Abstract
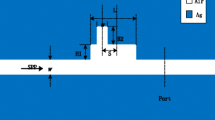
We propose a compact plasmonic structure comprising a metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) waveguide coupled with a side cavity and groove resonators. The proposed system is investigated by the finite element method. Simulation results show that the side-coupled cavity supports a local discrete state and the groove provides a continuous spectrum, the interaction between them, gives rise to the Fano resonance. The asymmetrical line shape and the resonant wavelength can be easily tuned by changing the geometrical parameters of the structure. Moreover, we can extend this plasmonic structure by the double side-coupled cavities to gain the multiple Fano resonances. The proposed structure can serve as an excellent plasmonic sensor with a sensitivity of ∼1900 nm/RIU and a figure of merit of about ∼3.8 × 104, which can find wide applications for nanosensors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Wang GX (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37(18):3780–3782
Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Wang GX (2011) Induced transparency in nanoscale plasmonic resonator systems. Opt Lett 36(16):3233–3235
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10(7):2342–2348
Xu T, Wu YK, Luo X, Guo LJ (2010) Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging. Nat Commun 1(5):118–124
Veronis G, Fan S (2010) Bends and splitters in metal-dielectric-metal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 87(13):131102
Economou EN, Veronis G, Fan S (2010) Surface plasmons in thin films. Phys Rev 182(2):539
Chen Z, Wang WH, Cui NL, Yu L, Duan GY, Zhao FY, Xiao JH (2015) Spectral splitting based on electromagnetically induced transparency in plasmonic waveguide resonator system. Plasmonics 10(3):721–727
Chen JJ, Li Z, Lei M, Fu XL, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2012) Plasmonic Y-splitters of high wavelength resolution based on strongly coupled-resonator effects. Plasmonics 7(3):441–445
Kou Y, Chen FX (2011) Multimode interference demultiplexers and splitters in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Opt Express 7(3):6042–6047
Tao J, Huang XG, Lin X, Chen J, Zhang Q, Jin X (2010) Systematical research on characteristics of double-side teeth-shaped nano-plasmonic waveguide filters. J Opt Soc Am B 27(2):323–327
Tao J, Huang XG, Lin X, Zhang Q, Jin X (2009) A narrow-band subwavelength plasmonic waveguide filter with asymmetrical multiple-teeth-shaped structure. Opt Express 17(16):13989–13994
Lu H, Wang GX, Liu XM (2013) Manipulation of light in MIM plasmonic waveguide systems. Chin Sci Bull 58(30):3607–3616
Lin XS, Huang XG (2008) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33(23):2874–2876
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang LL, Duan GY, Zhao FY, Xiao JH (2015) A refractive index nanosensor based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic waveguide system. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27(16):1695–1698
Chen Z, Cui LN, Song XK, Yu L, Xiao JH (2015) High sensitivity plasmonic sensing based on Fano interference in a rectangular ring waveguide. Opt Commun 340:1–4
Chen JJ, Li Z, Li J, Gong QH (2011) Compact and high-resolution plasmonic wavelength demultiplexers based on Fano interference. Opt Express 19(10):9976–9985
Lu H, Liu XM, Gong YK, Mao D, Wang LR (2011) Enhancement of transmission efficiency of nanoplasmonic wavelength demultiplexer based on channel drop filters and reflection nanocavities. Opt Express 19(14):12885–12890
Fano U (1961) Effects of configuration interaction on intensities and phase shifts. Phys Rev 124(16):1866–1878
Miroshnichenko AE, Flach S, Kivshar YS (1961) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82(3):2257
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Liang L, Zhen G (2015) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10(1):27–32
Chen JJ, Li Z, Zhang X, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2013) Submicron bidirectional all-optical plasmonic switches. Sci Rep 3:1451
Heuck M, Kristensen PT, Elesin Y, Mork J (2013) Improved switching using Fano resonances in photonic crystal structures. Opt Lett 38(14):22572466–2468
Fedotov VA, Rose M, Prosvirnin SL (2007) Sharp trapped-mode resonances in planar metamaterials with a broken structural symmetry. Phys Rev Lett 99(14):147401
Qi JW, Chen ZQ, Chen J, Li YD, Qiang W, Xu JJ, Sun Q (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T et al (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8(9):758–762
Hu FF, Yi HX, Zhou ZP (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Zhang Q, Huang XG, Lin XS, Tao J, Jin XP (2009) A subwavelength coupler-type MIM optical filter. Opt Express 17(9):7549–7554
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA, Polman A (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73(3):035407
Han ZH, Bozhevolnyi SI (2006) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry-Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19(4):3251–3257
Becker J, Trügler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Sönnichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5(2):161–167
Zhang YY, Li SL, Zhang XY, Chen YY, Wang LL, Zhang Y, Yu L (2016) Evolution of Fano resonance based on symmetric/asymmetric plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. Opt Commun 370(1):203–208
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China under Grant 2016 YFA 0301300 and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant 11374041, Grant 11574035, Grant 11404030, and Grant 61571060 and Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (Beijing University of Posts and Tele-communications), People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, S., Chen, Z. et al. Ultra-high Sensitivity Plasmonic Nanosensor Based on Multiple Fano Resonance in the MDM Side-Coupled Cavities. Plasmonics 12, 1099–1105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0363-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0363-6