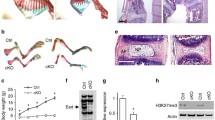
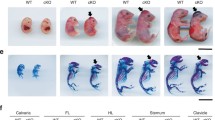
Abstract
Transcription factor, Nkx3.2, is a member of the NK family of developmental genes and is expressed during embryogenesis in a variety of mammalian model organisms, including chicken and mouse. It was first identified in Drosophila as the Bagpipe (bap) gene, where it has been demonstrated to be essential during formation of the midgut musculature. However, mammalian homolog Nkx3.2 has been shown to play a significant role in axial and limb skeletogenesis; in particular, the human skeletal disease, spondylo-megaepiphyseal-metaphyseal dysplasia (SMMD), is associated with mutations of the Nkx3.2 gene. In this review, we highlight the role of Nkx3.2 during musculoskeletal development, with an emphasis on the factor’s role in determining chondrogenic cell fate and its subsequent role in endochondral ossification and chondrocyte survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akazawa H, Komuro I, Sugitani Y, Yazaki Y, Nagai R, Noda T (2000). Targeted disruption of the homeobox transcription factor Bapx1 results in lethal skeletal dysplasia with asplenia and gastroduodenal malformation. Genes Cells, 5(6): 499–513
Asayesh A, Sharpe J, Watson R P, Hecksher-Sørensen J, Hastie N D, Hill R E, Ahlgren U (2006). Spleen versus pancreas: strict control of organ interrelationship revealed by analyses of Bapx1 -/- mice. Genes Dev, 20(16): 2208–221
Azpiazu N, Frasch M (1993). tinman and bagpipe: two homeo box genes that determine cell fates in the dorsal mesoderm of Drosophila. Genes Dev, 7(7b7B): 1325–1340
Baffi M O, Slattery E, Sohn P, Moses H L, Chytil A, Serra R (2004). Conditional deletion of the TGF-beta type II receptor in Col2a expressing cells results in defects in the axial skeleton without alterations in chondrocyte differentiation or embryonic development of long bones. Dev Biol, 276(1): 124–142
Bieberich C J, Fujita K, He W W, Jay G (1996). Prostate-specific and androgen-dependent expression of a novel homeobox gene. J Biol Chem, 271(50): 31779–31782
Brent A E, Tabin C J (2002). Developmental regulation of somite derivatives: muscle, cartilage and tendon. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 12(5): 548–557
Cairns D M, Liu R, Sen M, Canner J P, Schindeler A, Little D G, Zeng L (2012). Interplay of Nkx3.2, Sox9 and Pax3 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of muscle progenitor cells. PLoS ONE, 7(7): e39642
Cairns D M, Sato M E, Lee P G, Lassar A B, Zeng L (2008). A gradient of Shh establishes mutually repressing somitic cell fates induced by Nkx3.2 and Pax3. Dev Biol, 323(2): 152–165
Caron M M J, Emans P J, Cremers A, Surtel D A M, Coolsen M M E, van Rhijn L W, Welting T J M (2013). Hypertrophic differentiation during chondrogenic differentiation of progenitor cells is stimulated by BMP-2 but suppressed by BMP-7. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 21(4): 604–613
Choi S W, Jeong D U, Kim J A, Lee B, Joeng K S, Long F, Kim D W (2012). Indian Hedgehog signalling triggers Nkx3.2 protein degradation during chondrocyte maturation. Biochem J, 443(3): 789–798
Church V, Yamaguchi K, Tsang P, Akita K, Logan C, Francis-West P (2005). Expression and function of Bapx1 during chick limb development. Anat Embryol (Berl), 209(6): 461–469
Collins C A, Olsen I, Zammit P S, Heslop L, Petrie A, Partridge T A, Morgan J E (2005). Stem cell function, self-renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult muscle satellite cell niche. Cell, 122(2): 289–301
Ducy P, Schinke T, Karsenty G (2000). The osteoblast: a sophisticated fibroblast under central surveillance. Science, 289(5484): 1501–1504
Enomoto H, Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iwamoto M, Nomura S, Himeno M, Kitamura Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T (2000). Cbfa1 is a positive regulatory factor in chondrocyte maturation. J Biol Chem, 275(12): 8695–8702
Guo J, Chung U I, Yang D, Karsenty G, Bringhurst F R, Kronenberg H M (2006). PTH/PTHrP receptor delays chondrocyte hypertrophy via both Runx2-dependent and -independent pathways. Dev Biol, 292(1): 116–128
Guo X, Mak K K, Taketo M M, Yang Y (2009). The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway interacts differentially with PTHrP signaling to control chondrocyte hypertrophy and final maturation. PLoS ONE, 4(6): e6067
Hellemans J, Simon M, Dheedene A, Alanay Y, Mihci E, Rifai L, Sefiani A, van Bever Y, Meradji M, Superti-Furga A, Mortier G (2009). Homozygous inactivating mutations in the NKX3-2 gene result in spondylo-megaepiphyseal-metaphyseal dysplasia. Am J Hum Genet, 85(6): 916–922
Herbrand H, Pabst O, Hill R, Arnold H H (2002). Transcription factors Nkx3.1 and Nkx3.2 (Bapx1) play an overlapping role in sclerotomal development of the mouse. Mech Dev, 117(1–2): 217–224
Kawato Y, Hirao M, Ebina K, Shi K, Hashimoto J, Honjo Y, Yoshikawa H, Myoui A (2012). Nkx3.2 promotes primary chondrogenic differentiation by upregulating Col2a1 transcription. PLoS ONE, 7(4): e34703
Kawato Y, Hirao M, Ebina K, Tamai N, Shi K, Hashimoto J, Yoshikawa H, Myoui A (2011). Nkx3.2-induced suppression of Runx2 is a crucial mediator of hypoxia-dependent maintenance of chondrocyte phenotypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 416(1–2): 205–210
Kempf H, Ionescu A, Udager A M, Lassar A B (2007). Prochondrogenic signals induce a competence for Runx2 to activate hypertrophic chondrocyte gene expression. Dev Dyn, 236(7): 1954–1962
Kim D W, Lassar A B (2003). Smad-dependent recruitment of a histone deacetylase/Sin3A complex modulates the bone morphogenetic protein-dependent transcriptional repressor activity of Nkx3.2. Mol Cell Biol, 23(23): 8704–8717
Kim Y, Nirenberg M (1989). Drosophila NK-homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 86(20): 7716–7720
Kronenberg H M (2003). Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature, 423(6937): 332–336
Lefebvre V, Smits P (2005). Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today, 75(3): 200–212
Lei Q, Jiao J, Xin L, Chang C J, Wang S, Gao J, Gleave M E, Witte O N, Liu X, Wu H (2006). NKX3.1 stabilizes p53, inhibits AKT activation, and blocks prostate cancer initiation caused by PTEN loss. Cancer Cell, 9(5): 367–378
Lettice L, Hecksher-Sørensen J, Hill R (2001). The role of Bapx1 (Nkx3.2) in the development and evolution of the axial skeleton. J Anat, 199(Pt 1–2): 181–187
Mackie E J, Ahmed Y A, Tatarczuch L, Chen K S, Mirams M (2008). Endochondral ossification: how cartilage is converted into bone in the developing skeleton. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 40(1): 46–62
Murtaugh L C, Zeng L, Chyung J H, Lassar A B (2001). The chick transcriptional repressor Nkx3.2 acts downstream of Shh to promote BMP-dependent axial chondrogenesis. Dev Cell, 1(3): 411–422
Newman C S, Krieg P A (1999). The Xenopus bagpipe-related homeobox gene zampogna is expressed in the pharyngeal endoderm and the visceral musculature of the midgut. Dev Genes Evol, 209(2): 132–134
Pacifici M, Koyama E, Iwamoto M (2005). Mechanisms of synovial joint and articular cartilage formation: recent advances, but many lingering mysteries. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today, 75(3): 237–248
Park M, Yong Y, Choi S W, Kim J H, Lee J E, Kim D W (2007). Constitutive RelA activation mediated by Nkx3.2 controls chondrocyte viability. Nat Cell Biol, 9(3): 287–298
Provot S, Kempf H, Murtaugh L C, Chung U I, Kim D W, Chyung J, Kronenberg H M, Lassar A B (2006). Nkx3.2/Bapx1 acts as a negative regulator of chondrocyte maturation. Development, 133(4): 651–662
Rodrigo I, Hill R E, Balling R, Münsterberg A, Imai K (2003). Pax1 and Pax9 activate Bapx1 to induce chondrogenic differentiation in the sclerotome. Development, 130(3): 473–482
Schneider A, Mijalski T, Schlange T, Dai W, Overbeek P, Arnold H H, Brand T (1999). The homeobox gene NKX3.2 is a target of left-right signalling and is expressed on opposite sides in chick and mouse embryos. Curr Biol, 9(16): 911–914
Shen M M, Abate-Shen C (2003). Roles of the Nkx3.1 homeobox gene in prostate organogenesis and carcinogenesis. Dev Dyn, 228(4): 767–778
Simon M, Campos-Xavier A B, Mittaz-Crettol L, Valadares E R, Carvalho D, Speck-Martins C E, Nampoothiri S, Alanay Y, Mihci E, van Bever Y, Garcia-Segarra N, Cavalcanti D, Mortier G, Bonafé L, Superti-Furga A (2012). Severe neurologic manifestations from cervical spine instability in spondylo-megaepiphyseal-metaphyseal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet, 160C(3): 230–237
Takimoto A, Mohri H, Kokubu C, Hiraki Y, Shukunami C (2013). Pax1 acts as a negative regulator of chondrocyte maturation. Exp Cell Res, 319(20): 3128–3139
Tanaka M, Komuro I, Inagaki H, Jenkins N A, Copeland N G, Izumo S (2000). Nkx3.1, a murine homolog of Ddrosophila bagpipe, regulates epithelial ductal branching and proliferation of the prostate and palatine glands. Dev Dyn, 219(2): 248–260
Tribioli C, Frasch M, Lufkin T (1997). Bapx1: an evolutionary conserved homologue of the Drosophila bagpipe homeobox gene is expressed in splanchnic mesoderm and the embryonic skeleton. Mech Dev, 65(1–2): 145–162
Tribioli C, Lufkin T (1997). Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping and developmental expression of BAPX1, a novel human homeoboxcontaining gene homologous to Drosophila bagpipe. Gene, 203(2): 225–233
Tribioli C, Lufkin T (1999). The murine Bapx1 homeobox gene plays a critical role in embryonic development of the axial skeleton and spleen. Development, 126(24): 5699–5711
Tribioli C, Lufkin T (2006). Bapx1 homeobox gene gain-of-function mice show preaxial polydactyly and activated Shh signaling in the developing limb. Dev Dyn, 235(9): 2483–2492
Verzi M P, Stanfel M N, Moses K A, Kim B M, Zhang Y, Schwartz R J, Shivdasani R A, Zimmer W E (2009). Role of the homeodomain transcription factor Bapx1 in mouse distal stomach development. Gastroenterology, 136(5): 1701–1710
Yamashita S, Andoh M, Ueno-Kudoh H, Sato T, Miyaki S, Asahara H (2009). Sox9 directly promotes Bapx1 gene expression to repress Runx2 in chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res, 315(13): 2231–2240
Yong Y, Choi SW, Choi H J, Nam HW, Kim J A, Jeong D U, Kim D Y, Kim Y S, Kim D W (2011). Exogenous signal-independent nuclear IkappaB kinase activation triggered by Nkx3.2 enables constitutive nuclear degradation of IkappaB-alpha in chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biol, 31(14): 2802–2816
Yoon B S, Lyons K M (2004). Multiple functions of BMPs in chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem, 93(1): 93–103
Yoshiura K I, Murray J C (1997). Sequence and chromosomal assignment of human BAPX1, a bagpipe-related gene, to 4p16.1: a candidate gene for skeletal dysplasia. Genomics, 45(2): 425–428
Zeng L, Kempf H, Murtaugh L C, Sato M E, Lassar A B (2002). Shh establishes an Nkx3.2/Sox9 autoregulatory loop that is maintained by BMP signals to induce somitic chondrogenesis. Genes Dev, 16(15): 1990–2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rainbow, R.S., Kwon, H. & Zeng, L. The role of Nkx3.2 in chondrogenesis. Front. Biol. 9, 376–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-014-1321-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-014-1321-3