Abstract
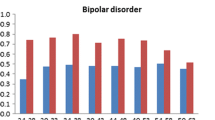
Zolpidem/zopiclone (Z-drugs) and benzodiazepines (BDZs) have different profiles of comorbidity, but studies have seldom explored these differences. This study examined psychiatric comorbidity in patients dependent on Z-drugs or BDZs attending substance abuse clinics in Hong Kong. In this retrospective chart review, the medical records of 207 patients (117 on Z-drugs and 90 on BDZs) treated between January 2008 and August 2012 were analysed. Demographic data, patterns of substance misuse and comorbid psychiatric diagnoses were recorded. Patients dependent on Z-drugs were younger (40.5 ± 10.4 vs. 46.8 ± 11.6; p < 0.001), had an earlier age of onset of drug misuse (p = 0.047) and were more likely to currently use cough syrup (29.5 ± 12.1 vs. 33.6 ± 14.5; p = 0.009) than the BDZs dependent patients. Overall, the Z-drugs and BDZs groups had a similar frequency of comorbid psychotic disorders, mood disorders and anxiety disorders. Mood disorders were the most common comorbid psychiatric disorders. The zopiclone group had a significantly higher percentage of psychotic disorders than the zolpidem group (25.5 % vs. 0; p = 0.022). To summarize, patients with Z-drugs or BDZs dependence have similar psychiatric comorbidities, with depressive disorder the most common comorbidity. Zopiclone is more likely to be associated with psychotic disorders than zolpidem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadie, P., Rioux, P., Scatton, B., Zarifian, E., Barre, L., Patat, A., et al. (1996). Central benzodiazepine receptor occupancy by zolpidem in the human brain as assessed by positron emission tomography. European Journal of Pharmacology, 295(1), 35–44.
Ansseau, M., Pitchot, W., Hansenne, M., & Gonzalez Moreno, A. (1992). Psychotic reactions to zolpidem. Lancet, 339(8796), 809.
Aranko, K., Henriksson, M., Hublin, C., & Seppalainen, A. M. (1991). Misuse of zopiclone and convulsions during withdrawal. Pharmacopsychiatry, 24(4), 138–140.
Brodeur, M. R., & Stirling, A. L. (2001). Delirium associated with zolpidem. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 35(12), 1562–1564.
Busto, U., Romach, M., & Sellers, E. (1996). Multiple drug use and psychiatric comorbidity in patients admitted to the hospital with severe benzodiazepine dependence. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 16(1), 51–57.
Goa, K. L., & Heel, R. C. (1986). Zopiclone. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy as an hypnotic. Drugs, 32(1), 48–65.
Hajak, G. (1999). A comparative assessment of the risks and benefits of zopiclone: a review of 15 years’ clinical experience. Drug Safety, 21(6), 457–469.
Hajak, G., Muller, W. E., Wittchen, H. U., Pittrow, D., & Kirch, W. (2003). Abuse and dependence potential for the non-benzodiazepine hypnotics zolpidem and zopiclone: a review of case reports and epidemiological data. Addiction, 98(10), 1371–1378.
Holbrook, A. (2004). Treating insomnia. BMJ, 329(7476), 1198–1199.
Holm, K. J., & Goa, K. L. (2000). Zolpidem: an update of its pharmacology, therapeutic efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of insomnia. Drugs, 59(4), 865–889.
Huang, C. L., Chang, C. J., Hung, C. F., & Lin, H. Y. (2003). Zolpidem-induced distortion in visual perception. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 37(5), 683–686.
Huedo-Medina, T., Kirsch, I., Middlemass, J., Klonizakis, M., & Siriwardena, A. (2011). Effectiveness of non-benzodiazepine hypnotics in treatment of adult insomnia: meta-analysis of data submitted to the food and drug administration. BMJ, 345, e8343.
Islam, M., Conigrave, K., Day, C., Nguyen, Y., & Haber, P. (2014). Twenty-years trends in benzodiazepine dispensing in the Australian population. Internal Medicine Journal, 44(1), 57–64.
Jones, I. R., & Sullivan, G. (1998). Physical dependence on zopiclone: case reports. BMJ, 316(7125), 117.
Kahlert, I., & Brune, M. (2001). A case of primary zopiclone dependence. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift, 126(22), 653–654.
Kapil, V., Green, J., Le Lait, C., Wood, D., & Dargan, P. (2014). Misuse of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs in the UK. British Journal of Psychiatry, 205(5), 407–408.
Kripke, D., Langer, R., & Kline, L. (2012). Hypnotics’ association with mortality or cancer: a matched cohort study. BMJ Open, 2(1), e000850.
Krueger, T. H., Kropp, S., & Huber, T. J. (2005). High-dose zolpidem dependence in a patient with chronic facial pain. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 39(4), 773–774.
Lagnaoui, R., Depont, F., Fourrier, A., Abouelfath, A., Bégaud, B., Verdoux, H., et al. (2004). Patterns and correlates of benzodiazepine use in the french general population. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 60(7), 523–529.
Lam, M. (2005). Retrospective Study on Characteristics of 104 Zopiclone Abusers in a Substance Abuse Clinic in Hong Kong. Paper presented at the International Conference on Tackling Drug Abuse, Hong Kong.
Langer, S. Z., & Arbilla, S. (1988). Imidazopyridines as a tool for the characterization of benzodiazepine receptors: a proposal for a pharmacological classification as omega receptor subtypes. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 29(4), 763–766.
Malcolm, R., Brady, K., Johnston, A., & Cunningham, M. (1993). Types of benzodiazepines abused by chemically dependent inpatients. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 25(4), 315–319.
Markowitz, J. S., & Brewerton, T. D. (1996). Zolpidem-induced psychosis. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 8(2), 89–91.
Markowitz, J. S., Rames, L. J., Reeves, N., & Thomas, S. G. (1997). Zolpidem and hallucinations. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 29(2), 300–301.
Mortaz Hejri, S., Faizi, M., & Babaeian, M. (2013). Zolpidem-induced suicide attempt: a case report. Daru, 21(1), 77.
Neckelmann, D., Mykletun, A., & Dahl, A. (2007). Chronic insomnia as a risk factor for developing anxiety and depression. Sleep, 30, 873–880.
Pallavicini, J., & Acevedo, X. (1997). Zopiclone dependence. Report of one case. Revista Médica de Chile, 125(3), 336–340.
Pitner, J. K., Gardner, M., Neville, M., & Mintzer, J. (1997). Zolpidem-induced psychosis in an older woman. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 45(4), 533–534.
Sanger, D., & Depoortere, H. (1998). The pharmacology and mechanism of action of zolpidem. CNS Drug Reviews, 4(4), 323–340.
Sethi, P. K., & Khandelwal, D. C. (2005). Zolpidem at supratherapeutic doses can cause drug abuse, dependence and withdrawal seizure. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 53, 139–140.
Sikdar, S., & Ruben, S. M. (1996). Zopiclone abuse among polydrug users. Addiction, 91(2), 285–286.
Singh, G. P., & Loona, N. (2013). Zolpidem-induced hallucinations: a brief case report from the Indian subcontinent. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 35(2), 212–213.
Siriwardena, A., Qureshi, M., Dyas, J., Middleton, H., & Orner, R. (2008). Magic bullets for insomnia? Patients’ use and experiences of newer (Z drugs) versus older (benzodiazepine) hypnotics for sleep problems in primary care. British Journal of General Practice, 58, 417–422.
Straand, J., & Rokstad, K. (1997). General practitioners’ prescribing patterns of benzodiazepine hypnotics: are elderly patients at particular risk for overprescribing? A report from the møre & romsdal prescription study. Scandinavian Journal of Primary Health Care, 15(1), 16–21.
Stranks, E., & Crowe, S. (2014). The acute cognitive effects of zopiclone, zolpidem, zaleplon, and eszopiclone: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 36(7), 691–700.
Victorri-Vigneau, C., Dailly, E., Veyrac, G., & Jolliet, P. (2007). Evidence of zolpidem abuse and dependence: results of the french centre for evaluation and information on pharmacodependence (CEIP) network survey. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 64(2), 198–209.
Victorri-Vigneau, C., Feuillet, F., Wainstein, L., Grall-Bronnec, M., Pivette, J., Chaslerie, A., et al. (2013). Pharmacoepidemiological characterisation of zolpidem and zopiclone usage. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 69(11), 1965–1972.
Wadworth, A. N., & McTavish, D. (1993). Zopiclone. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy as an hypnotic. Drugs and Aging, 3(5), 441–459.
Walsh, J., & Schweitzer, P. (1999). Ten-years trends in the pharmacological treatment of insomnia. Sleep, 22(3), 371–375.
Wilson, D. (2011). Zolpidem-induced mania in a patient with schizoaffective disorder. Psychosomatics, 52(5), 493–494.
Wong, G. Y., Bastiampillai, T., & Dhillon, R. (2010). Potential antipsychotic effects of zolpidem. Australia and New Zezland Journal of Psychiatry, 44(2), 190.
Zandstra, S., Furer, J., van de Lisdonk, E., Van’t, H., Bor, J., van Weel, C., et al. (2002). Different study criteria affect the prevalence of benzodiazepine use. Socical Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 37(3), 139–144.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr Shruti Srivastava (Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, University College of Medical Sciences, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, India) for his review and suggestions on the draft of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Financial Support
Nothing declared.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares none conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Tang, W.K., Liang, H.J. et al. Psychiatric Morbidity in Dependent Z-Drugs and Benzodiazepine Users. Int J Ment Health Addiction 15, 555–564 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-016-9679-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-016-9679-x