Abstract
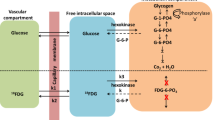
Mathematical modeling of brain function is an important tool needed for a better understanding of experimental results and clinical situations. In the present study, we are constructing and testing a mathematical model capable of simulating changes in brain energy metabolism that develop in real time under various pathophysiological conditions. The model incorporates the following parameters: cerebral blood flow, partial oxygen pressure, mitochondrial NADH redox state, and extracellular potassium. Accordingly, all the model variables are only time dependent (`point-model' approach). Numerical runs demonstrate the ability of the model to mimic pathological conditions, such as complete and partial ischemia, cortical spreading depression under normoxic and partial ischemic conditions. They also show that, when properly tuned, a model of this type permits the monitoring of only one or two crucial variables and the computation of the remaining variables in real time during clinical or experimental procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, J.E., 1998. Mathematical modeling and analysis in biochemical engineering: Past accomplishments and future opportunities. Biotechnol. Prog. 14, 8–20.
Barbiro, E., Zurovsky, Y., Mayevsky, A., 1998. Real time monitoring of rat liver energy state during ischemia. Microvasc. Res. 56, 253–260.
Bolognese, P., Miller, J.I., Heger, I.M., Milhorat, T.H., 1993. Laser-Doppler flowmetry in neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 5, 151–158.
Chance, B., Oshino, N., Sugano, T., Mayevsky, A., 1973. Basic principles of tissue oxygen determination from mitochondrial signals. In: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Plenum, New York, pp. 239–244.
Erecinska, M., Silver, I.A., 1989. ATP and brain function. J. CBF Metab. 9, 2–19.
Friedli, C.M., Sclarsky, D.S., Mayevsky, A., 1982. Multiprobe monitoring of ionic, metabolic and electrical activities in the awake brain. Am. J. Physiol. 243, R462–R469.
Gershenfeld, N.A., 1999. The Nature of MathematicalModeling. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gombert, A., Nielsen, J., 2000. Mathematical modelling of metabolism. Curr. Opin Biotechnol. 11: 180–186.
Haberl, R.L., Heizer, M.L., Marmarou, A., Ellis, E.F., 1989. Laser Doppler assessment of brain microcirculation: Effect of systemic alterations. Am. J. Physiol. 256, H1247–H1254.
Haberl, R.L., Villringer, A., Dirnagl, U., 1993. Applicability of laser-Doppler flowmetry for cerebral blood flow monitoring in neurological intensive care. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 59, 64–68.
Hatzimanikatis, V., Floudas, C., Bailey, J., 1995. A mathematical model for the G1/S transition of the mamalian cell cycle. Biotechnol. Lett. 17, 669–674.
Hudetz, A. G., 1999. Mathematical model of oxygen transport in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 817, 75–83.
Kraut, A., Barbiro-Michaely, E., Zurovsky, Y., Mayevsky, A., 2003. Multiorgan monitoring of hemodynamic and mitochondrial responses to anoxia and cardiac arrest in the rat. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 510, 299–304.
Mayevsky, A., Manor, T., Pevzner, E., Deutsch, A., Etziony, R., Dekel, N., Jaronkin, A., 2004. Tissue spectroscope: a new in vivo approach to monitor tissue vitality in real time. J. Biomed. Optics. 9, 1028–1045.
Mayevsky, A., 1983a. Metabolic, ionic and electrical responses to experimental epilepsy in the awake rat. In: Baldy, M., Moulinier, D.H., Ingvar, D.H., Meldrum, B.S. (Eds.), Proceedings of the First International Congress of Cerebral Blood Flow, Metabolism and Epilepsy. John Libbey, pp. 263–270. London, England.
Mayevsky, A., 1983b. Multiparameter monitoring of the awake brain under hyperbaric oxygenation. J. Appl. Physiol. 54, 740–748.
Mayevsky, A., 1984. Brain NADH redox state monitored in vivo by fiber optic surface fluorometry. Brain Res. Rev. 7, 49–68.
Mayevsky, A., 1990. Level of ischemia and brain functions in the Mongolian gerbil in vivo. Brain Res. 524, 1–9.
Mayevsky, A., 1992. Cerebral blood flow and brain mitochondrial redox state responses to various perturbations in gerbils. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 317, 707–716.
Mayevsky, A., 1993. Biochemical and physiological activities of the brain as in vivo markers of brain pathology. In: Bernstein, E.F., Callow, A.D., Nicolaides, A.N., Shifrin, E.G. (Eds.), Cerebral, Revascularization. Med-Orion, pp. 51–69. London, England.
Mayevsky, A., Chance, B., 1974. Repetitive patterns of metabolic changes during cortical spreading depression of the awake rat. Brain Res. 65, 529–533.
Mayevsky, A., Chance, B., 1975. Metabolic responses of the awake cerebral cortex to anoxia, hypoxia, spreading depression and epileptiform activity. Brain Res. 98, 149–165.
Mayevsky, A., Chance, B., 1982. Intracellular oxidation reduction state measured in situ by a multichannel fiber-optic-surface fluorometer. Science 217, 537–540.
Mayevsky, A., Doron, A., Manor, T., Meilin, S., Zarchin, N., Ouaknine, G.E., 1996. Cortical spreading depression recorded from the human brain using a multiparametric monitoring system. Brain Res. 740, 268–274.
Mayevsky, A., Manor, T., Pevzner, E., Deutsch, A., Etziony, R., Dekel, N., 2002. Real-time optical monitoring of tissue vitality in vivo. SPIE 4616, 30–39.
Mayevsky, A., Meilin, S., Manor, T., Ornstein, E., Zarchin, N., Sonn, J., 1998. Multiparametric monitoring of brain oxygen balance under experimental and clinical conditions. Neurol. Res. 20, S76–S80.
Mayevsky, A., Sclarsky, D.S., 1983. Correlation of brain NADH redox state, K+, PO2 and electrical activity during hypoxia, ischemia and spreading depression. In: Oxygen Transport to Tissue, vol. IV. Plenum, New York, pp. 129–141.
Mayevsky, A., Weiss, H.R., 1991. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in cortical spreading depression. J. CBF Metab. 11, 829–836.
Mayevsky, A., Zarchin, N., Tannenbaum, B., 1984. Brain responses to experimental oxygen deficiency in the Mongolian gerbil. In: Bruley, D., Bicher, H.I., Reneau, D. (Eds.), Oxygen Transport to Tissue, vol. VI. Plenum, New York, pp. 191–202.
Meilin, S., Zarchin, N., Mayevsky, A., 1999. Inter-relation between hemodynamic, metabolic, ionic and electrical activities during ischemia and reperfusion in the gerbil brain. Neurol. Res. 21, 699–704.
Pevzner, E., Deutsch, A., Manor, T., Dekel, N., Etziony, R., Derzy, I., Razon, N., Mayevsky, A., 2003. Real-time multiparametric spectroscopy as a practical tool for evaluation of tissue vitality in vivo. In: Vo-Dinh, T., Grundfest, W.S., Benaron, D.A., Cohn, G.G. (Eds.), Advances Biomedical and Clinical Diagnostic Systems, Proceedings of the SPIE, pp. 171–182. SPIE - The International Society for optical Engineering, Washington, D.C., USA.
Reggia, J. A., Ruppin, E., Berndt, R.S., 1997. Computer modeling: A new approach to the investigation of disease. MD Comput. 14, 160–164.
Revett, K., Ruppin, E., Goodall, S., Reggia, J.A., 1998. Spreading depression in focal ischemia: A computational study. J. CBF Metab. 18, 998–1007.
Ruppin, E., Ofer, E., Reggia, J.A., Revett, K., Goodall, S., 1999. Pathogenic mechanisms in ischemic damage: A computational study. Comput. Biol. Med. 29, 39–59.
Sonn, J., Mayevsky, A., Acad, B., Guggenheimer, E., Kedem, J., 1982. Effect of local ischemia on the myocardial oxygen balance and its response to heart rate elevation. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 67, 335–348.
Wadhwani, K. C., Rapoport, S.I., 1990. Blood flow in the central and peripheral nervous systems. In: Shepherd, A.P., Oberg, P.A. (Eds.), Laser Doppler Blood Flowmetry. Kluwer Academic, Boston, pp. 265–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vatov, L., Kizner, Z., Ruppin, E. et al. Modeling Brain Energy Metabolism and Function: A Multiparametric Monitoring Approach. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 275–291 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-005-9008-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-005-9008-1