Abstract
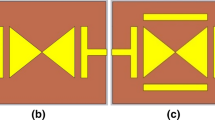
Metamaterials are considered to be a promising candidate of making THz absorber for function devices to replace natural materials. Based on geometry evolution, the electromagnetic characteristics of metamaterials can be tailed to enhance the weak THz response of natural materials. Appropriate constituent selection and inhomogeneous geometry constructions are proved to be effective to extend the narrow frequency band of traditional metal resonator-based metamaterial absorbers. In this work, doped silicon was used as the only constituent, and the inhomogeneous geometry was designed in a very simple way (so-called square nut structure) with the assistant of transmission line theory and geometry evolution methodology. Ultra-broadband absorption from 1.6 to 5 THz was verified numerically with an efficiency over 90 %. Various plasmonic resonance modes including surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) together with local surface plasmonic resonance (LSPR) tuned by the inhomogeneous structures and cavities contributed to this broadband absorption. Further working with this geometrical variation concept, our “wheel hub-like” structure achieved ultra-broadband absorption from 0.98 to 5 THz. Our investigations could provide an alternative design methodology for the design of metamaterial THz absorbers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federici JF, Schulkin B, Huang F, Gary D, Barat R, Oliveira F, Zimdars D (2005) THz imaging and sensing for security applications—explosives, weapons and drugs. Semicond Sci Technol 20(7):S266–S280. doi:10.1088/0268-1242/20/7/018
Seeds AJ, Shams H, Fice MJ, Renaud CC (2015) Terahertz photonics for wireless communications. J Lightwave Technol 33(3):9
Zhao X, Yuan C, Lv W, Xu S, Yao J (2015) A polarization-independent terahertz plasmon-induced transparency metamaterial based on hybrid graphene-gold structure for bio-sensing. J Mod Opt:1–7. doi:10.1080/09500340.2015.1073803
Liu S, Zhuang S, Petelin MI, Xiang L, Wu B, Ying CP, Wang HF, Zhang P, Liu HY, Jiang B (2015) Terahertz metrology on power, frequency, spectroscopy, and pulse parameters. 9795:97953L. doi:10.1117/12.2214929
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Padilla WJ (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100(20):207402. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402
Tao H, Landy NI, Bingham CM, Zhang X, Averitt RD, Padilla WJ (2008) A metamaterial absorber for the terahertz regime: design, fabrication and characterization. Opt Express 16(10):8
Tao H, Bingham CM, Strikwerda AC, Pilon D, Shrekenhamer D, Landy NI, Fan K, Zhang X, Padilla WJ, Averitt RD (2008) Highly flexible wide angle of incidence terahertz metamaterial absorber: design, fabrication, and characterization. Phys Rev B 78(24). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.241103
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10(7):2342–2348. doi:10.1021/nl9041033
Zhu B, Wang Z, Huang C, Feng Y, Zhao J, Jiang T (2010) Polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber with wide incident angle. Prog Electromagn Res 101:9
Li L, Yang Y, Liang C (2011) A wide-angle polarization-insensitive ultra-thin metamaterial absorber with three resonant modes. J Appl Phys 110(6):063702. doi:10.1063/1.3638118
Chen S, Cheng H, Yang H, Li J, Duan X, Gu C, Tian J (2011) Polarization insensitive and omnidirectional broadband near perfect planar metamaterial absorber in the near infrared regime. Appl Phys Lett 99(25):253104. doi:10.1063/1.3670333
Zhu W, Zhao X (2009) Metamaterial absorber with dendritic cells. J Opt Soc Am B 26(12):4
Avitzour Y, Urzhumov YA, Shvets G (2009) Wide-angle infrared absorber based on a negative-index plasmonic metamaterial. Phys Rev B 79(4). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.79.045131
Cheng C-W, Abbas MN, Chiu C-W, Lai K-T, Shih M-H, Chang Y-C (2012) Wide-angle polarization independent infrared broadband absorbers based on metallic multi-sized disk arrays. Opt Express 20(9):6
Wen Q-Y, Zhang H-W, Xie Y-S, Yang Q-H, Liu Y-L (2009) Dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber: design, fabrication, and characterization. Appl Phys Lett 95(24):241111. doi:10.1063/1.3276072
Zhang B, Zhao Y, Hao Q, Kiraly B, Khoo I-C, Chen S, Huang TJ (2011) Polarization-independent dual-band infrared perfect absorber based on a metal-dielectric-metal elliptical nanodisk array. Opt Express 19(16):8
Jiang ZH, Yun S, Toor F, H.Werner D, Mayer TS (2011) Conformal dual-band near-perfectly absorbing mid-infrared metamaterial coating. ACS Nano 5(6):7
Hendrickson J, Guo J, Zhang B, Buchwald W, Soref R (2012) Wideband perfect light absorber at midwave infrared using multiplexed metal structures. Opt Lett 37(3):3
Cui Y, Fung KH, Xu J, Ma H, Jin Y, He S, Fang NX (2012) Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab. Nano Lett 12(3):1443–1447. doi:10.1021/nl204118h
Xu H-X, Wang G-M, Qi M-Q, Liang J-G, Gong J-Q, Xu Z-M (2012) Triple-band polarization-insensitive wide-angle ultra-miniature metamaterial transmission line absorber. Phys Rev B 86(20). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.205104
Zhang N, Zhou P, Wang S, Weng X, Xie J, Deng L (2015) Broadband absorption in mid-infrared metamaterial absorbers with multiple dielectric layers. Opt Commun 338:388–392. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2014.11.008
Pu M, Wang M, Hu C, Huang C, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Luo X (2012) Engineering heavily doped silicon for broadband absorber in the terahertz regime. Opt Express 20(23):7
Withayachumnankul W, Shah CM, Fumeaux C, Ung BSY, Padilla WJ, Bhaskaran M, Abbott D, Sriram S (2014) Plasmonic resonance toward terahertz perfect absorbers. ACS Photonics 1(7):625–630. doi:10.1021/ph500110t
Zhang Y, Han Z (2015) Efficient and broadband terahertz plasmonic absorbers using highly doped Si as the plasmonic material. AIP Adv 5(1):017113. doi:10.1063/1.4905888
Cheng YZ, Withayachumnankul W, Upadhyay A, Headland D, Nie Y, Gong RZ, Bhaskaran M, Sriram S, Abbott D (2015) Ultrabroadband plasmonic absorber for terahertz waves. Advanced Optical Materials 3(3):376–380. doi:10.1002/adom.201400368
Yin S, Zhu J, Xu W, Jiang W, Yuan J, Yin G, Xie L, Ying Y, Ma Y (2015) High-performance terahertz wave absorbers made of silicon-based metamaterials. Appl Phys Lett 107(7):073903. doi:10.1063/1.4929151
Peng Y, Zang X, Zhu Y, Shi C, Chen L, Cai B, Zhuang S (2015) Ultra-broadband terahertz perfect absorber by exciting multi-order diffractions in a double-layered grating structure. Opt Express 23(3):2032–2039. doi:10.1364/OE.23.002032
Zang X, Shi C, Chen L, Cai B, Zhu Y, Zhuang S (2015) Ultra-broadband terahertz absorption by exciting the orthogonal diffraction in dumbbell-shaped gratings. Scientific reports 5:8901. doi:10.1038/srep08901
Hanham SM, Fernandez-Dominguez AI, Teng JH, Ang SS, Lim KP, Yoon SF, Ngo CY, Klein N, Pendry JB, Maier SA (2012) Broadband terahertz plasmonic response of touching InSb disks. Adv Mater 24(35):OP226–OP230. doi:10.1002/adma.201202003
Matthaei GL, Young L, Jones EMT (1964) Microwave filters, impedance-matching networks, and coupling structures. McGraw-Hill
Caglayan H, Hong SH, Edwards B, Kagan CR, Engheta N (2013) Near-infrared metatronic nanocircuits by design. Phys Rev Lett 111(7):073904. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.073904
Sun Y, Edwards B, Alu A, Engheta N (2012) Experimental realization of optical lumped nanocircuits at infrared wavelengths. Nat Mater 11(3):208–212. doi:10.1038/nmat3230
Zhang Q, Bai L, Liu X, Liu C, Cui X (2016) Simplified transparent conductive oxides-based ultrabroadband absorber design. J Lightwave Technol 34(4):1354–1359. doi:10.1109/JLT.2016.2515643
Hashimshony D, Geltner I, Cohen G, Avitzour Y, Zigler A, Smith C (2001) Characterization of the electrical properties and thickness of thin epitaxial semiconductor layers by THz reflection spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 90(11):5778. doi:10.1063/1.1412574
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of CAEP under Grant 2014A0302014 and the fund from the Science and Technology on Plasma Physics Laboratory, Research Center of Laser Fusion, CAEP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhang, Q. & Cui, X. Ultra-broadband Polarization-Independent Wide-Angle THz Absorber Based on Plasmonic Resonances in Semiconductor Square Nut-Shaped Metamaterials. Plasmonics 12, 1137–1144 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0368-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0368-1