Abstract
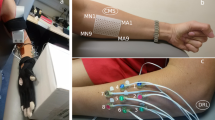
In order to optimize procedure for the assessment of evoked potentials and to provide visualization of the flow of action potentials along the motor systems, we introduced array electrodes for stimulation and recording and developed software for the analysis of the recordings. The system uses a stimulator connected to an electrode array for the generation of evoked potentials, an electrode array connected to the amplifier, A/D converter and computer for the recording of evoked potentials, and a dedicated software application. The method has been tested for the assessment of the H-reflex on the triceps surae muscle in six healthy humans. The electrode array with 16 pads was positioned over the posterior aspect of the thigh, while the recording electrode array with 16 pads was positioned over the triceps surae muscle. The stimulator activated all the pads of the stimulation electrode array asynchronously, while the signals were recorded continuously at all the recording sites. The results are topography maps (spatial distribution of evoked potentials) and matrices (spatial visualization of nerve excitability). The software allows the automatic selection of the lowest stimulation intensity to achieve maximal H-reflex amplitude and selection of the recording/stimulation pads according to predefined criteria. The analysis of results shows that the method provides rich information compared with the conventional recording of the H-reflex with regard the spatial distribution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Andersen JL, Magnusson P, Dyhre-Poulsen P (2002) Neural adaptation to resistance training: changes in evoked V-wave and H-reflex responses. J Appl Physiol 92:2309–2318
Alrowayeh HN, Sabbahi MA, Etnyre B (2011) Similarities and differences of the soleus and gastrocnemius H-reflexes during varied body postures, foot positions, and muscle function: multifactor designs for repeated measures. BMC Neurol 11:65
Bosenberg AT, Raw R, Boezaart AP (2002) Surface mapping of peripheral nerves in children with a nerve stimulator. Pediatr Anesth 12(5):398–403
Brinkworth RSA, Tuncer M, Tucker KJ, Jaberzadeh S, Turker KS (2007) Standardization of H-reflex analysis. J Neurosci Methods 162(1–2):1–7
Campanini I, Merlo A, Degola P, Merletti R, Vezzosi G, Farina D (2007) Effect of electrode location on EMG signal envelope in leg muscles during gait. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 17(4):515–526
Chen YS, Zhou S (2011) Soleus H-reflex and its relation to static postural control. Gait Posture 33(2):169–178
Clair JM, Anderson-Reid JM, Graham CM, Collins DF (2011) Postactivation depression and recovery of reflex transmission during repetitive electrical stimulation of the human tibial nerve. J Neurophysiol 106(1):184–192
Costa J, Guzman J, Vallderiola F, Rumia J, Tolosa E, Casanova-Molla J, Valls-Sole J (2011) Modulation of the soleus H reflex by electrical subcortical stimuli in humans. Exp Brain Res 212(3):439–448
De Luca CJ, Kuznetsov M, Gilmore LD, Roy SH (2011) Inter-electrode spacing of surface EMG sensors: reduction of crosstalk contamination during voluntary contractions. J Biomech 45(3):555–561
Elsaify A (2005) A self-optimizing portable FES system using an electrode array and movement sensors. PhD Thesis, Department of Engineering, University of Leicester, UK
Farina D, Enoka RM (2011) Surface EMG decomposition requires an appropriate validation. J Neurophysiol 105(2):981–982
Farina D, Falla D (2008) Estimation of muscle fiber conduction velocity from two-dimensional surface EMG recordings in dynamic tasks. Biomed Signal Process 3(2):138–144
Farina D, Negro F, Gazzoni M, Enoka RM (2008) Detecting the unique representation of motor-unit action potentials in the surface electromyogram. J Neurophysiol 100(3):1223–1233
Gerilovsky L, Tsvetinov P, Trenkova G (1989) Peripheral effects on the amplitude of monopolar and bipolar H-reflex potentials from the soleus muscle. Exp Brain Res 76(1):173–181
Hadzic A, Vloka JD, Claudio RE, Hadzic N, Thys DM, Santos AC (2005) Electrical nerve localization: effects of cutaneous electrode placement and duration of the stimulus on motor response. Anesthesiology 100(4):976–981
Hermens HJ, Freriks B, Disselhorst-Klug C, Rau G (2000) Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 10(5):361–374
Imura S, Kishikawa M, Wada T, Iwai A, Fuziwara M (1997) Changes in the H-reflex amplitude causes by fluctuation of stimulus frequency. J Phys Ther Sci 9(2):111–119
Inghilleri M, Lorenzano C, Conte A, Frasca V, Manfredi M, Berardelli A (2003) Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on the H reflex and F wave in hand muscles. Clin Neurophysiol 114(6):1096–1101
Kennedy PM, Cresswell AG, Chua R, Inglis JT (2004) Vestibulospinal influences on lower limb motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 82(8–9):675–681
Kennedy PM, Inglis JT (2002) Interaction effects of galvanic vestibular stimulation and head position on the soleus H reflex in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 113(11):1709–1714
Kerasnoudis A, Pitarokoili K, Behrendt V, Gold R, Yoon MS (2013) Correlation of nerve ultrasound, electrophysiological, and clinical findings in post Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst 18(3):232–240
Kleine BU, Schumann NP, Stegeman DF, Scholle HC (2000) Surface EMG mapping of human trapezius muscle: the topography of monopolar and bipolar surface EMG amplitude and spectrum parameters at varied forces and in fatigue. Clin Neurophysiol 111(4):686–693
Knikou M (2008) The H-reflex as a probe: pathways and pitfalls. J Neurosci Methods 171(1):1–12
Kojić V, Miljković N, Malešević N, Popović DB (2012) H-reflex recorded by multi-pad EMG electrodes. 11th Symposium on Neural Network Applications in Electrical Engineering, NEUREL 2012. IEEE Press, Belgrade, pp 119–122
Malešević NM, Popović Maneski LZ, Ilić V, Jorgovanović N, Bijelić G, Keller T, Popović DB (2012) A multi-pad electrode based functional electrical stimulation system for restoration of grasp. J Neuroeng Rehabil 9:66
McNulty PA, Jankelowitz SK, Wiendels TM, Burke D (2008) Postactivation depression of the soleus H reflex measured using threshold tracking. J Neurophysiol 100(6):3275–3284
McNulty PA, Shiner CT, Thayaparan GK, Burke D (2012) The stability of Mmax and Hmax amplitude over time. Exp Brain Res 218(4):601–607
Merletti R, Holobar A, Farina D (2008) Analysis of motor units with high-density surface electromyogram. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18(16):879–890
Misiaszek JE (2003) The H-reflex as a tool in neurophysiology: its limitations and uses in understanding nervous system function. Muscle Nerve 28(2):144–160
Palmieri RM, Ingersoll CD, Hoffman MA (2004) The Hoffmann reflex: methodologic considerations and applications for use in sports medicine and athletic training research. J Athl Train 39(3):268–277
Pinniger GJ, Nordlund MM, Steele JR, Cresswell AG (2001) H-reflex modulation during passive lengthening and shortening of the human triceps surae. J Physiol 534(3):913–923
Popović-Bijelić A, Bijelić G, Jorgovanović N, Bojanić D, Popović MB, Popović DB (2005) Multi-field surface electrode for selective electrical stimulation. Artif Organs 29(6):448–452
Thompson AK, Chen XY, Wolpow JR (2009) Acquisition of a simple motor skill: task-dependent adaptation plus long-term change in the human soleus H-reflex. J Neurosci 29(18):5784–5792
Tucker K, Falla D, Graven-Nielsen T, Farina D (2009) Electromyographic mapping of the erector spinae muscle with varying load and during sustained contraction. J Electromyogr Kines 19(3):373–379
Acknowledgments
The work on this project was supported partly by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, Grant OI175016. The authors would like to thank all the volunteers involved in this study and PhD MD Laszlo Schwirtlih, MD Radoje Čobeljić, PhD MD Ksenija Ribarić, and MT Mihajlo Tančić for their valuable help in the design of the method and measurements. We would like to acknowledge both Tecnalia Serbia Ltd. for designing the electrode arrays for stimulation and EMG measurements and for providing us with the stimulator. The authors would like to thank Prof. Roberto Merletti for his valuable advice on the preparation of the manuscript and Prof. Milan R. Dimitrijević for his valuable advice during all phases of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miljković, N., Malešević, N., Kojić, V. et al. Recording and assessment of evoked potentials with electrode arrays. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 857–867 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1292-9