Abstract
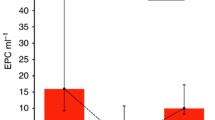
We have carried out a stratified phase II study of sorafenib (So) in patients with advanced angiosarcoma (n = 32) and epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (n = 13). This report concerns the correlative analysis of the predictive values of circulating pro/anti-angiogenetic biomarkers. Using the ELISA method (R&D Systems), circulating biomarkers (VEGF-A, in picograms per milliliter), thrombospondin-1 (TSP1, in micrograms per milliliter), stem cell factor (SCF, in picograms per milliliter), placental growth factor (PlGF, in picograms per milliliter), VEGF-C (in picograms per milliliter), and E-selectin (in nanograms per milliliter) were measured before So treatment and after 7 days. VEGF-A (mean value 475 vs. 541, p = 0.002), TSP1 (16 vs. 24, p = 0.0002), and PlGF (20.9 vs. 40.7, p = 0.0001) significantly increased during the treatment. Treatment did not affect the levels of SCF, VEGF-C, and E-selectin. Only two biomarkers were associated with better outcome as follows: VEGF-A and PlGF. Best objective response and non-progression at 180 days were associated with low level of VEGF-A at baseline (p = 0.04 and 0.03, respectively). There was a correlation between the circulating level of VEGF-A and time to progression (TTP) (r = −0.47, p = 0.001). Best objective response and non-progression at 180 days were not associated with baseline level of PIGF, but there was a correlation between the circulating level of PIGF at baseline and TTP. Low level of VEGF-A at baseline (<500) was significantly associated with better outcome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Penel N, Marreaud S, Robin YM, Hohenberger P (2011) Angiosarcoma: state of the art and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 80:257–263
Penel N, Bui BN, Bay JO, Cupissol D, Ray-Coquard I, Piperno-Neumann S, Kerbrat P, Fournier C, Taieb S, Jimenez M, Isambert N, Peyrade F, Chevreau C, Bompas E, Brain EG, Blay JY (2008) Phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel for unresectable angiosarcoma: the ANGIOTAX study. J Clin Oncol 26:5269–5274
Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, Schemmer P, Hallscheidt P, Schirmacher P, Weitz J, Friess H, Buchler MW, Schmidt J (2006) Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Cancer 107:2108–2121
Kitaichi M, Nagai S, Nishimura K, Itoh H, Asamoto H, Izumi T, Dail DH (1998) Pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in 21 patients, including three with partial spontaneous regression. Eur Respir J 12:89–96
Flaherty KT (2007) Sorafenib: delivering a targeted drug to the right targets. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 7:617–626
Adnane L, Trail PA, Taylor I, Wilhelm SM (2006) Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol 407:597–612
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA (2004) BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:7099–7109
Brown L, Tognazzi K, Dvorak HF, Harrist TJ (1996) Strong expression of kinase insert domain-containing receptor, a vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor in AIDS-associated Kaposi and cutaneous angiosarcoma. Am J Pathol 148:1065–1074
Naito S, Shimizu K, Nakashima M, Ito T, Ito M, Yamashita S, Sekine I (2000) Overexpression of Ets-1 transcription factor in angiosarcoma of the skin. Pathol Res Pract 196:103–109
Itakura E, Yamaoto H, Oda Y, Tsuneyoshi M (2008) Detection and characterization of vascular endothelia growth factors and their receptors in a series of angiosarcoma. J Surg Oncol 97:74–81
LaMontagne KR Jr, Moses MA, Wiederschain D, Mahajan S, Holden J, Ghazizadeh H, Frank DA, Arbiser JL (2000) Inhibition of MAP kinases causes morphological reversion and dissociation between soft agar growth and in vivo tumorigenesis in angiosarcoma cells. Am J Pathol 157:1937–1945
Antonescu CR, Yoshida A, Guo T, Chang NE, Zhang L, Agaram NP, Qin LX, Brennan MF, Singer S, Maki RG (2009) KDR activating mutations in human angiosarcomas are sensitive to specific kinase inhibition. Cancer Res 69:71–79
Lahat G, Dhuka AR, Hallevi H, Xiao L, Zou C, Smith KD, Phung TL, Pollock RE, Benjamin R, Hunt KK, Lazar AJ, Lev D (2010) Angiosarcoma: clinical and molecular insights. Ann Surg 251:1098–1106
Emamaullee JA, Edgar R, Toso C, Thiesen A, Bain V, Bigam D, Kneteman N, Shapiro AM (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: implications for treatment and surgical management. Liver Transpl 16:191–197
Hatva E, Böhling T, Jääskeläinen J, Persico MG, Haltia M, Alitalo K (1996) Vascular growth factors and receptors in capillary hemangioblastomas and hemangiopericytomas. Am J Pathol 148:763–775
Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Bompas E, Le Cesne A, Robin YM, Chevreau C, Bay JO, Bousquet G, Piperno-Neumann S, Isambert N, Lemaitre L, Fournier C, Gauthier E, Collard O, Cupissol D, Clisant S, Blay JY, Penel N, French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO) (2012) Sorafenib for patients with advanced angiosarcoma : a phase II trial from the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Oncologist 17:260–266
Chevreau C, Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Cioffi A, Isambert N, Robin YM, Fournier C, Clisant S, Chaigneau L, Bay JO, Bompas E, Gauthier E, Blay JY, Penel N (2013) Sorafenib in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a phase 2 study by the Fench Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Cancer. doi:10.1002/cncr.28109
Tokuyama W, Mikami T, Masuzawa M, Okayasu I (2010) Autocrine and paracrine roles of VEGF/VEGFR-2 and VEGF-C/VEGFR63 signaling in angiosarcomas of the scalp and face. Hum Pathol 41:407–414
Lovet JM, Pena CE, Lathia CD, Shan M, Meinherdt G, Bruix J, SHARP Investigators Study Group (2012) Plasma biomarkers as predictors of outcome in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 18:2290–2300
Pena C, Lathia C, Shan M, Escudier B, Bukowski RM (2010) Biomarkers predicting outcome in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: results from sorafenib phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. Clin Cancer Res 16:4853–4863
Raut CP, Boucher Y, Duda DG, Morgan JA, Quek R, Ancukiewicz M et al (2012) Effects of sorafenib on intra-tumoral interstitial fluid pressure and circulating biomarkers in patients with refractory sarcomas (NCI protocol 6948). PLoS One 7:e26331
Sleijfer S, Gorlia T, Lamers C, Burger H, Blay JY, Le Cesne A et al (2012) Cytokine and angiogenic factors associated with efficacy and toxicity of pazopanib in advanced soft tissue sarcoma: an EORTC-STBSG study. Eur J Cancer 107:639–645
Sleijfer S, Ouali M, Van Glabbeke M, Krarup-Hansen A, Rodenhuis S, Le Cesne A et al (2010) Prognostic and predictive factors for outcome to first-line ifosfamide-containing chemotherapy for adult patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas: an exploratory, retrospective analysis on large series from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (EORTC-STBSG). Eur J Cancer 46:72–83
Acknowledgments
We would like to take this opportunity to thank the patients and their families. We would like to thank all the staff of Oscar Lambret Center Clinical Research Unit (Yvette Vendel, Marie Vanseymortier, Laurence Delannoy, Emilie Decoupigny) and Séverine Marchant for editing this manuscript.
This is an investigator-initiated trial supported financially by Bayer-HealthCare France and the French National Cancer Institute (“Institut National du Cancer” (PHRC-2007)).
Funded by the French National Cancer Institute Grant (INCA; 2007-PHRC) and Bayer-Healthcare France.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penel, N., Ray-Coquard, I., Bal-Mahieu, C. et al. Low level of baseline circulating VEGF-A is associated with better outcome in patients with vascular sarcomas receiving sorafenib: an ancillary study from a phase II trial. Targ Oncol 9, 273–277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-013-0299-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-013-0299-0