort, S. C.D., Airlie, M.A.A., Hill, J.E., Carson, E.R., Flenley, D.C., Warren, P.M., 1994. Modelling the dynamic ventilatory response to hypoxia in normal subjects. J. Theor. Biol. 166, 135–147.
Kuboyama, T., Hori, A., Sato, T., Mikami, T., Yamaki, T., Ueda, S., 1997. Changes in cerebral blood flow velocity in healthy young men during overnight sleep and while awake. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 102(2), 125–131.
Levine, M., Cleave, J.P., Dodds, C., 1995. Can periodic breathing have advantages for oxygenation? J. Theor. Biol. 172(4), 355–368.
Longobardo, G.S., Cherniack, N.S., Gothe, B., 1989. Factors affecting respiratory system stability. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 17, 377–396.
Longobardo, G.S., Evangelisti, C.J., Cherniack, N.S., 2002. Effects of neural drives on breathing in the awake state in humans. Respir. Physiol. 129(3), 279–402.
Longobardo, G.S., Goethe, B., Goldman, M.D., Cherniack, N.S., 1982. Sleep apnea considered as a control system instability. Respir. Physiol. 50, 311–333.
Marcus, C.L., Glomb, W.B., Basinski, D.J., Davidson, S.L., Keens, T.G., 1994. Developmental pattern of hypercapnic and hypoxic ventilatory responses from childhood to adulthood. J. Appl. Physiol. 76(1), 314–320.
Maxima Development Team 2004. Maxima: A sophisticated computer algebra system. (Maxima was previously knows as DOE Macsyma).
Mitchell, G.S., Douse, M.A., Foley, K.T., 1990. Receptor interactions in modulating ventilatory activity. Am. J. Physiol. 259, 911–920.
Moreau, K.L., Donato, A.J., Tanaka, H., Jones, P.P., Gates, P.E., Seals, D.R., 2003. Basal leg blood flow in healthy women is related to age and hormone replacement therary status. J. Physiol. 547, 309–316.
NIST, 2004. Standard Reference Database 40. NIST, http://kinetics.nist.gov/ solution/index.php. NDRL/NIST Solution Kinetics Database on the Web.
Noshiro, M., Furuya, M., Linkens, D., Goode, K., 1993. Nonlinear identification of the P CO 2 control system in man. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 40(3), 189–202.
Orr-Walker, B.J., Horne, A.M., Evans, M.C., Grey, A.B., Murray, M. A.F., McNeil, A.R., Reid, I.R., 1999. Hormone replacement therapy causes a respiratory alkalosis in normal posmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84(6), 1997–2001.
Pedersen, M. E.F., Fatemian, M., Robbins, P.A., 1999. Identification of fast and slow ventilatory responses to carbon dioxide under hypoxic and hyperoxic conditions in humans. J. Physiol. 521(1), 273–287.
Prabhakar, N.R., Peng, Y.-J., 2004. Peripheral chemoreceptors in health and disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 96, 359–366.
R Development Core Team 2004. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-00-3.
Saaresranta, T., Polo, O., 2002. Hormones and breathing. Chest 122, 2165–2182.
Saunders, K.B., Bali, H.N., Carson, E.R., 1980. A breathing model of the respiratory system: The controlled system. J. Theor. Biol. 84, 135–161.
Saunders, K.B., Stradling, J., 1993. Chemoreceptor drives and short sleep-wake cycles during hypoxia: a simulation study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 21, 465–474.
Ursino, M., Magosso, E., Avanzolini, G., 2001a. An integrated model of the human ventilatory control system: The response to hypercapnia. Clin. Physiol. 21(4), 447–464.
Ursino, M., Magosso, E., Avanzolini, G., 2001b. An integrated model of the human ventilatory control system: the response to hypoxia. Clin. Physiol. 21(4), 465–477.
Vielle, B., 2000. A new explicit stability criterion for human periodic breathing. J. Math. Biol. 41(6), 546–558.
Vielle, B., Chauvet, G., 1998. Delay equation analysis of human respiratory stability. Math. Biosci. 152, 105–122.
West, J.B., 1977. Bioengineering Aspects of the Lung, vol. 3. Marcel Dekker.
Whiteley, J.P., Gavaghan, D.J., Hahn, C.E.W., 2003. Periodic breathing induced by arterial oxygen partial pressure oscillations. Math. Med. Biol. 20, 205–224.
Williams, A.J., 1998. Abc of oxygen: Assessing and interpreting arterial blood gases and acid-base balance. BMJ 317, 1213–1216. clinical review.
Younes, M., Ostoroski, M., Thompson, W., Colleen, L., Shewchuk, W., 2001. Chemical control stability in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163(5), 1181–1190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aittokallio, T., Gyllenberg, M., Polo, O. et al. Model-Based Analysis of Mechanisms Responsible for Sleep-Induced Carbon Dioxide Differences. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 315–341 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-005-9059-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-005-9059-3